Abstract
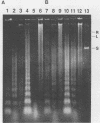
Target cell DNA damage is an early event in cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL)-mediated killing. It has been hypothesized that this DNA damage may serve as one mechanism of destroying viral genetic material inside infected cells. We directly examined the fate of viral DNA in target cells during CTL-mediated lysis. Polyomavirus DNA in transfected murine P815 mastocytoma targets was digested along with cellular DNA into oligonucleosome-sized fragments, although intact forms, possibly virion-associated DNA, were also present. In infected BALB/3T3 murine fibroblasts, which normally undergo single-stranded nicks when killed by CTL, polyomavirus DNA was converted to relaxed forms in the presence of CTL. These results suggest that the fate of the viral DNA depends on the stage of the viral life cycle and corresponds to the fate of the host cell DNA. Cleavage of the viral genome prior to assembly may thus be an important mechanism in specific antiviral immunity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J., Byrne J. A., Schreiber R., Patterson S., Oldstone M. B. Biology of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: clearance of virus and in vitro properties. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):552–560. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.552-560.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V. Mechanisms of recovery from a generalized viral infection: mousepox. II. Passive transfer of recovery mechanisms with immune lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1074–1089. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne J. A., Oldstone M. B. Biology of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: clearance of virus in vivo. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.682-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. A., Villarreal L. P. Lymphoid and other tissue-specific phenotypes of polyomavirus enhancer recombinants: positive and negative combinational effects on enhancer specificity and activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2068–2079. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouston W. M., Kerr J. F. Apoptosis, lymphocytotoxicity and the containment of viral infections. Med Hypotheses. 1985 Dec;18(4):399–404. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(85)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C., Chervenak R., Sellins K. S., Olson L. K. DNA fragmentation in targets of CTL: an example of programmed cell death in the immune system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;184:493–508. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8326-0_32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Chervenak R., Cohen J. J. Endogenous endonuclease-induced DNA fragmentation: an early event in cell-mediated cytolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Cohen J. J., Chervenak R. Differences in target cell DNA fragmentation induced by mouse cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1442–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frearson P. M., Crawford L. V. Polyoma virus basic proteins. J Gen Virol. 1972 Feb;14(2):141–155. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-14-2-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K., Deininger P. L., Friedmann T., Linney E. Mutation near the polyoma DNA replication origin permits productive infection of F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):809–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90445-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. M., Martz E. Intracellular reovirus survives cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated lysis of its host cell. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2899–2907. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. M., Martz E. The degree of CTL-induced DNA solubilization is not determined by the human vs mouse origin of the target cell. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3695–3698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Biological properties of an influenza A virus-specific killer T cell clone. Inhibition of virus replication in vivo and induction of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):225–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay R. L., Consigli R. A. Early events in polyoma virus infection: attachment, penetration, and nuclear entry. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):620–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.620-636.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillen J., Consigli R. A. Immunological reactivity of antisera to sodium dodecyl sulfate-derived polypeptides of polyoma virions. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1113–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1113-1120.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miovic M. L., Pizer L. I. Characterization of RNA synthesized in isolated nuclei of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected KB cells. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):567–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.567-571.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Blount P., Southern P. J., Lampert P. W. Cytoimmunotherapy for persistent virus infection reveals a unique clearance pattern from the central nervous system. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):239–243. doi: 10.1038/321239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Crawford L. V. The arrangement of nucleosomes in nucleoprotein complexes from polyoma virus and SV40. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):35–49. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Crew F., Crawford L. V. Comparison of nuclease digestion of polyoma virus nucleoprotein complex and mouse chromatin. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):175–186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.175-186.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Masakowski V. R., Dobos C. B. Mechanisms of immune lysis. I. Physiological distinction between target cell death mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and antibody plus complement. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1100–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Masakowski V., Rucinsky T., Phillips G. Mechanisms of immune lysis. III. Characterization of the nature and kinetics of the cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced nuclear lesion in the target. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2087–2094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton E. R., Wassarman P. M., DePamphilis M. L. Structure of Simian virus 40 chromosomes in nuclei from infected monkey cells. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 15;125(4):491–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap K. L., Ada G. L. Cytotoxic T cells specific for influenza virus-infected target cells. Immunology. 1977 Feb;32(2):151–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap K. L., Ada G. L., McKenzie I. F. Transfer of specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes protects mice inoculated with influenza virus. Nature. 1978 May 18;273(5659):238–239. doi: 10.1038/273238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap K. L., Ada G. L. The recovery of mice from influenza A virus infection: adoptive transfer of immunity with influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognizing a common virion antigen. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(5):413–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap K. L., Ada G. L. The recovery of mice from influenza virus infection: adoptive transfer of immunity with immune T lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(5):389–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap K. L., Braciale T. J., Ada G. L. Role of T-cell function in recovery from murine influenza infection. Cell Immunol. 1979 Mar 15;43(2):341–351. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Althage A. Antiviral protection by virus-immune cytotoxic T cells: infected target cells are lysed before infectious virus progeny is assembled. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):644–651. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Welsh R. M. H-2 compatibility requirement for virus-specific T cell-mediated effector functions in vivo. I. Specificity of T cells conferring antiviral protection against lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus is associated with H-2K and H-2D. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1495–1502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]