Abstract
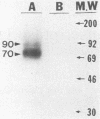
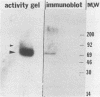
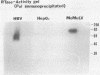
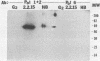
We have used activity gel analysis and immunoblotting to provide evidence linking the hepatitis B virus (HBV) reverse transcriptase with its longest unassigned open reading frame (polymerase [Pol]-ORF). Activity gel analysis demonstrated that infectious HBV particles secreted by the Hep 2.2.15 cell line contain major (approximately 70 kilodaltons [kDa]) and minor (approximately 90 kDa) reverse transcriptase activities. By Western immunoblotting, we detected in both HBV particles and Hep 2.2.15 cell extract a approximately 70-kDa Pol-specific peptide. This approximately 70-kDa peptide reacted with antisera directed against the carboxy terminus of the pol gene product. No such immunoreactivity was observed with antisera against the amino terminus of the Pol peptide. The reverse transcriptase protein which was eluted from the major approximately 70-kDa region detected on an activity gel reacted with Pol-specific antisera. Furthermore, reverse transcriptase activity was immunoprecipitated from dissociated HBV particles by using Pol-specific antisera. On the basis of our results, we suggest that HBV encodes its reverse transcriptase from the Pol-ORF.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acs G., Sells M. A., Purcell R. H., Price P., Engle R., Shapiro M., Popper H. Hepatitis B virus produced by transfected Hep G2 cells causes hepatitis in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4641–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavand M. R., Laub O. Two proteins with reverse transcriptase activities associated with hepatitis B virus-like particles. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.626-628.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelson M. A., DeTolla L. J., Zhou X. D. A chronic carrierlike state is established in nude mice injected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1408–1415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1408-1415.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D. Persistent infection of humans with hepatitis B virus: mechanisms and consequences. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Sep-Oct;4(5):1026–1047. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.5.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. M., Greenman R. L., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Robinson W. S. DNA polymerase associated with human hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):995–1005. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.995-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laub O., Rall L. B., Truett M., Shaul Y., Standring D. N., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J. Synthesis of hepatitis B surface antigen in mammalian cells: expression of the entire gene and the coding region. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):271–280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.271-280.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Hepatitis B viral DNA-RNA hybrid molecules in particles from infected liver are converted to viral DNA molecules during an endogenous DNA polymerase reaction. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):64–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh H., Hayashida H., Miyata T. Sequence homology between retroviral reverse transcriptase and putative polymerases of hepatitis B virus and cauliflower mosaic virus. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):827–829. doi: 10.1038/305827a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]