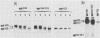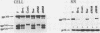Abstract
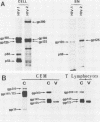
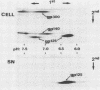
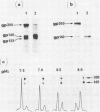
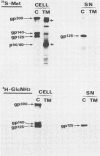
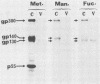
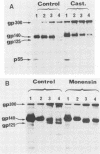
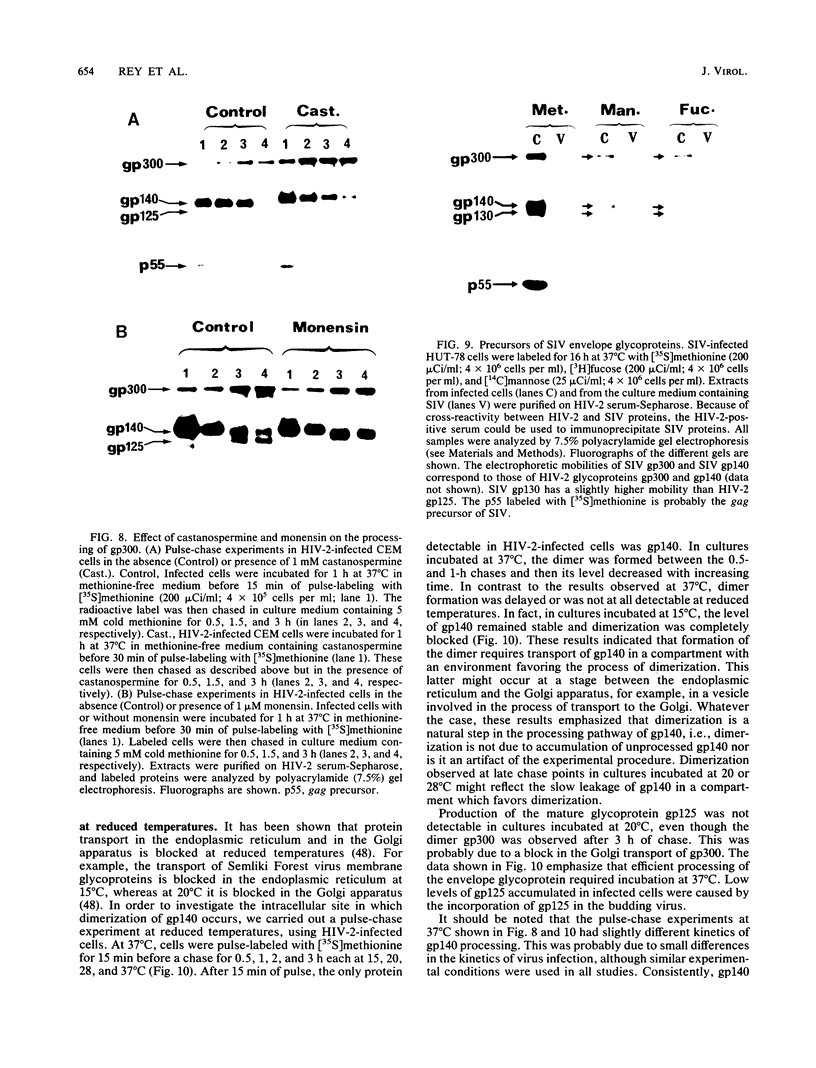
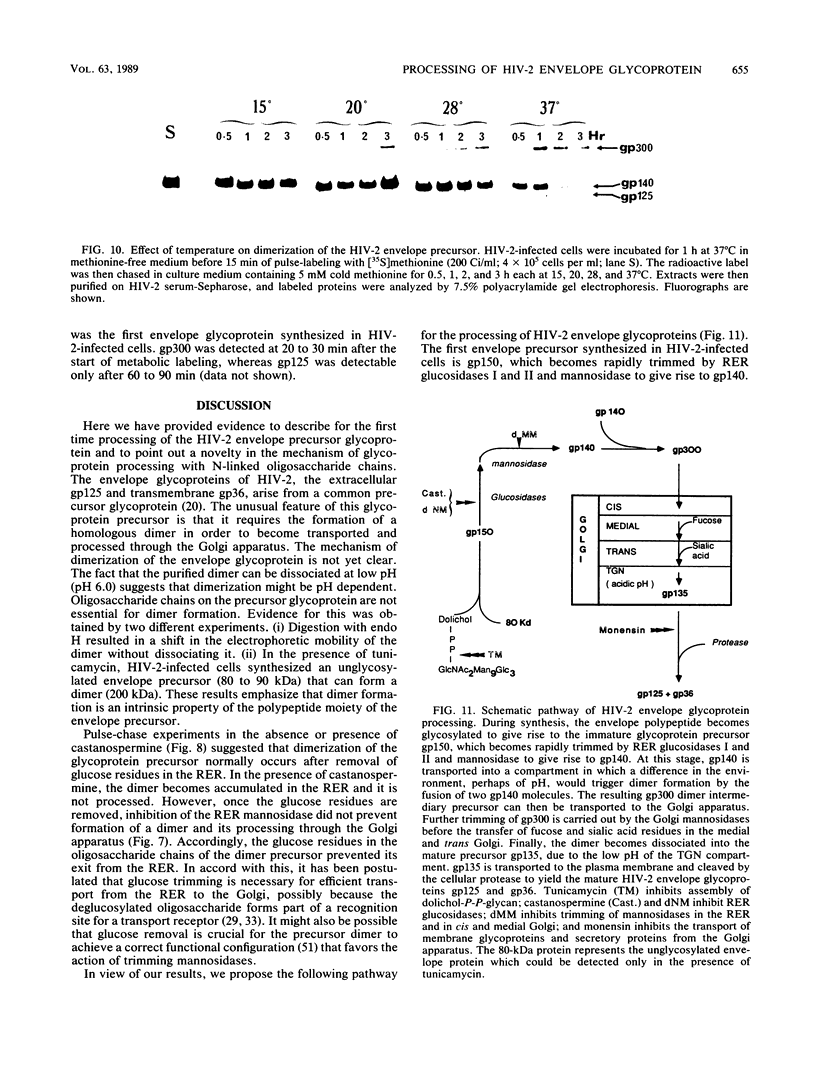
Four glycoproteins with apparent molecular weights of 300,000, 140,000, 125,000, and 36,000 (gp300, gp140, gp125, and gp36) were detectable in human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2)-infected cells. gp125 and gp36 are the external and transmembrane components, respectively, of the envelope glycoproteins of HIV-2 mature virions. gp300 and gp140 are only detectable in virus-infected cells. They have identical isoelectric points, suggesting that gp300 might be a dimeric form of the immature precursor, gp140. The purified gp300 can be dissociated in a slightly acidic buffer to give rise to monomers of 140,000 molecular weight. Such dissociated monomers and the purified gp140 showed identical patterns of polypeptides after partial proteolysis with Staphylococcus aureus V8 protease. Pulse-chase experiments indicated that gp300 is formed after synthesis of gp140 and before the detection of the mature external envelope glycoprotein, gp125. These results were confirmed by using various inhibitors of glycosylation and inhibitors of trimming enzymes. Dimer formation of the envelope glycoprotein precursor was also observed in cells infected with simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV), a virus closely related to HIV-2. On the other hand, the envelope glycoprotein precursor of HIV-1 did not form a dimer during its processing. Therefore, dimer formation seems to be a specific property of HIV-2 and SIV envelope gene expression. Such transient dimerization of the glycoprotein precursor might be required for its efficient transport to the Golgi apparatus and for its processing.
Full text
PDF

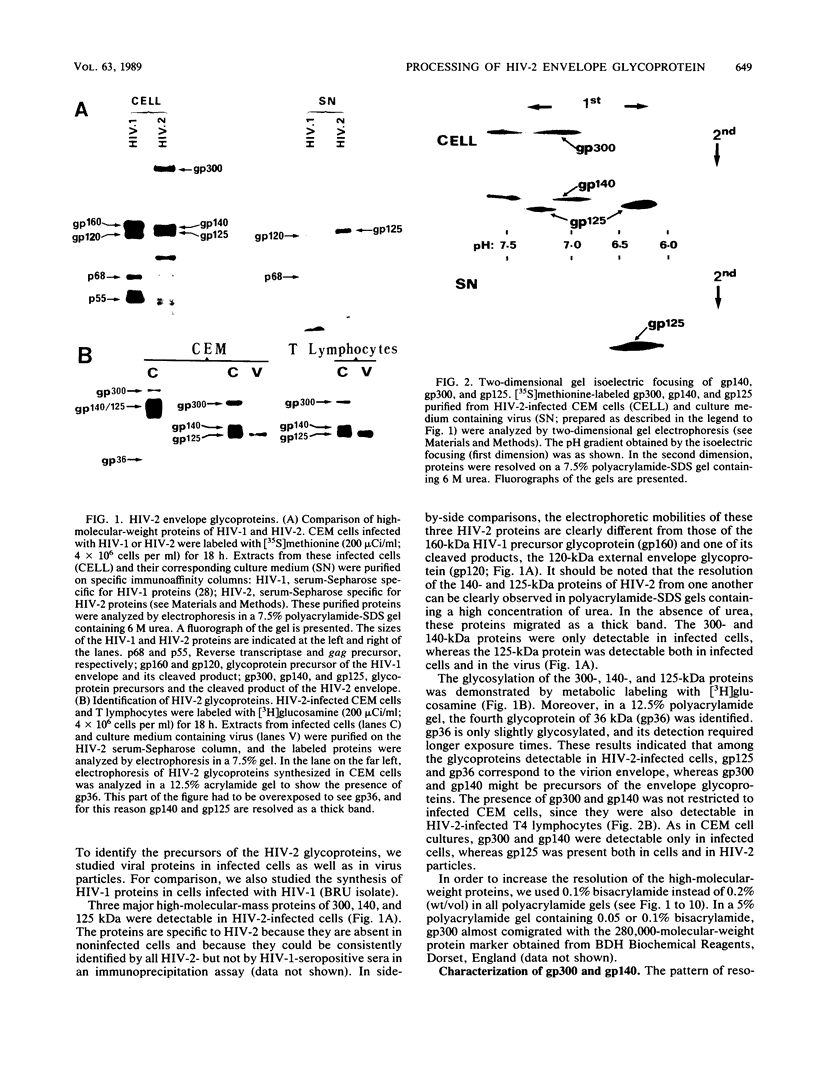





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Pathak R. K. Vesicles and cisternae in the trans Golgi apparatus of human fibroblasts are acidic compartments. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K. Sequential antibody affinity chromatography of human leukocyte interferon. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(1-2):77–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun-Vezinet F., Rey M. A., Katlama C., Girard P. M., Roulot D., Yeni P., Lenoble L., Clavel F., Alizon M., Gadelle S. Lymphadenopathy-associated virus type 2 in AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Clinical and virological features in four patients. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):128–132. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91967-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Guyader M., Guétard D., Sallé M., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Molecular cloning and polymorphism of the human immune deficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):691–695. doi: 10.1038/324691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Guétard D., Brun-Vézinet F., Chamaret S., Rey M. A., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Laurent A. G., Dauguet C., Katlama C., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a new human retrovirus from West African patients with AIDS. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2425430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Mansinho K., Chamaret S., Guetard D., Favier V., Nina J., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Champalimaud J. L., Montagnier L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 infection associated with AIDS in West Africa. N Engl J Med. 1987 May 7;316(19):1180–1185. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198705073161903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Letvin N. L., King N. W., Kannagi M., Sehgal P. K., Hunt R. D., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Desrosiers R. C. Isolation of T-cell tropic HTLV-III-like retrovirus from macaques. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1201–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.3159089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datema R., Romero P. A., Legler G., Schwarz R. T. Inhibition of formation of complex oligosaccharides by the glucosidase inhibitor bromoconduritol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6787–6791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Gurgo C., Guo H. G., Gallo R. C., Collalti E., Fargnoli K. A., Hall L. F., Wong-Staal F., Reitz M. S., Jr Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus and its relationship to the human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):539–543. doi: 10.1038/328539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann U., Bause E., Legler G., Ploegh H. Novel mannosidase inhibitor blocking conversion of high mannose to complex oligosaccharides. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):755–758. doi: 10.1038/307755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann U., Bause E., Ploegh H. Inhibitors of oligosaccharide processing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 24;825(2):95–110. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., McClure H. M., Anderson D. C., Swenson R. B., Anand R., Srinivasan A. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from naturally infected sooty mangabey monkeys (Cercocebus atys). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5286–5290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Carney D. N., Bunn P. A., Russell E. K., Jaffe E. S., Schechter G. P., Guccion J. G. Mitogen requirements for the in vitro propagation of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Quinn P., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from medial to trans Golgi cisternae in baby hamster kidney cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):835–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifetz A., Keenan R. W., Elbein A. D. Mechanism of action of tunicamycin on the UDP-GlcNAc:dolichyl-phosphate Glc-NAc-1-phosphate transferase. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2186–2192. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmard J., Drapeau G. R. Staphylococcal protease: a proteolytic enzyme specific for glutamoyl bonds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3506–3509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Schlesinger M. J. Vesicular stomatitis virus and sindbis virus glycoprotein transport to the cell surface is inhibited by ionophores. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):407–424. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi M., Yetz J. M., Letvin N. L. In vitro growth characteristics of simian T-lymphotropic virus type III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7053–7057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust B., Laurent A. G., Le Guern A., Jeannequin O., Montagnier L., Hovanessian A. G. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for the HIV-1 precursor glycoprotein. AIDS. 1988 Feb;2(1):17–24. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198802000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemansky P., Gieselmann V., Hasilik A., von Figura K. Cathepsin D and beta-hexosaminidase synthesized in the presence of 1-deoxynojirimycin accumulate in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10129–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Hoffman A. D., Kramer S. M., Landis J. A., Shimabukuro J. M., Oshiro L. S. Isolation of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from San Francisco patients with AIDS. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):840–842. doi: 10.1126/science.6206563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Tabas I., Kornfeld S. The synthesis of complex-type oligosaccharides. I. Structure of the lipid-linked oligosaccharide precursor of the complex-type oligosaccharides of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7762–7770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N. Glucose removal from N-linked oligosaccharides is required for efficient maturation of certain secretory glycoproteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1720–1729. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of CD4-bearing cells occurs by a pH-independent mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):513–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Kennedy M. S., Sligh J. M., Cort S. P., Mawle A., Nicholson J. K. Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.3001934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Mawle A., Cort S. P., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Scheppler-Campbell J. A., Hicks D., Sligh J. Cellular tropism of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV. I. Role of T cell activation and expression of the T4 antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3151–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagnier L., Clavel F., Krust B., Chamaret S., Rey F., Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C. Identification and antigenicity of the major envelope glycoprotein of lymphadenopathy-associated virus. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):283–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90326-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novikoff A. B. The endoplasmic reticulum: a cytochemist's view (a review). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2781–2787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Pratt R. M., Yamada K. M. Role of carbohydrates in protein secretion and turnover: effects of tunicamycin on the major cell surface glycoprotein of chick embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):461–473. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Powell S. K., Quinn D. L., Moore H. P. The trans-most cisternae of the Golgi complex: a compartment for sorting of secretory and plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peyrieras N., Bause E., Legler G., Vasilov R., Claesson L., Peterson P., Ploegh H. Effects of the glucosidase inhibitors nojirimycin and deoxynojirimycin on the biosynthesis of membrane and secretory glycoproteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):823–832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Kuismanen E. Pre- and post-Golgi vacuoles operate in the transport of Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins to the cell surface. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul R., Chambers J. P., Molyneux R. J., Elbein A. D. Castanospermine, a tetrahydroxylated alkaloid that inhibits beta-glucosidase and beta-glucocerebrosidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):593–597. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer R. Characterization of sialic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:64–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger S., Malfer C., Schlesinger M. J. The formation of vesicular stomatitis virus (San Juan strain) becomes temperature-sensitive when glucose residues are retained on the oligosaccharides of the glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7597–7601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz R. T., Rohrschneider J. M., Schmidt M. F. Suppression of glycoprotein formation of Semliki Forest, influenza, and avian sarcoma virus by tunicamycin. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):782–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.782-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Alizon M., Staskus K., Klatzmann D., Cole S., Danos O., Retzel E., Tiollais P., Haase A., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of the visna lentivirus: relationship to the AIDS virus. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):369–382. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein B. S., Gowda S. D., Lifson J. D., Penhallow R. C., Bensch K. G., Engleman E. G. pH-independent HIV entry into CD4-positive T cells via virus envelope fusion to the plasma membrane. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):659–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90542-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strous G. J., Lodish H. F. Intracellular transport of secretory and membrane proteins in hepatoma cells infected by vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90547-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Vassalli P. Plasma cell immunoglobulin secretion: arrest is accompanied by alterations of the golgi complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Nov 1;146(5):1332–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Harris T. M., Touster O. Swainsonine inhibits the biosynthesis of complex glycoproteins by inhibition of Golgi mannosidase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7936–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Alizon M., Montagnier L. Relationship of AIDS to other retroviruses. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):743–743. doi: 10.1038/313743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Danos O., Cole S., Alizon M. Nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, LAV. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A. Receptor molecule blocks HIV. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):15–15. doi: 10.1038/331015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]