Abstract
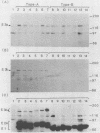
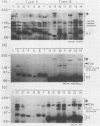
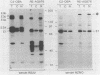
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigens EBNA 3a, 3b, and 3c have recently been mapped to adjacent reading frames in the BamHI L and E fragments of the B95.8 EBV genome. We studied by immunoblotting the expression of the family of EBNA 3 proteins in a panel of 20 EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) carrying either type A (EBNA 2A-encoding) or type B (EBNA 2B-encoding) virus isolates. Certain human sera from donors naturally infected with type A isolates detected the EBNA 3a, 3b, and 3c proteins in all type A virus-transformed LCLs (with a single exception in which EBNA 3b was not detected) but detected only EBNA 3a in LCLs carrying type B isolates. These results were confirmed with human and murine antibodies with specific reactivity against sequences of the type A EBNA 3a, 3b, or 3c expressed in bacterial fusion proteins. Conversely, selected human sera from donors naturally infected with type B strains of EBV identified the EBNA 3a encoded by both types of isolates plus two novel EBNAs present only in type B, and not in type A, virus-transformed LCLs; these novel proteins appear to be the type B homologs of EBNA 3b and 3c. The distinction between type A and type B EBV isolates therefore extends beyond the EBNA 2 gene to the EBNA 3 family of proteins. This has important implications with respect to the evolutionary origin of these two EBV types and also places in a new light recent studies which identified differences between type A and type B transformants in terms of growth phenotype (A. B. Rickinson, L. S. Young, and M. Rowe, J. Virol. 61:1310-1317, 1987) and of detection by EBV-specific cytotoxic T cells (D. J. Moss, I. S. Misko, S. R. Burrows, K. Burman, R. McCarthy, and T. B. Sculley, Nature [London] 331:719-721, 1988).
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adldinger H. K., Delius H., Freese U. K., Clarke J., Bornkamm G. W. A putative transforming gene of Jijoye virus differs from that of Epstein-Barr virus prototypes. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Griffin B. E. Prediction and demonstration of a novel Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4353–4367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrand J. R., Young L. S., Tugwood J. D. Two families of sequences in the small RNA-encoding region of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) correlate with EBV types A and B. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):983–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.983-986.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ernberg I., Uno M., Ono Y., Klein G., Lerner R. A. An Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA5) partly encoded by the transformation-associated Bam WYH region of EBV DNA: preferential expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Klein G., Jörnvall H., Alexander H., Lerner R. Antibodies against synthetic peptides react with the second Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1813–1818. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B. The Epstein-Barr virus proteins. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;50:95–158. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Sternås L., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Jörnvall H., Klein G., Lerner R. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide identify the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4652–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Smith C. M., Neville A. M., O'Hare M. J. A human-hybridoma system based on a fast-growing mutant of the ARH-77 plasma cell leukemia-derived line. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Aug;12(8):641–648. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finke J., Rowe M., Kallin B., Ernberg I., Rosén A., Dillner J., Klein G. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies against Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 5 (EBNA-5) detect multiple protein species in Burkitt's lymphoma and lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3870–3878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3870-3878.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. K., Robert M. F., Shedd D., Summers W. P., Robinson J. E., Wolak J., Stefano J. E., Miller G. Identification of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen polypeptide in mouse and monkey cells after gene transfer with a cloned 2.9-kilobase-pair subfragment of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Walker L., Guy G., Brown G., Rowe M., Rickinson A. Control of human B-lymphocyte replication. II. Transforming Epstein-Barr virus exploits three distinct viral signals to undermine three separate control points in B-cell growth. Immunology. 1986 Aug;58(4):591–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Kieff E. A third viral nuclear protein in lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5944–5948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. A second nuclear protein is encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent infection. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2983420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Wang F., Bushman E. W., Kieff E. Definitive identification of a member of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Rowe D. T., Bodescot M., Nicolas J. C., Farrell P. J., Perricaudet M. Mapping of the gene coding for Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen EBNA3 and its transient overexpression in a human cell line by using an adenovirus expression vector. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3340–3344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3340-3344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Dambaugh T., Heller M., Dowling J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA XII. A variable region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome is included in the P3HR-1 deletion. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):979–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.979-986.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin N., Aman P., Mellstedt H., Zech L., Klein G. Direct outgrowth of in vivo Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells into permanent lines. Int J Cancer. 1988 Jun 15;41(6):892–895. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G. Biological differences between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) strains with regard to lymphocyte transforming ability, superinfection and antigen induction. Exp Cell Res. 1975 May;92(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Misko I. S., Burrows S. R., Burman K., McCarthy R., Sculley T. B. Cytotoxic T-cell clones discriminate between A- and B-type Epstein-Barr virus transformants. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):719–721. doi: 10.1038/331719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller-Lantzsch N., Lenoir G. M., Sauter M., Takaki K., Béchet J. M., Kuklik-Roos C., Wunderlich D., Bornkamm G. W. Identification of the coding region for a second Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA 2) by transfection of cloned DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1805–1811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Kieff E. A sixth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3B) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2173–2178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2173-2178.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Sample J., Wang F., Kieff E. A fifth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3C) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1330–1338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1330-1338.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H., Horne M. K., Scott W. Transformation of foetal human keukocytes in vitro by filtrates of a human leukaemic cell line containing herpes-like virus. Int J Cancer. 1968 Nov 15;3(6):857–866. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Young L. S., Rowe M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1310-1317.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Kallin B., Alexander H., Dillner J., Fåhraeus R., Klein G., Lerner R., Rymo L. BamHI E region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome encodes three transformation-associated nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):995–999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Evans H. S., Young L. S., Hennessy K., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Monoclonal antibodies to the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus reveal heterogeneity of the protein and inducible expression in virus-transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1575–1586. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rymo L., Klein G., Ricksten A. Expression of a second Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen in mouse cells after gene transfer with a cloned fragment of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3435–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu N., Yamaki M., Sakuma S., Ono Y., Takada K. Three Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigens induced by the BamHI E region of EBV DNA. Int J Cancer. 1988 May 15;41(5):744–751. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Farley J., Strominger J. L., Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Transformation by Epstein-Barr virus requires DNA sequences in the region of BamHI fragments Y and H. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.286-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Petti L., Braun D., Seung S., Kieff E. A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):945–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.945-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Dawson C. W., Clark D., Rupani H., Busson P., Tursz T., Johnson A., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Gen Virol. 1988 May;69(Pt 5):1051–1065. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-5-1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Yao Q. Y., Rooney C. M., Sculley T. B., Moss D. J., Rupani H., Laux G., Bornkamm G. W., Rickinson A. B. New type B isolates of Epstein-Barr virus from Burkitt's lymphoma and from normal individuals in endemic areas. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2853–2862. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber U., Adldinger H. K., Lenoir G. M., Vuillaume M., Knebel-Doeberitz M. V., Laux G., Desgranges C., Wittmann P., Freese U. K., Schneider U. Geographical prevalence of two types of Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):56–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]