Abstract
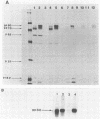
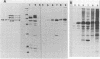
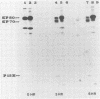
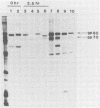
The envelope glycoprotein (gp70) of a molecularly cloned, replication-defective feline leukemia virus (FeLV-FAIDS clone 61C) carries determinants for induction of fatal immunodeficiency disease, whereas the gp70 of its companion replication-competent, probably parent virus (clone 61E) does not. Immunoprecipitation analysis of the extracellular glycoproteins of 61E and EECC, a replication-competent viral construct composed of the 61C env and 3' long terminal repeat fused to the 61E gag-pol genes, demonstrated that the gp70 of EECC could be distinguished from that of 61E by both feline immune serum and a murine monoclonal antibody. Molecular weights of both the envelope precursor polyprotein (gp80) and the mature extracellular glycoprotein (gp70) of 61E were smaller than the corresponding proteins from the pathogenic EECC. Both the molecular weight disparity and monoclonal antibody discrimination of the two gp80s were abolished by inhibition of envelope protein glycosylation with tunicamycin, whereas the apparent gp70 size differences were resolved by enzymatic removal of N-linked oligosaccharides. Pulse-chase studies in EECC-infected cells demonstrated that processing of gp80 to gp70 was delayed and that this retardation of envelope glycoprotein processing could be simulated in 61E-infected cells by treatment with the glucosidase inhibitor N-methyldeoxynojirimycin, a compound that causes retention of oligosaccharides in the high-mannose form. The resultant 61E gp70 then could be recognized by sera from EECC-immunized cats. The presence of a higher content of sialic acid on the apathogenic 61E gp70 indicated that oligosaccharides of 61E and EECC gp70 were processed differently. These data suggested that the unique biochemical properties which distinguish the envelope glycoproteins of the FeLV-FAIDS variant from its companion apathogenic parent virus were responsible for T-cell cytopathicity and induction of immunodeficiency disease. Further biochemical characterization of these glycoproteins should be useful in understanding the pathogenic mechanisms of immunodeficiency disease induced by retroviruses.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. S., Coligan J. E., Barin F., McLane M. F., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lee T. H., Essex M. Major glycoprotein antigens that induce antibodies in AIDS patients are encoded by HTLV-III. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1091–1094. doi: 10.1126/science.2986290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barin F., McLane M. F., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Groopman J. E., Essex M. Virus envelope protein of HTLV-III represents major target antigen for antibodies in AIDS patients. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1094–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.2986291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi D. P., Langlois A. J., Schäfer W. Polypeptides of mammalian oncornaviruses. IV. Structural components of murine leukemia virus released as soluble antigens in cell culture. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):550–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90297-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue P. R., Hoover E. A., Beltz G. A., Riedel N., Hirsch V. M., Overbaugh J., Mullins J. I. Strong sequence conservation among horizontally transmissible, minimally pathogenic feline leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):722–731. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.722-731.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Coffin J. M. Determinants for receptor interaction and cell killing on the avian retrovirus glycoprotein gp85. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90322-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichberg J. W., Zarling J. M., Alter H. J., Levy J. A., Berman P. W., Gregory T., Lasky L. A., McClure J., Cobb K. E., Moran P. A. T-cell responses to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and its recombinant antigens in HIV-infected chimpanzees. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3804–3808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3804-3808.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., McGee J. S., Alexander S. Carbohydrate side chains of Rauscher leukemia virus envelope glycoproteins are not required to elicit a neutralizing antibody response. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):340–342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.340-342.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Risser R. The role of envelope glycoprotein processing in murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2852–2856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2852-2856.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann U., Bause E., Legler G., Ploegh H. Novel mannosidase inhibitor blocking conversion of high mannose to complex oligosaccharides. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):755–758. doi: 10.1038/307755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg N., Kuismanen E., Keränen S., Pettersson R. F. Uukuniemi virus glycoproteins accumulate in and cause morphological changes of the Golgi complex in the absence of virus maturation. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):899–906. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.899-906.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. K., Ernisse B. J., Jarrett O., Jones F. R. Feline leukemia virus envelope gp70 of subgroups B and C defined by monoclonal antibodies with cytotoxic and neutralizing functions. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3042–3048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruters R. A., Neefjes J. J., Tersmette M., de Goede R. E., Tulp A., Huisman H. G., Miedema F., Ploegh H. L. Interference with HIV-induced syncytium formation and viral infectivity by inhibitors of trimming glucosidase. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):74–77. doi: 10.1038/330074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Taylor M. E., Redfield R. R., Markham P. D., Salahuddin S. Z., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Parks E. S., Parks W. P. Genetic variation in HTLV-III/LAV over time in patients with AIDS or at risk for AIDS. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1548–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.3012778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Hunter E. Rous sarcoma virus mutant LA3382 is defective in virion glycoprotein assembly. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):752–761. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.752-761.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Kaplan J. C., Rackauskas I. E., Gurney M. E. Second conserved domain of gp120 is important for HIV infectivity and antibody neutralization. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1021–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2830667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I., Quackenbush S. L., Gasper P. W. Experimental transmission and pathogenesis of immunodeficiency syndrome in cats. Blood. 1987 Dec;70(6):1880–1892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Rosner M. R., Robbins P. W. Host-dependent variation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides at individual glycosylation sites of Sindbis virus glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2548–2554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt L. A. Oligosaccharides of the Hazelhurst vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein are more extensively processed in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed baby hamster kidney cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 16;924(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. C., Barbet A. F., Klevjer-Anderson P., McGuire T. C. Preferential immune response to virion surface glycoproteins by caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus-infected goats. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):657–665. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.657-665.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevjer-Anderson P., McGuire T. C. Neutralizing antibody response of rabbits and goats to caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):455–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.455-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Tanner W. The specific site of tunicamycin inhibition in the formation of dolichol-bound N-acetylglucosamine derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80922-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Bestwick R. K., Machida C., Kabat D. Role of a membrane glycoprotein in Friend virus erythroleukemia: nucleotide sequences of nonleukemogenic mutant and spontaneous revertant viruses. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):534–538. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.534-538.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Menke J. G., Ruscetti S. K., Evans L. H., Scolnick E. M. Envelope gene sequences which encode the gp52 protein of spleen focus-forming virus are required for the induction of erythroid cell proliferation. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):223–233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.223-233.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida C. A., Bestwick R. K., Boswell B. A., Kabat D. Role of a membrane glycoprotein in Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia: studies of mutant and revertant viruses. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):158–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews T. J., Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Langlois A. J., Wigzell H., Bolognesi D. P. Interaction between the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type IIIB envelope glycoprotein gp120 and the surface antigen CD4: role of carbohydrate in binding and cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5424–5428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Parekh B., Orrego A., Issel C. J. Antigenic variation during persistent infection by equine infectious anemia virus, a retrovirus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10539–10544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Chen C. S., Hoover E. A. Disease-specific and tissue-specific production of unintegrated feline leukaemia virus variant DNA in feline AIDS. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):333–336. doi: 10.1038/319333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbaugh J., Donahue P. R., Quackenbush S. L., Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I. Molecular cloning of a feline leukemia virus that induces fatal immunodeficiency disease in cats. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):906–910. doi: 10.1126/science.2893454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Chen T. E., Lowy A., Cortez N. G., Silagi S. Ecotropic murine leukemia virus-induced fusion of murine cells. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1048–1054. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1048-1054.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Li J. S. Studies with inhibitors of oligosaccharide processing indicate a functional role for complex sugars in the transport and proteolysis of Friend mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia virus envelope proteins. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):196–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle S. W., Dubois G. C., Robey W. G., Bess J. W., Jr, Fischinger P. J., Arthur L. O. Purification and characterization of the external envelope glycoprotein from two human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants, HTLV-IIIB and HTLV-IIIRF. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2258–2264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2258-2264.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. A., Datema R., Schwarz R. T. N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin, a novel inhibitor of glycoprotein processing, and its effect on fowl plague virus maturation. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. R., Grinna L. S., Robbins P. W. Differences in glycosylation patterns of closely related murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):67–71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Montelaro R. C. Comparison of glycoproteins by two-dimensional mapping of glycosylated peptides. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;157(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Kaaden O., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Hunsmann G. Shedding and interspecies type sero-reactivity of the envelope glycopolypeptide gp120 of the human immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2533–2538. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. C., Neckameyer W. S., Hayward W. S., Smith R. E. Genetic determinants of neoplastic diseases induced by a subgroup F avian leukosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1203–1212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1203-1212.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szurek P. F., Yuen P. H., Jerzy R., Wong P. K. Identification of point mutations in the envelope gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB temperature-sensitive paralytogenic mutant ts1: molecular determinants for neurovirulence. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):357–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.357-360.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco S. J., Robbins P. W. The initial stages of processing of protein-bound oligosaccharides in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4560–4567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen P. H., Tzeng E., Knupp C., Wong P. K. The neurovirulent determinants of ts1, a paralytogenic mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB, are localized in at least two functionally distinct regions of the genome. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):59–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.59-65.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]