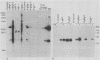
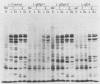
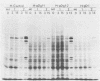
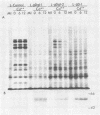
Abstract
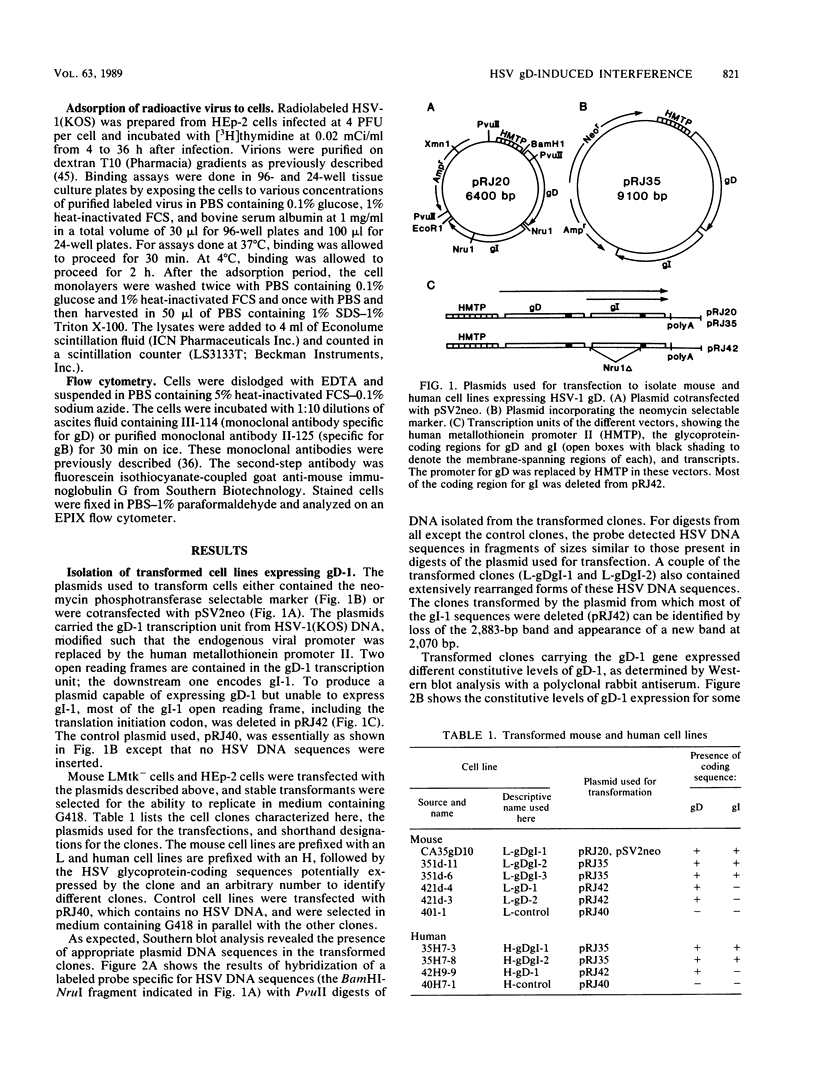
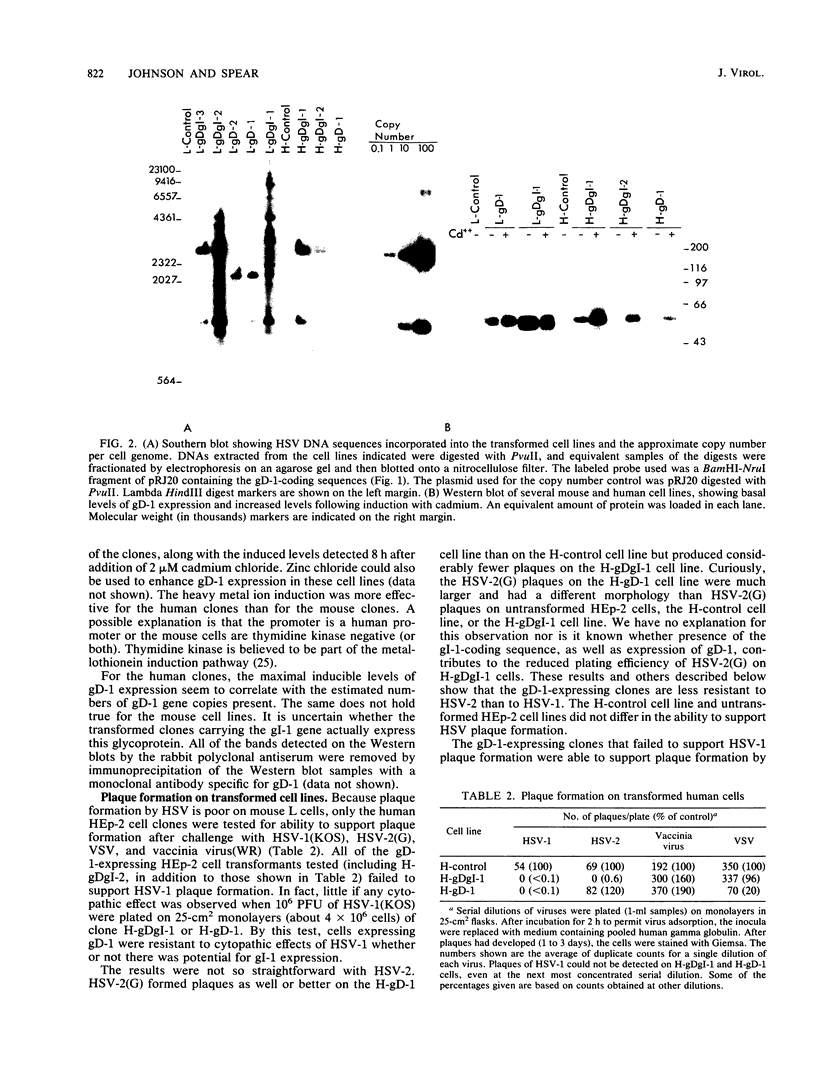
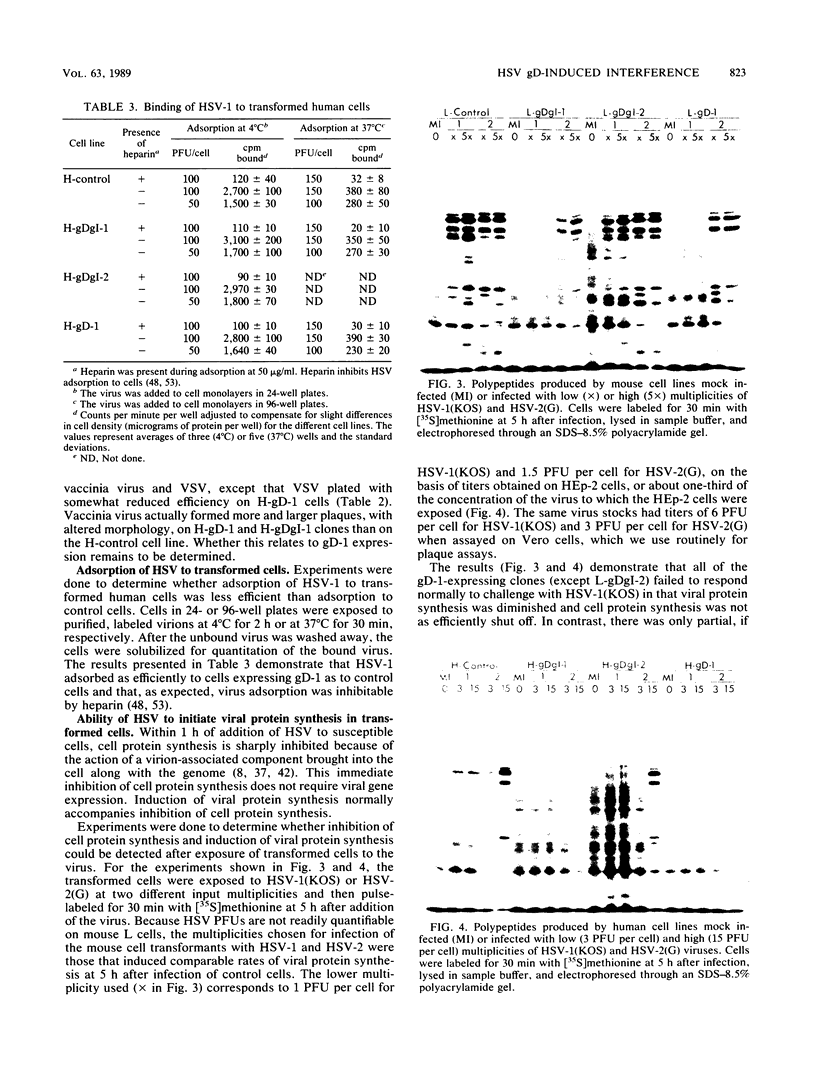
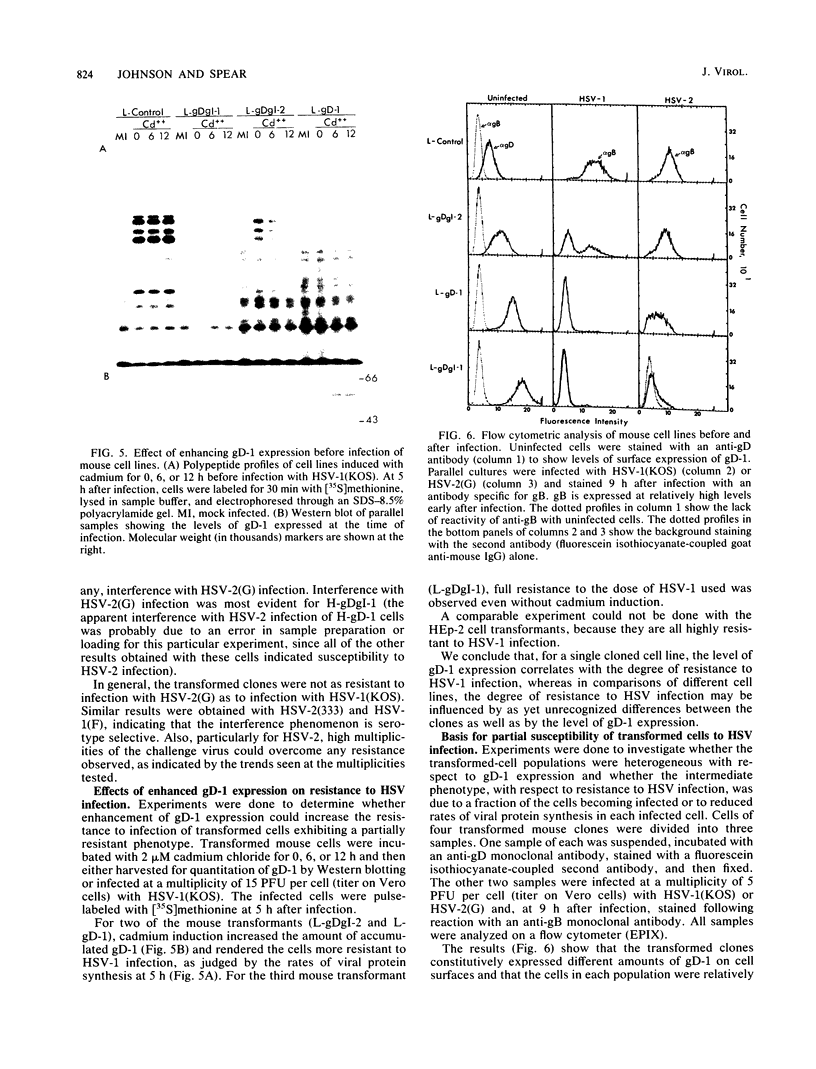
We showed that the expression of a single protein, glycoprotein D (gD-1), specified by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) renders cells resistant to infection by HSV but not to infection by other viruses. Mouse (LMtk-) and human (HEp-2) cell lines containing the gene for gD-1 under control of the human metallothionein promoter II expressed various levels of gD-1 constitutively and could be induced to express higher levels with heavy metal ions. Radiolabeled viruses bound equally well to gD-1-expressing and control cell lines. Adsorbed viruses were unable to penetrate cells expressing sufficient levels of gD-1, based on lack of any cytopathic effects of the challenge virus and on failure to detect either the induction of viral protein synthesis or the shutoff of host protein synthesis normally mediated by a virion-associated factor. The resistance to HSV infection conferred by gD-1 expression was not absolute and depended on several variables, including the amount of gD-1 expressed, the dosage of the challenge virus, the serotype of the challenge virus, and the properties of the cells themselves. The interference activity of gD-1 is discussed in relation to the role of gD-1 in virion infectivity and its possible role in permitting escape of progeny HSV from infected cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Longnecker R., Roizman B., Pereira L. Identification, properties, and gene location of a novel glycoprotein specified by herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):207–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Dowbenko D., Lasky L. A., Simonsen C. C. Detection of antibodies to herpes simplex virus with a continuous cell line expressing cloned glycoprotein D. Science. 1983 Nov 4;222(4623):524–527. doi: 10.1126/science.6312563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklaws B. A., Nash A. A., Darby G. Specificity of the immune response of mice to herpes simplex virus glycoproteins B and D constitutively expressed on L cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1103–1114. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Z., Person S., Warner S. C., Zhou J. H., DeLuca N. A. Linker-insertion nonsense and restriction-site deletion mutations of the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):714–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.714-721.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Arsenakis M., Farabegoli F., Roizman B. Entry of herpes simplex virus 1 in BJ cells that constitutively express viral glycoprotein D is by endocytosis and results in degradation of the virus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):159–167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.159-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai P. J., Schaffer P. A., Minson A. C. Excretion of non-infectious virus particles lacking glycoprotein H by a temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1: evidence that gH is essential for virion infectivity. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1147–1156. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L., Clark J. Early and delayed shut-off of host protein synthesis in cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jul;61(Pt 50):121–125. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Marsden H. S., McGeoch D. J. Novel herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins identified by antiserum against a synthetic oligopeptide from the predicted product of gene US4. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):745–751. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Triezenberg S. J., McKnight S. L. Expression of a truncated viral trans-activator selectively impedes lytic infection by its cognate virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):452–454. doi: 10.1038/335452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Anti-glycoprotein D antibodies that permit adsorption but block infection by herpes simplex virus 1 prevent virion-cell fusion at the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Specificities of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that inhibit adsorption of herpes simplex virus to cells and lack of inhibition by potent neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.475-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U., Minson A. The properties and sequence of glycoprotein H of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):230–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGGAN M. D., ROIZMAN B. The isolation and properties of a variant of Herpes simplex producing multinucleated giant cells in monolayer cultures in the presence of antibody. Am J Hyg. 1959 Sep;70:208–219. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander S. L., Sutherland S. L., Gage P. J., Johnson D. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies specific for herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D inhibit virus penetration. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3356–3364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3356-3364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Alpers J. D., Rackowski J. L., Huebner K., Haggarty B. S., Cedarbaum A. J., Reed J. C. Alterations in T4 (CD4) protein and mRNA synthesis in cells infected with HIV. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3095925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura K., Betz J. L., Sadler J. R., Pizer L. I. RNAs transcribed from a 3.6-kilobase SmaI fragment of the short unique region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):460–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.460-471.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Smiley J. R. Intracellular transport of herpes simplex virus gD occurs more rapidly in uninfected cells than in infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):682–689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.682-689.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. Monensin inhibits the processing of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins, their transport to the cell surface, and the egress of virions from infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1102–1112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1102-1112.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M. The expression of the syn- gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. I. Morphology of infected cells. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):490–499. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90479-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Spear P. G. Viral and cellular factors that influence cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):402–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Bendicenti di Girolamo A. Activation of metallothionein expression is potentiated by DNA sequences present in the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):292–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80681-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Identification of a herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein gene within a gene cluster dispensable for growth in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Clustering of genes dispensable for growth in culture in the S component of the HSV-1 genome. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.3033823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen B., Price M. P., Goverman J. M., McMillan M., White J., Kappler J., Marrack P., Pierres A., Pierres M., Hood L. Gene transfer of H-2 class II genes: antigen presentation by mouse fibroblast and hamster B-cell lines. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt H., Schröder C. H., Kaerner H. C. Herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein E is not indispensable for viral infectivity. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):600–603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.600-603.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble A. G., Lee G. T., Sprague R., Parish M. L., Spear P. G. Anti-gD monoclonal antibodies inhibit cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):218–224. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90409-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P., Tobita K., Ueda M., Compans R. W. Characterization of temperature sensitive influenza virus mutants defective in neuraminidase. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Parish M. L., Noble A. G., Spear P. G. Potent neutralizing activity associated with anti-glycoprotein D specificity among monoclonal antibodies selected for binding to herpes simplex virions. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):483–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.483-488.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B. Polykaryocytosis induced by viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Feb;48:228–234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.2.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read G. S., Frenkel N. Herpes simplex virus mutants defective in the virion-associated shutoff of host polypeptide synthesis and exhibiting abnormal synthesis of alpha (immediate early) viral polypeptides. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):498–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.498-512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Buckmaster A., Bell S., Hodgman C., Minson A. C. Identification of a new glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1 and genetic mapping of the gene that codes for it. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):647–655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.647-655.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Norrild B., Chan C., Pereira L. Identification and preliminary mapping with monoclonal antibodies of a herpes simplex virus 2 glycoprotein lacking a known type 1 counterpart. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schek N., Bachenheimer S. L. Degradation of cellular mRNAs induced by a virion-associated factor during herpes simplex virus infection of Vero cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):601–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.601-610.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. V. Purification and structural proteins of the herpesvirion. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):143–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.143-159.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Meier C., Mann A. M., Chapman N., Wasiak A. Envelope glycoprotein of HIV induces interference and cytolysis resistance in CD4+ cells: mechanism for persistence in AIDS. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90168-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Zhang X. H., Volsky D. J. Downregulation of cell surface molecules during noncytopathic infection of T cells with human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3741–3748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3741-3748.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P. K. Avian tumor viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1965;11:293–385. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60549-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Herpes simplex virus type-1 glycoprotein D gene: nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.6289440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Rapid identification of nonessential genes of herpes simplex virus type 1 by Tn5 mutagenesis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):576–579. doi: 10.1126/science.3033824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WuDunn D., Spear P. G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.52-58.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]