Abstract
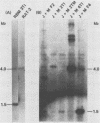
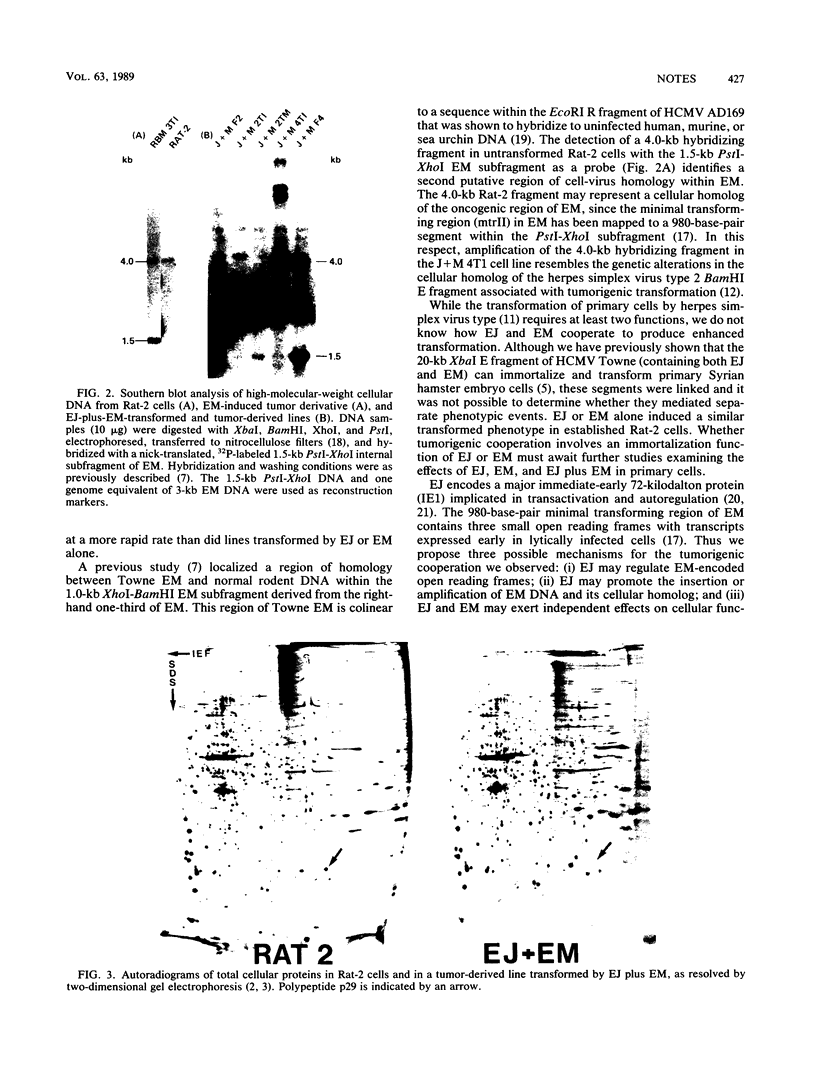
The terminal fragments (EJ and EM) of the XbaI-E transforming segment of human cytomegalovirus can independently induce the tumorigenic conversion of immortalized cells. To study their interaction, Rat-2 cells were transfected singly or with a combination of cloned EJ and EM DNAs. Large transformed foci were induced at a 10-fold higher frequency by EJ plus EM than by either DNA fragment alone. Focus-derived lines transformed by EJ plus EM produced tumors in syngeneic rats at a much faster rate (5 to 7 days) than did cell lines transformed by EJ or EM alone (25 to 35 days). Southern hybridizations showed that EM-homologous DNA was retained, exhibiting a complex pattern of multiple and amplified bands in EJ-plus-EM lines compared to a simple pattern in EM-induced lines. EJ DNA was not detected in the single or double transformants. The levels of p29, a 29-kilodalton transformation-sensitive marker in Rat-2 cells, were decreased 10- to 100-fold in cell lines transformed by EJ or EM fragment alone. Synthesis of p29 was shut off in EJ- plus-EM transformants. These data demonstrate that two unlinked transforming regions of human cytomegalovirus can cooperate to produce an aggressive tumorigenic phenotype.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht T., Rapp F. Malignant transformation of hamster embryo fibroblasts following exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Anderson N. L. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXI. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple isoelectric focusing. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. L., Anderson N. G. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXII. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple gradient-slab gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):341–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldogh I., Beth E., Huang E. S., Kyalwazi S. K., Giraldo G. Kaposi's sarcoma. IV. Detection of CMV DNA, CMV RNA and CMNA in tumor biopsies. Int J Cancer. 1981 Oct 15;28(4):469–474. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clanton D. J., Jariwalla R. J., Kress C., Rosenthal L. J. Neoplastic transformation by a cloned human cytomegalovirus DNA fragment uniquely homologous to one of the transforming regions of herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3826–3830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Mintz L., Miner R. C., Sands M., Ketterer B. Prevalence of cytomegalovirus infection in homosexual men. J Infect Dis. 1981 Feb;143(2):188–192. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.2.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geder L., Sanford E. J., Rohner T. J., Rapp F. Cytomegalovirus and cancer of the prostate: in vitro transformation of human cells. Cancer Treat Rep. 1977 Mar-Apr;61(2):139–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo G., Beth E., Henle W., Henle G., Mike V., Safai B., Huraux J. M., McHardy J., deThé G. Antibody patterns to herpesviruses in Kaposi's sarcoma. II. Serological association of American Kaposi's sarcoma with cytomegalovirus. Int J Cancer. 1978 Aug 15;22(2):126–131. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910220204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Immortalization and neoplastic transformation of normal diploid cells by defined cloned DNA fragments of herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5902–5906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Tanczos B., Jones C., Ortiz J., Salimi-Lopez S. DNA amplification and neoplastic transformation mediated by a herpes simplex DNA fragment containing cell-related sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1738–1742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt J., Gunning P., Kedes L., Jariwalla R. Smooth muscle alpha-action is a transformation-sensitive marker for mouse NIH 3T3 and Rat-2 cells. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):840–842. doi: 10.1038/316840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüleci G., Sakízlí M., Günalp A. Selective chromosomal damage caused by human cytomegalovirus. Acta Virol. 1980 Sep;24(5):341–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Fleckenstein B., Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells with cloned fragments of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):83–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.83-91.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Fleckenstein B., Jahn G., Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. Structure of the transforming region of human cytomegalovirus AD169. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.109-115.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque A., Jahan N., McWeeney D., Jariwalla R. J., Jones C., Brady J., Rosenthal L. J. Localization and DNA sequence analysis of the transforming domain (mtrII) of human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5709–5713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. 2.2-kilobase class of early transcripts encoded by cell-related sequences in human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):591–602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.591-602.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Stinski M. F. Autoregulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):676–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.676-682.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Beik T., Razzaque A., Jariwalla R., Cihlar R. L., Rosenthal L. J. Multiple transforming regions of human cytomegalovirus DNA. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):645–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.645-652.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]