Abstract
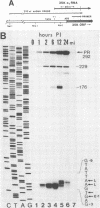
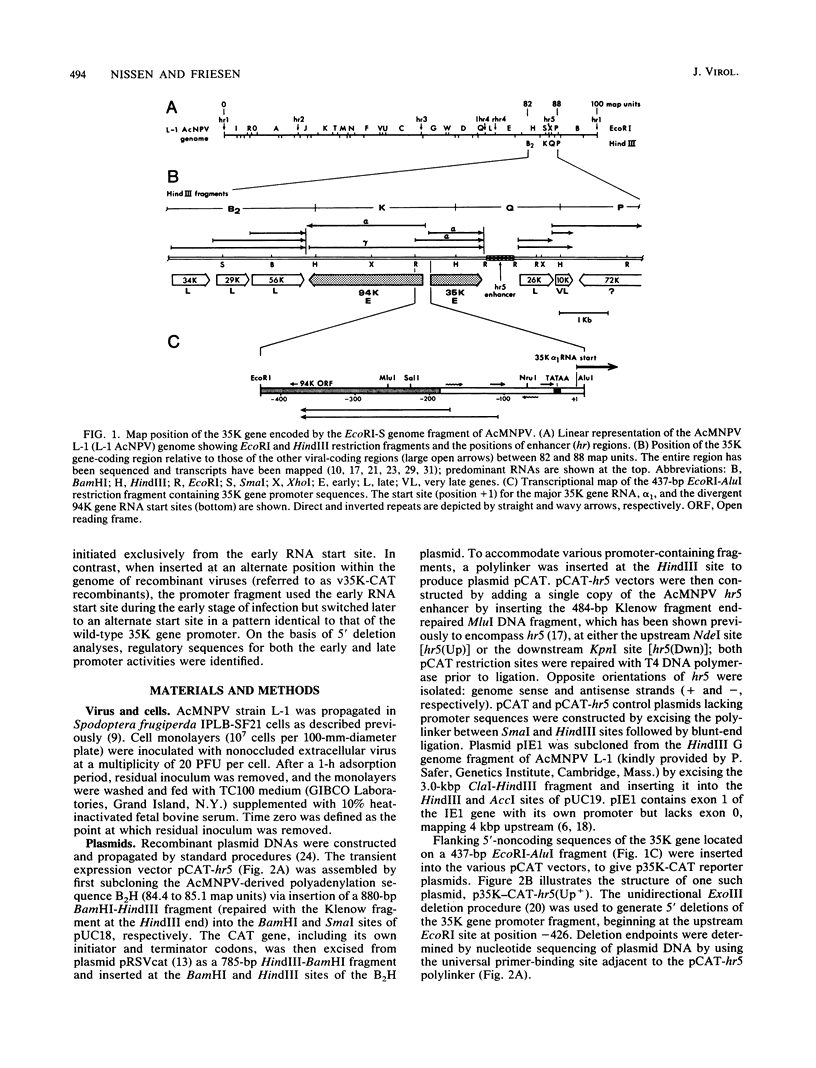
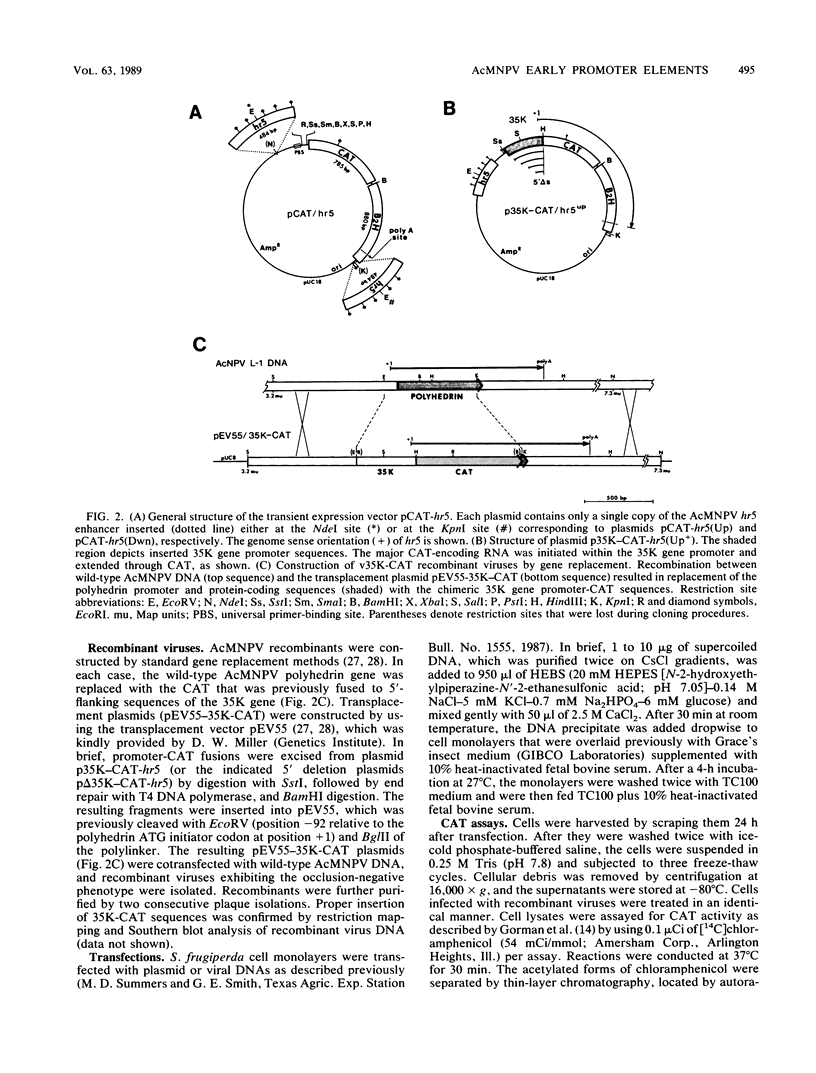
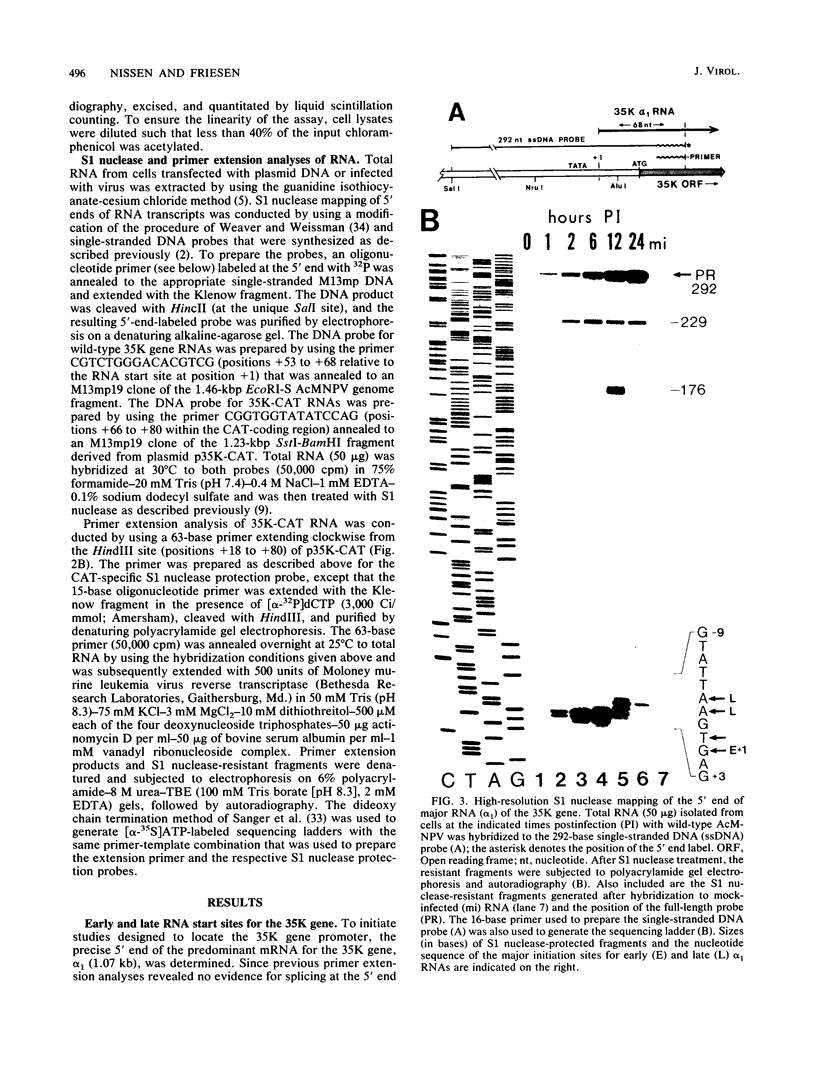
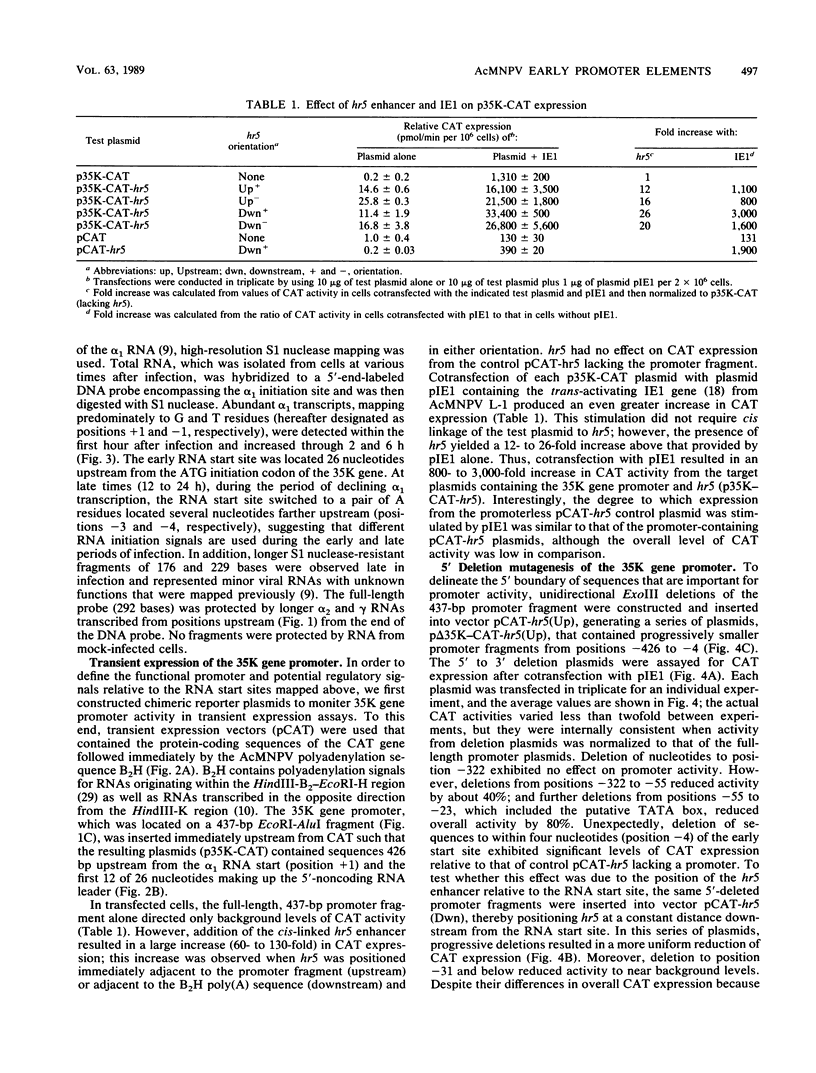
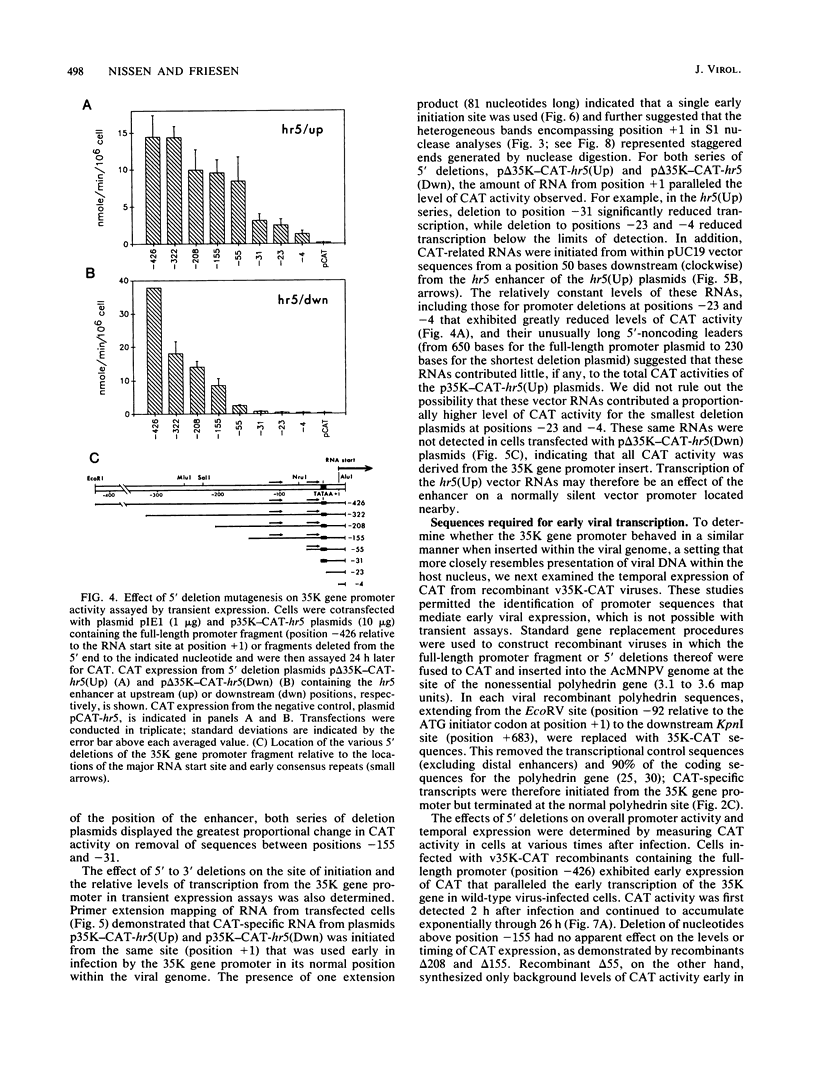
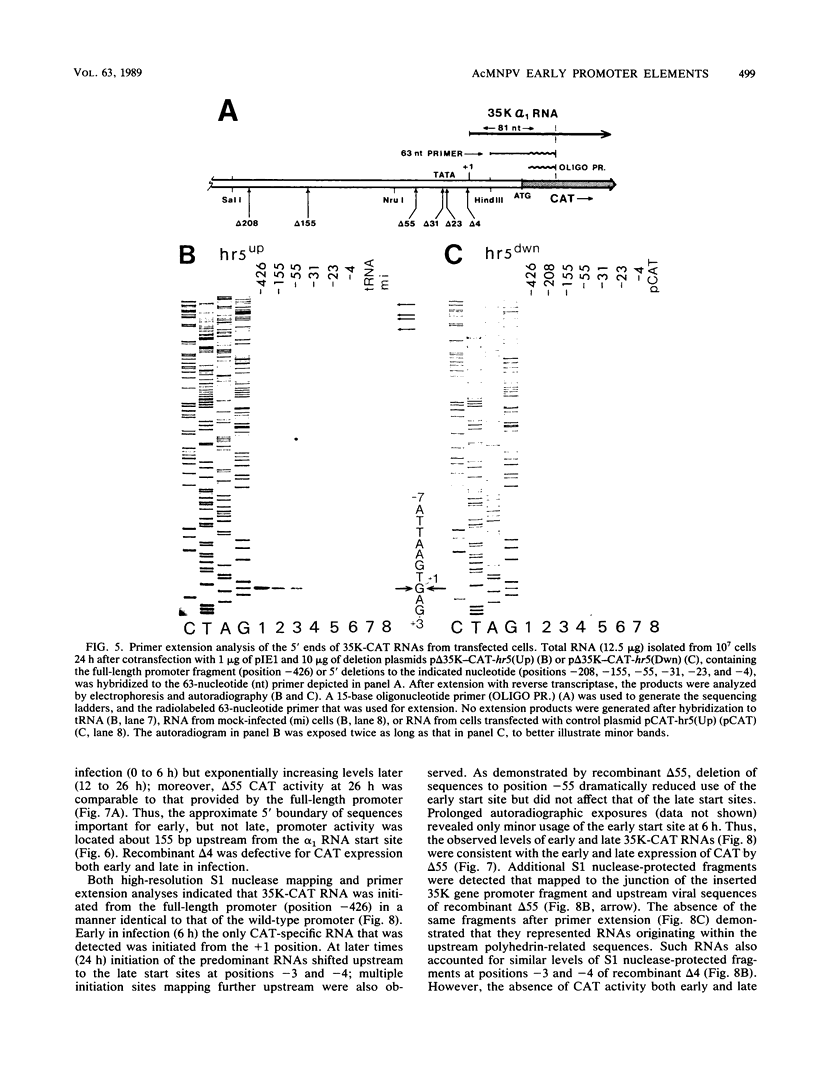
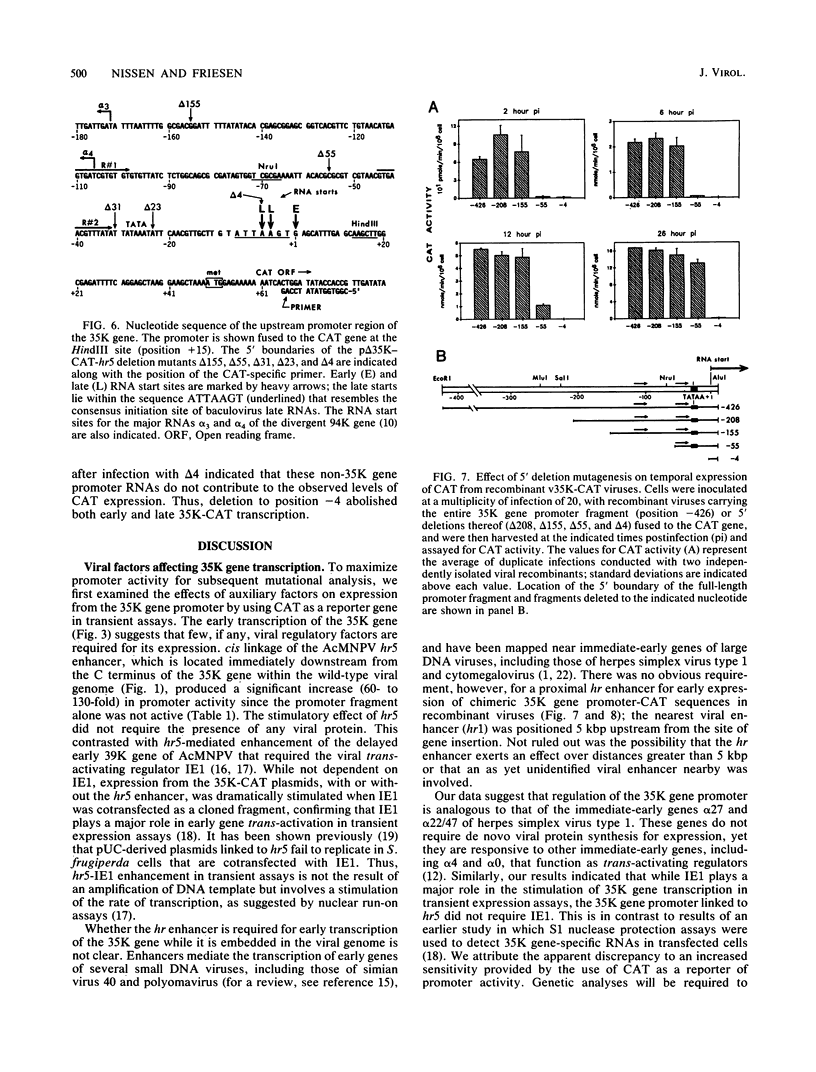
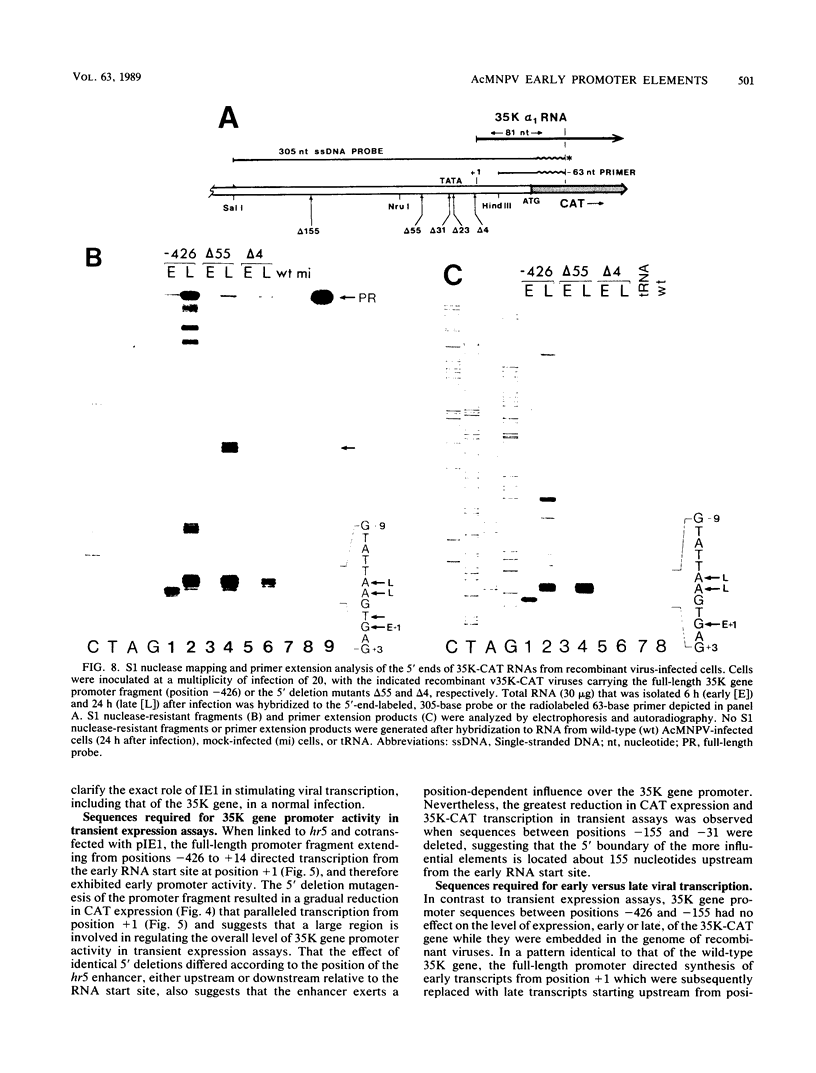
Transcription of the gene encoding a 35,000-molecular-weight protein (35K protein) from the EcoRI-S region (86.8 to 87.8 map units) of Autographa california nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV) occurs early in infection and declines later. The region promoting the gene for the 35K protein, extending from 426 base pairs (bp) upstream to 12 bp downstream from the RNA start site, was linked to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene (CAT) for analysis. CAT expression was monitored in cells that were transfected with plasmids containing the promoter-CAT fusion as well as cells infected with recombinant viruses containing the chimeric gene inserted into the AcMNPV genome. Mapping of the 5' ends of CAT-specific RNAs indicated that transcription initiated from the proper sites in both assays; moreover, the promoter fragment retained its early activity, despite an alternate location in the viral genome. The 5' boundary of upstream regulatory sequences was determined by constructing deletions of the promoter fragment extending toward the early RNA start site (position +1). In transient assays, a gradual reduction in CAT expression occurred as sequences from positions -426 to -31 were removed. In contrast, promoter deletions from positions -426 to -155 in recombinant viruses exhibited no effect on CAT expression, whereas deletions to position -55 abolished early expression but had no effect on late expression. Late CAT expression was eliminated when deletions to position -4 removed part of the late RNA start site. DNA signals potentiating early transcription were therefore located upstream (between positions -155 and -55) from those involved in late transcription of the gene encoding the 35K protein. Potential consensus sequences for early and late regulatory elements were identified.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. F. High-sensitivity S1 mapping with single-stranded [32P]DNA probes synthesized from bacteriophage M13mp templates. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonell L. F., Klowden M. J., Miller L. K. Baculovirus-mediated expression of bacterial genes in dipteran and mammalian cells. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.153-160.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. D., Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of an AcNPV immediately early gene which augments expression of the IE-1 trans-activated 39K gene. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):444–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm G. E., Henner D. J. Multiple early transcripts and splicing of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus IE-1 gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3193–3200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3193-3200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. M., Miller L. K. Characterization of an early gene accelerating expression of late genes of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2773–2781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2773-2781.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with specific nucleotide sequences in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6067–6083. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Divergent transcription of early 35- and 94-kilodalton protein genes encoded by the HindIII K genome fragment of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2264–2272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2264-2272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Temporal regulation of baculovirus RNA: overlapping early and late transcripts. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):392–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.392-400.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs L. Y., Woods M. S., Weaver R. F. Viral Transcription During Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Infection: a Novel RNA Polymerase Induced in Infected Spodoptera frugiperda Cells. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):641–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.641-646.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Herpes simplex virus immediate-early promoters are responsive to virus and cell trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2286–2296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2286-2296.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P. Magic enhancers? DNA. 1984;3(1):1–5. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of Autographa california nuclear polyhedrosis virus genes required for late gene expression. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.463-471.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Interspersed Homologous DNA of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Enhances Delayed-Early Gene Expression. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):215–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.215-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Nucleotide sequence and temporal expression of a baculovirus regulatory gene. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2091–2099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2091-2099.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A., Qin J. C., Rankin C., Hardin S. E., Weaver R. F. Nucleotide sequence of a portion of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome containing the EcoRI site-rich region (hr5) and an open reading frame just 5' of the p10 gene. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2565–2570. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N., Spector D., Mavromara-Nazos P., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. The DNA-binding properties of the major regulatory protein alpha 4 of herpes simplex viruses. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1531–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2832940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K. Baculoviruses as gene expression vectors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:177–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oellig C., Happ B., Müller T., Doerfler W. Overlapping sets of viral RNAs reflect the array of polypeptides in the EcoRI J and N fragments (map positions 81.2 to 85.0) of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3048–3057. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3048-3057.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possee R. D., Howard S. C. Analysis of the polyhedrin gene promoter of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10233–10248. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin C., Ladin B. F., Weaver R. F. Physical mapping of temporally regulated, overlapping transcripts in the region of the 10K protein gene in Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.18-27.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin C., Ooi B. G., Miller L. K. Eight base pairs encompassing the transcriptional start point are the major determinant for baculovirus polyhedrin gene expression. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann G. F. Polyhedrin structure. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1499–1513. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]