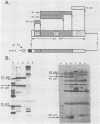
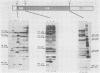
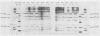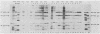Abstract
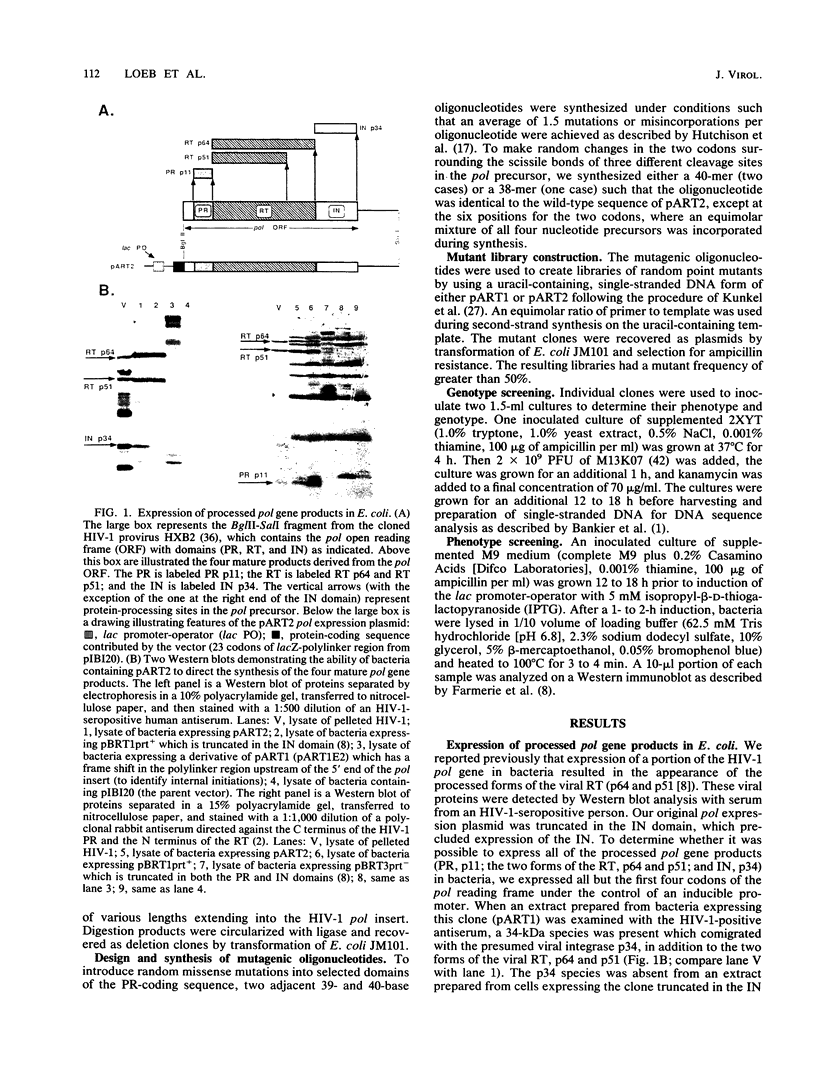
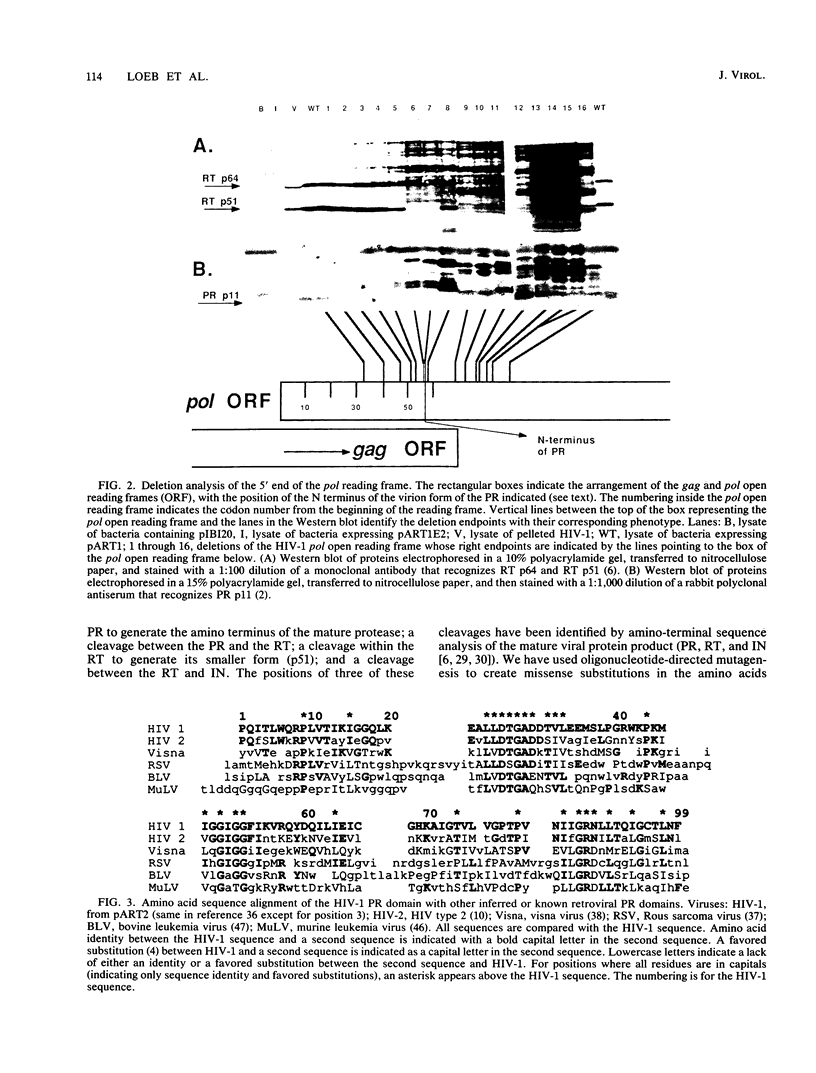
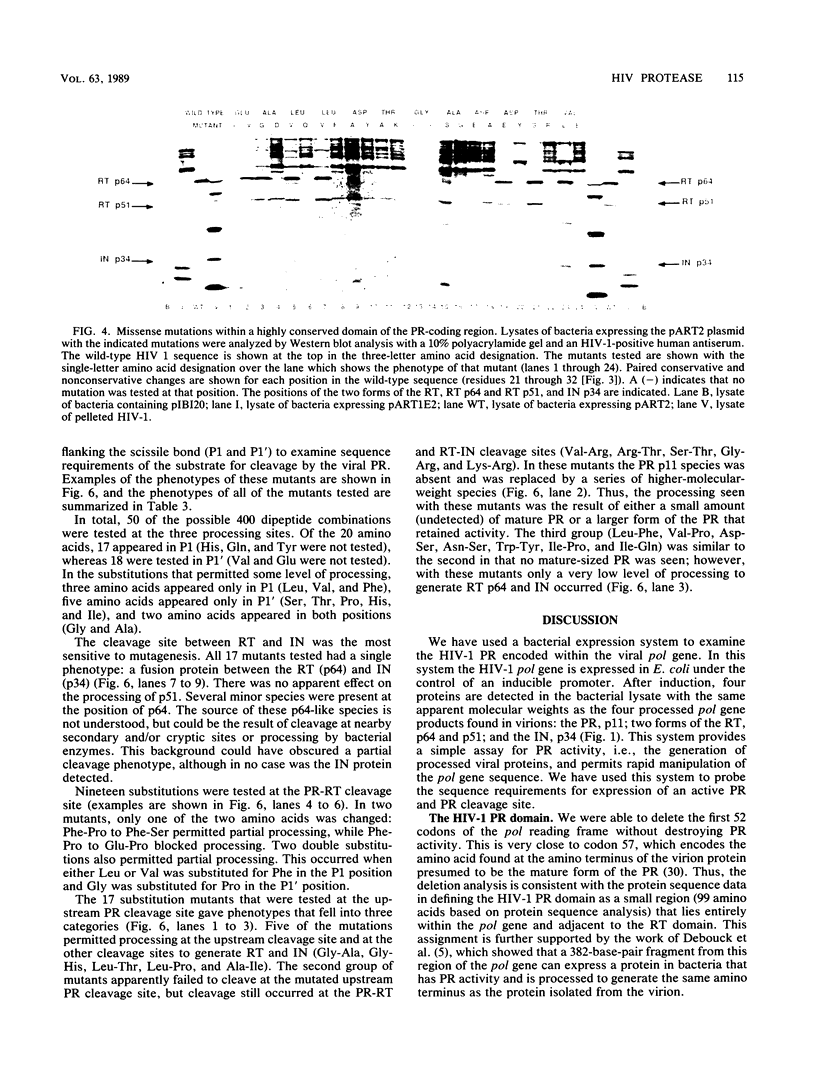
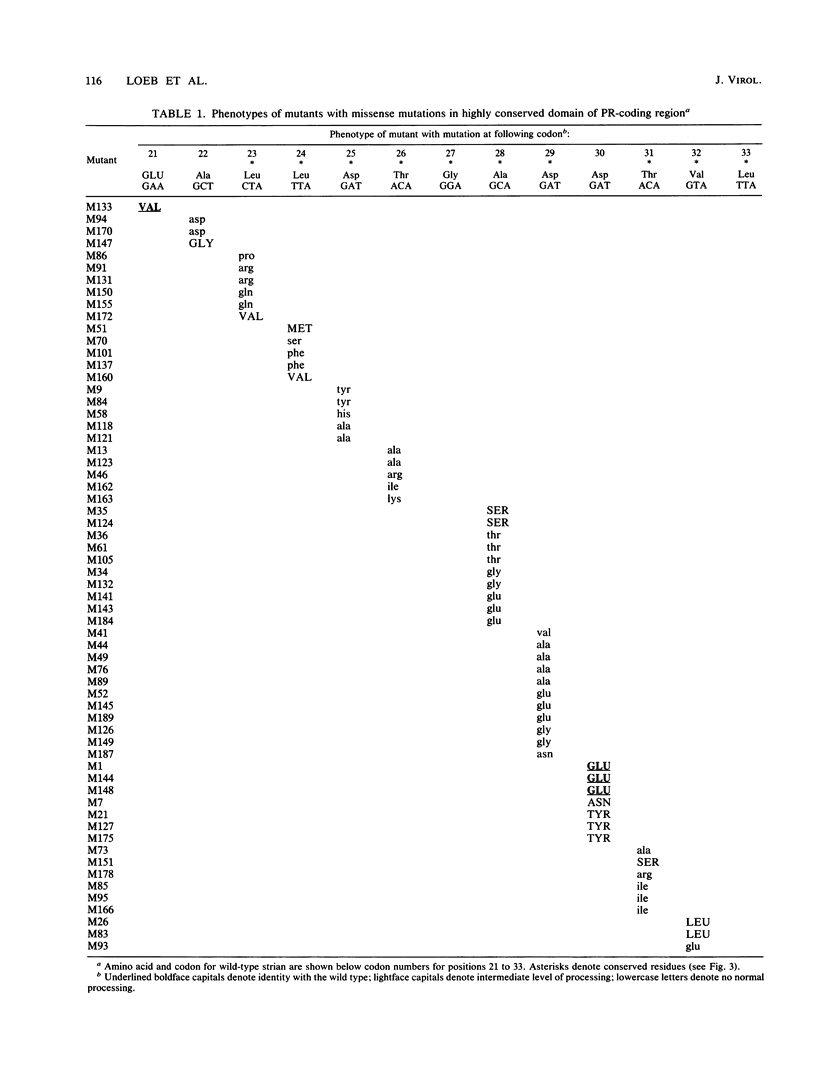
Processing of the retroviral gag and pol gene products is mediated by a viral protease. Bacterial expression systems have been developed which permit genetic analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease as measured by cleavage of the pol protein precursor. Deletion analysis of the pol reading frame locates the sequences required to encode a protein with appropriate proteolytic activity near the left end of the pol reading frame but largely outside the gag-pol overlap region, which is at the extreme left end of pol. Most missense mutations within an 11-amino-acid domain highly conserved among retroviral proteases and with sequence similarity to the active site of aspartic proteinases abolish appropriate processing, suggesting that the retrovirus proteases share a catalytic mechanism with aspartic proteinases. Substitution of the amino acids flanking the scissile bond at three of the processing sites encoded by pol demonstrates distinct sequence requirements for cleavage at these different sites. The inclusion of a charged amino acid at the processing site blocks cleavage. A subset of these substitutions also inhibits processing at the nonmutated sites.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankier A. T., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford S., Goff S. P. A deletion mutation in the 5' part of the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus blocks proteolytic processing of the gag and pol polyproteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.899-907.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debouck C., Gorniak J. G., Strickler J. E., Meek T. D., Metcalf B. W., Rosenberg M. Human immunodeficiency virus protease expressed in Escherichia coli exhibits autoprocessing and specific maturation of the gag precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8903–8906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittmar K. J., Moelling K. Biochemical properties of p15-associated protease in an avian RNA tumor virus. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):106–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.106-118.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmerie W. G., Loeb D. D., Casavant N. C., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H., Swanstrom R. Expression and processing of the AIDS virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. Science. 1987 Apr 17;236(4799):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2436298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Lim J. J., Heimer E. P., Kramer R. A. An 11-kDa form of human immunodeficiency virus protease expressed in Escherichia coli is sufficient for enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2449–2453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Billich S., Schulze T., Sukrow S., Moelling K. Partial purification and substrate analysis of bacterially expressed HIV protease by means of monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1785–1791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Mellert W., Moelling K. Identification and characterization of HIV-specific RNase H by monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):239–243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Moelling K. RNase H activity associated with bacterially expressed reverse transcriptase of human T-cell lymphotropic virus III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Benveniste R. E., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. Molecular characterization of gag proteins from simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVMne). J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2587–2595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2587-2595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoheisel J., Pohl F. M. Simplified preparation of unidirectional deletion clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3605–3605. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Nordeen S. K., Vogt K., Edgell M. H. A complete library of point substitution mutations in the glucocorticoid response element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):710–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Power M. D., Masiarz F. R., Luciw P. A., Barr P. J., Varmus H. E. Characterization of ribosomal frameshifting in HIV-1 gag-pol expression. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):280–283. doi: 10.1038/331280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Townsley K., Varmus H. E., Majors J. Two efficient ribosomal frameshifting events are required for synthesis of mouse mammary tumor virus gag-related polyproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Varmus H. E. Expression of the Rous sarcoma virus pol gene by ribosomal frameshifting. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1237–1242. doi: 10.1126/science.2416054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yasunaga T., Ikawa Y., Yoshinaka Y. Inhibition of retroviral protease activity by an aspartyl proteinase inhibitor. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):654–656. doi: 10.1038/329654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yoshinaka Y., Rein A., Shibuya M., Odaka T., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus maturation: protease region required for conversion from "immature" to "mature" core form and for virus infectivity. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):280–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Davis L. J., Heimbach J. C., Dixon R. A., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Active human immunodeficiency virus protease is required for viral infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4686–4690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler M., Katz R. A., Danho W., Leis J., Skalka A. M. Synthetic peptides as substrates and inhibitors of a retroviral protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4185–4189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. Activity of avian retroviral protease expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2696–2700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2696-2700.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. A., Schaber M. D., Skalka A. M., Ganguly K., Wong-Staal F., Reddy E. P. HTLV-III gag protein is processed in yeast cells by the virus pol-protease. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1580–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2420008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grice S. F., Beuck V., Mous J. Expression of biologically active human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III reverse transcriptase in Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1987;55(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoote M. M., Coligan J. E., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Martin M. A., Venkatesan S. Structural characterization of reverse transcriptase and endonuclease polypeptides of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):771–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.771-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillehoj E. P., Salazar F. H., Mervis R. J., Raum M. G., Chan H. W., Ahmad N., Venkatesan S. Purification and structural characterization of the putative gag-pol protease of human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3053–3058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3053-3058.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermer B., Malamy M., Coffin J. M. Rous sarcoma virus contains sequences which permit expression of the gag gene in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1746–1758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R., Dixon M., Smith R., Peters G., Dickson C. Complete nucleotide sequence of a milk-transmitted mouse mammary tumor virus: two frameshift suppression events are required for translation of gag and pol. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):480–490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.480-490.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mous J., Heimer E. P., Le Grice S. F. Processing protease and reverse transcriptase from human immunodeficiency virus type I polyprotein in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1433–1436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1433-1436.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Copeland T. D. Primary structure and processing of gag and env gene products of human T-cell leukemia viruses HTLV-ICR and HTLV-IATK. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;115:221–233. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70113-9_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl L. H., Taylor W. R. A structural model for the retroviral proteases. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):351–354. doi: 10.1038/329351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Fisher A., Jagodzinski L. L., Mitsuya H., Liou R. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Complete nucleotide sequences of functional clones of the AIDS virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Spring;3(1):57–69. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Allen D. W., Niall H. D. Amino acid sequence of p15 from avian myeloblastosis virus complex. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3784–3791. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Alizon M., Staskus K., Klatzmann D., Cole S., Danos O., Retzel E., Tiollais P., Haase A., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of the visna lentivirus: relationship to the AIDS virus. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):369–382. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang J., James M. N., Hsu I. N., Jenkins J. A., Blundell T. L. Structural evidence for gene duplication in the evolution of the acid proteases. Nature. 1978 Feb 16;271(5646):618–621. doi: 10.1038/271618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Kikuno R., Hayashida H., Miyata T., Kugimiya W., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. Close structural resemblance between putative polymerase of a Drosophila transposable genetic element 17.6 and pol gene product of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1267–1272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Wight A., Eisenman R. In vitro cleavage of avian retrovirus gag proteins by viral protease p15. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):154–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Relationship of retrovirus polyprotein cleavages to virion maturation studied with temperature-sensitive murine leukemia virus mutants. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):750–761. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.750-761.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Katoh I., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus protease is encoded by the gag-pol gene and is synthesized through suppression of an amber termination codon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1618–1622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Katoh I., Copeland T. D., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Bovine leukemia virus protease: purification, chemical analysis, and in vitro processing of gag precursor polyproteins. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):826–832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.826-832.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaka Y., Luftig R. B. Properties of a P70 proteolytic factor of murine leukemia viruses. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Marzo Veronese F., Copeland T. D., DeVico A. L., Rahman R., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of highly immunogenic p66/p51 as the reverse transcriptase of HTLV-III/LAV. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.2418504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Helm K. Cleavage of Rous sarcoma viral polypeptide precursor into internal structural proteins in vitro involves viral protein p15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):911–915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]