Abstract
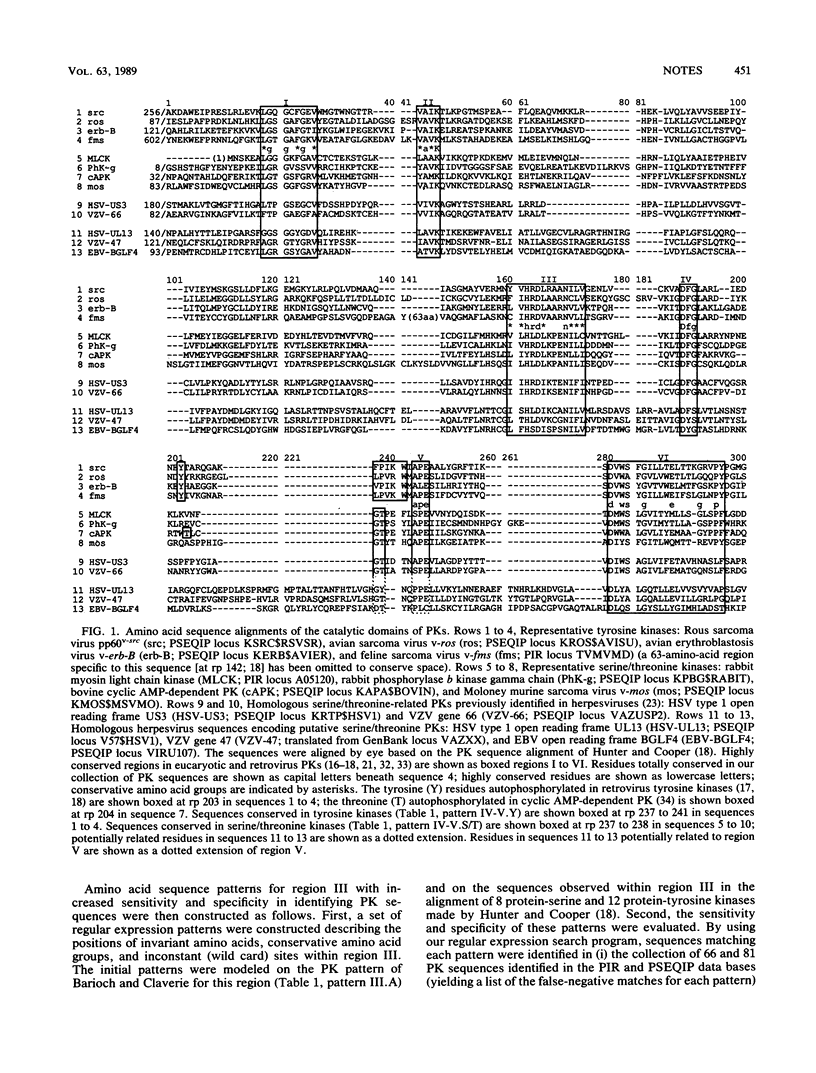
By using amino acid sequence patterns (motifs) diagnostic of conserved regions within the catalytic domains of protein kinases, homologous open reading frames of three herpesviruses were identified as protein kinase-related genes. The three sequences, herpes simplex virus gene UL13, varicella-zoster virus gene 47, and Epstein-Barr virus gene BGLF4, resemble serine/threonine kinases rather than tyrosine kinases.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue W. T., Stobbs D. G. Isolation of a protein kinase induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):383–388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.383-388.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks C., Fickett J. W., Goad W. B., Kanehisa M., Lewitter F. I., Rindone W. P., Swindell C. D., Tung C. S., Bilofsky H. S. The GenBank nucleic acid sequence database. Comput Appl Biosci. 1985 Dec;1(4):225–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M., Bricault L. PseqIP: a nonredundant and exhaustive protein sequence data bank generated from 4 major existing collections. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):60–65. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Draper K. G., Banks L., Powell K. L., Cohen G., Eisenberg R., Wagner E. K. High-resolution characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts encoding alkaline exonuclease and a 50,000-dalton protein tentatively identified as a capsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):591–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.591-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Taylor P. Genetic relations between varicella-zoster virus and Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1067–1079. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Darai G. Protein kinase and specific phosphate acceptor proteins associated with tupaia herpesvirus. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.410-415.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Purves F. C., McGeoch D. J., Marsden H. S., Leader D. P. Identification of the herpes simplex virus protein kinase as the product of viral gene US3. J Gen Virol. 1987 Oct;68(Pt 10):2699–2704. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-10-2699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. The protein identification resource (PIR). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):11–15. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K. Homology probing: identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):388–392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. The elucidation of protein function from its amino acid sequence. Comput Appl Biosci. 1986 Sep;2(3):181–187. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/2.3.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowicz T., Leader D. P. A major phosphoprotein of cells infected with pseudorabies virus is phosphorylated by cellular casein kinase II. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1159–1163. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katan M., Stevely W. S., Leader D. P. Partial purification and characterization of a new phosphoprotein kinase from cells infected with pseudorabies virus. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):57–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaster S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. II. Characterization of the virion protein kinase and of the polypeptides phosphorylated in the virion. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):798–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.798-811.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Davison A. J. Alphaherpesviruses possess a gene homologous to the protein kinase gene family of eukaryotes and retroviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1765–1777. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C. DNA sequence of the region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1 containing the exonuclease gene and neighbouring genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3435–3448. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson S., Tardy-Panit M., Bârzu O. Properties of a human cytomegalovirus-induced protein kinase. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montalvo E. A., Grose C. Varicella zoster virus glycoprotein gpI is selectively phosphorylated by a virus-induced protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8967–8971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Sclafani R. A., Fangman W. L., Rosamond J. Molecular characterization of cell cycle gene CDC7 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1590–1598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Deana A. D., Marchiori F., Leader D. P., Pinna L. A. The substrate specificity of the protein kinase induced in cells infected with herpesviruses: studies with synthetic substrates [corrected] indicate structural requirements distinct from other protein kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 28;889(2):208–215. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Katan M., Stevely W. S., Leader D. P. Characteristics of the induction of a new protein kinase in cells infected with herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1049–1057. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Longnecker R. M., Leader D. P., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 protein kinase is encoded by open reading frame US3 which is not essential for virus growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2896–2901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2896-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall C. C., Rogers H. W., Downer D. N., Gentry G. A. Protein kinase activity in equine herpesvirus. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):216–222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.216-222.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Padmanabha R., Glover C. V. Isolation and sequencing of cDNA clones encoding alpha and beta subunits of Drosophila melanogaster casein kinase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3409–3417. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji S., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Fischer E. H., Titani K. Amino acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of bovine type II adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3702–3709. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevely W. S., Katan M., Stirling V., Smith G., Leader D. P. Protein kinase activities associated with the virions of pseudorabies and herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):661–673. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S. Protein kinases: a diverse family of related proteins. Bioessays. 1987 Jul;7(1):24–29. doi: 10.1002/bies.950070106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster T. A., Lathrop R. H., Smith T. F. Pattern descriptors and the unidentified reading frame 6 human mtDNA dinucleotide-binding site. Proteins. 1988;3(2):97–101. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



