Abstract
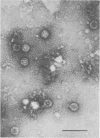
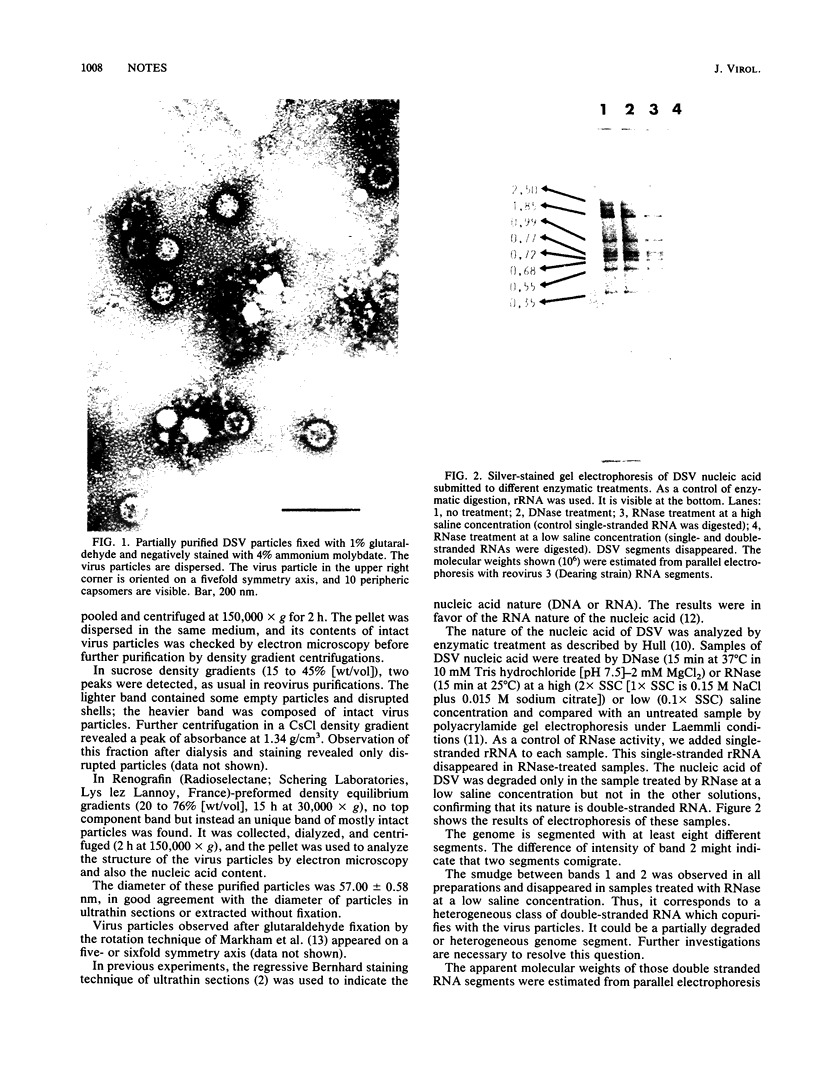
The S character of Drosophila simulans, the absence or malformation or both of bristles and other cuticular structures, was described by Comendador (Drosophila Inf. Serv. 55:26-28, 1980). Its characteristics (maternal transmission, low pathogenicity, and sensitivity to temperature) suggested the existence of a virus as the causative agent. Indeed, reoviruslike particles were found in subcuticular cells of S individuals, and its association with S phenotypic expression was shown. This virus was called Drosophila S virus (DSV) (C. Louis, M. López-Ferber, N. Plus, G. Kuhl, and S. Baker, J. Virol. 62:1266-1270, 1988). We report here the purification and analysis of some properties of DSV particles, the morphology (spherical, 60 nm in diameter with an electron dense central core and less dense shell) and genome composition (double-stranded RNA divided into segments), which classify DSV as a new member of the family Reoviridae.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhard W. A new staining procedure for electron microscopical cytology. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 May;27(3):250–265. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eley S. M., Gardner R., Molyneux D. H., Moore N. F. A reovirus from the bedbug, Cimex lectularius. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):195–199. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis C., Lopez-Ferber M., Comendador M., Plus N., Kuhl G., Baker S. Drosophila S virus, a hereditary reolike virus, probable agent of the morphological S character in Drosophila simulans. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1266–1270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1266-1270.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Genome RNAs and polypeptides of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):726–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.726-733.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas-Orillard M. Modifications of Mean Ovariole Number, Fresh Weight of Adult Females and Developmental Time in DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER Induced by Drosophila C Virus. Genetics. 1984 Aug;107(4):635–644. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.4.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]