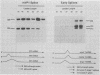
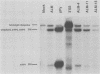
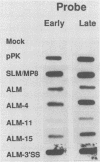
Abstract
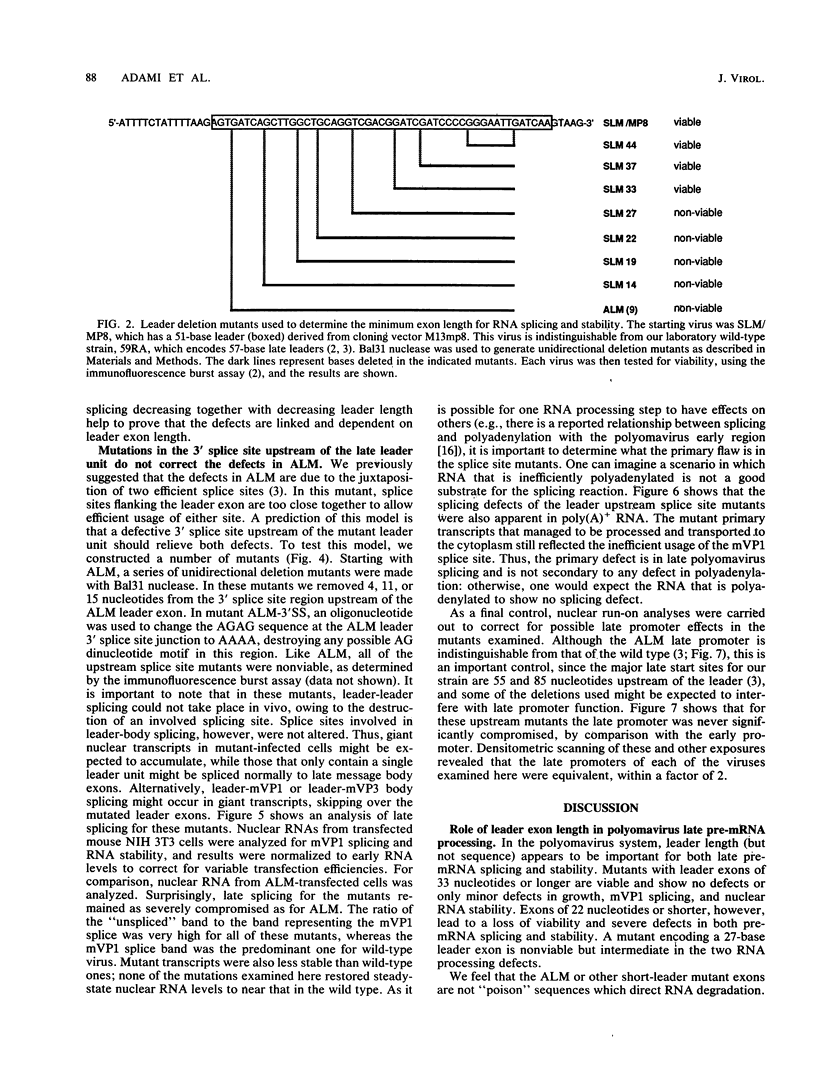
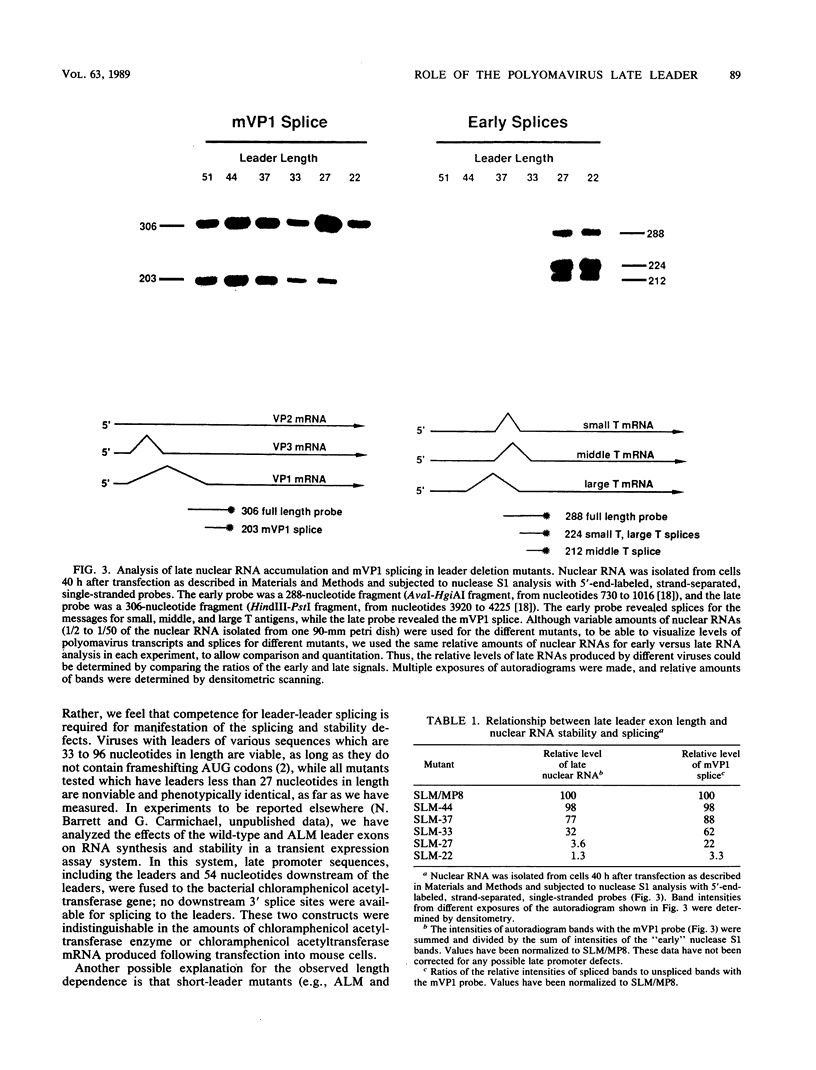
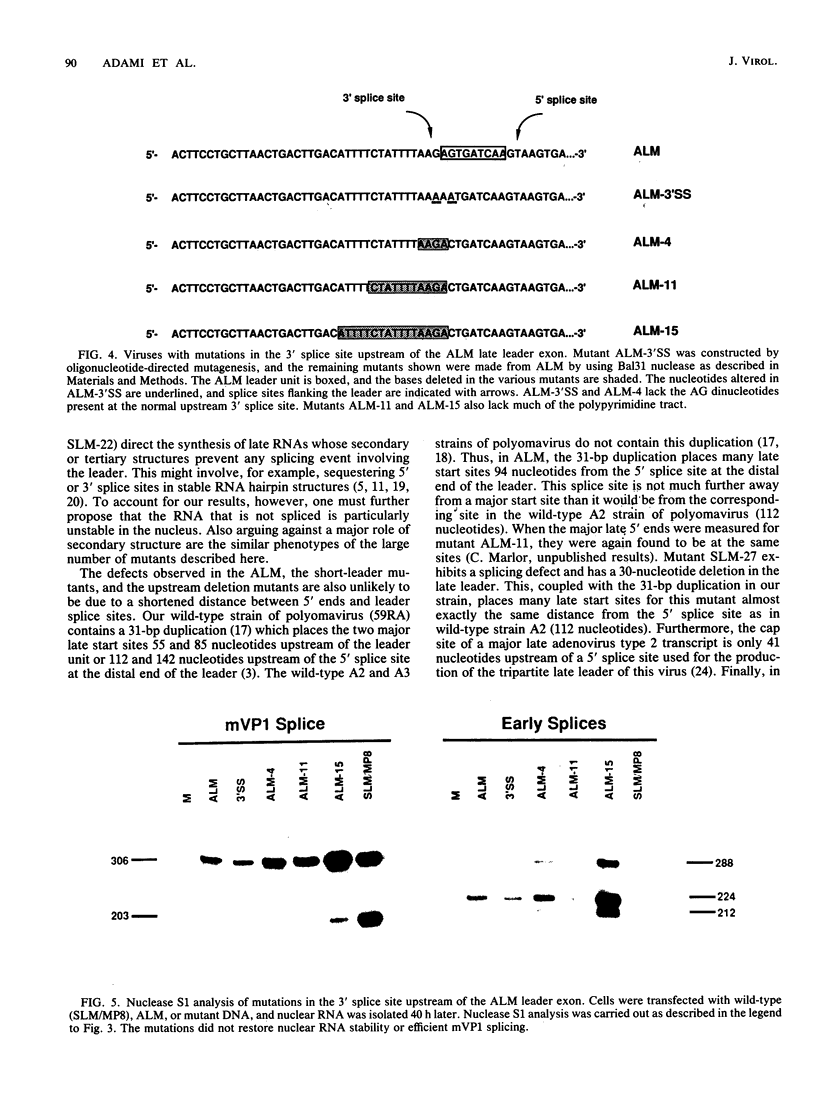
Polyomavirus late mRNA molecules contain multiple, tandem copies of a noncoding 57-base "late leader" exon at their 5' ends. This exon is encoded only once in the genome. Leader multiplicity arises from leader-leader splicing in giant primary transcripts, which are the result of multiple circuits of the viral genome by RNA polymerase II. We have been interested in learning more about the role of the leader exon in late viral gene expression. We recently showed that an abbreviated-leader mutant virus (ALM) with a 9-base leader exon is nonviable (G. R. Adami and G. G. Carmichael, Nucleic Acids Res. 15:2593-2610, 1987) and has a severe defect in both late pre-mRNA splicing and stability. However, a mutant virus with a different, substituted leader sequence of 51 nucleotides (SLM/MP8) is viable and has no apparent defects. Here we examined further the role of the late leader exon in late pre-mRNA processing. When the leader exon length was gradually reduced from 51 nucleotides to 9 nucleotides in a series of mutants, RNA splicing and stability defects were coupled. In this system there was a minimum exon size of between 33 and 27 nucleotides. Next, a number of mutations were introduced into the 3' splice site which precedes the late leader. Such mutations blocked leader-leader splicing. Surprisingly, they also interfered with leader-mVP1 body splicing and resulted in unstable primary transcripts. Thus, polyomavirus leader-leader splicing appears to be important for the efficient accumulation of late viral mRNA molecules.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H. Polyoma virus giant RNAs contain tandem repeats of the nucleotide sequence of the entire viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4754–4758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Carmichael G. G. Polyomavirus late leader region serves an essential spacer function necessary for viability and late gene expression. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):417–425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.417-425.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Carmichael G. G. The length but not the sequence of the polyoma virus late leader exon is important for both late RNA splicing and stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2593–2610. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Developmentally induced, muscle-specific trans factors control the differential splicing of alternative and constitutive troponin T exons. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):793–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Definition of essential sequences and functional equivalence of elements downstream of the adenovirus E2A and the early simian virus 40 polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2975–2983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern F. G., Bovi P. D., Basilico C. A reiterated leader sequence is present in polyomavirus late transcripts produced by a transformed rat cell line. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4055–4059. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4055-4059.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P., Dhar R., Lai C. J. Processing and expression of early SV40 mRNA: a role for RNA conformation in splicing. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanoix J., Acheson N. H. A rabbit beta-globin polyadenylation signal directs efficient termination of transcription of polyomavirus DNA. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2515–2522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Kamen R. Amplification in the leader sequence of late polyoma virus mRNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):373–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Definition and mapping of adenovirus 2 nuclear transcription. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):768–785. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C. J., Fried M. Polyomavirus early region alternative poly(A) site: 3'-end heterogeneity and altered splicing pattern. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3754–3758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3754-3758.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E., Fried M. Sequence repeats in a polyoma virus DNA region important for gene expression. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.233-237.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Lee S. I. Amount of RNA secondary structure required to induce an alternative splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Characterisation of polyoma late mRNA leader sequences by molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4867–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Kamen R. Structure of polyoma virus late nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):273–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng R. W., Acheson N. H. Use of a novel S1 nuclease RNA-mapping technique to measure efficiency of transcription termination on polyomavirus DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1624–1632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zain S., Sambrook J., Roberts R. J., Keller W., Fried M., Dunn A. R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the leader segments in a cloned copy of adenovirus 2 fiber mRNA. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):851–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]