Abstract
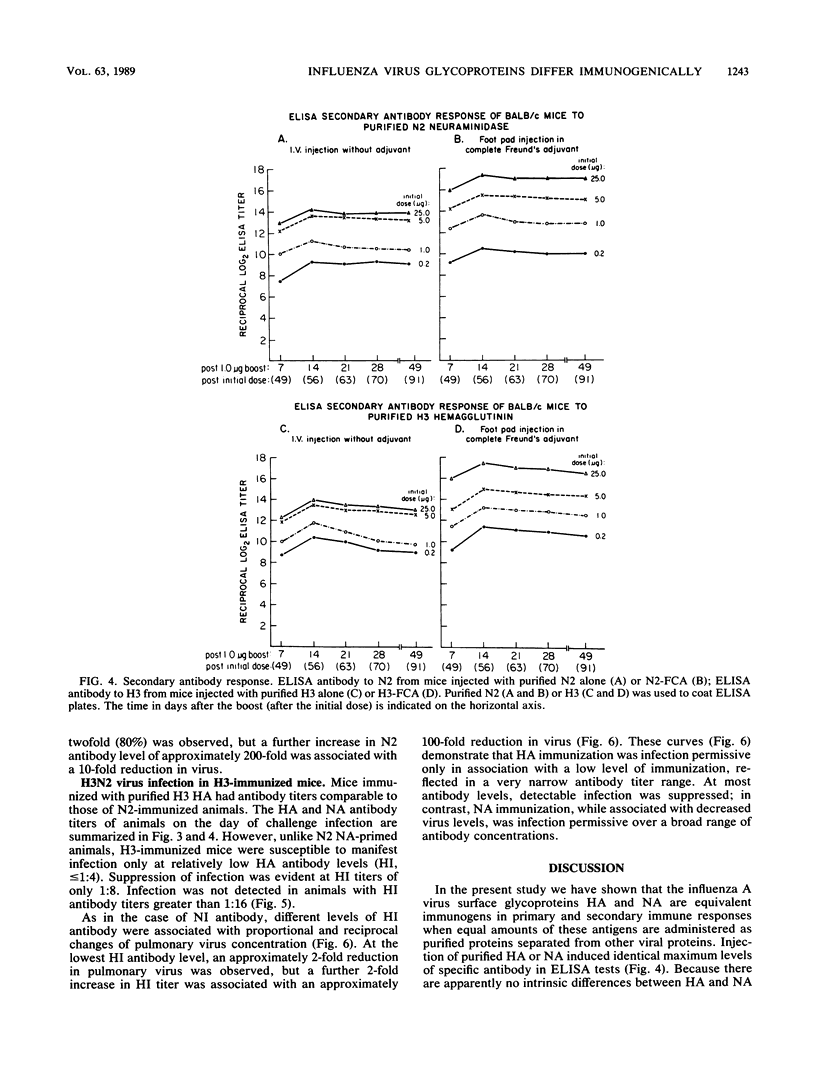
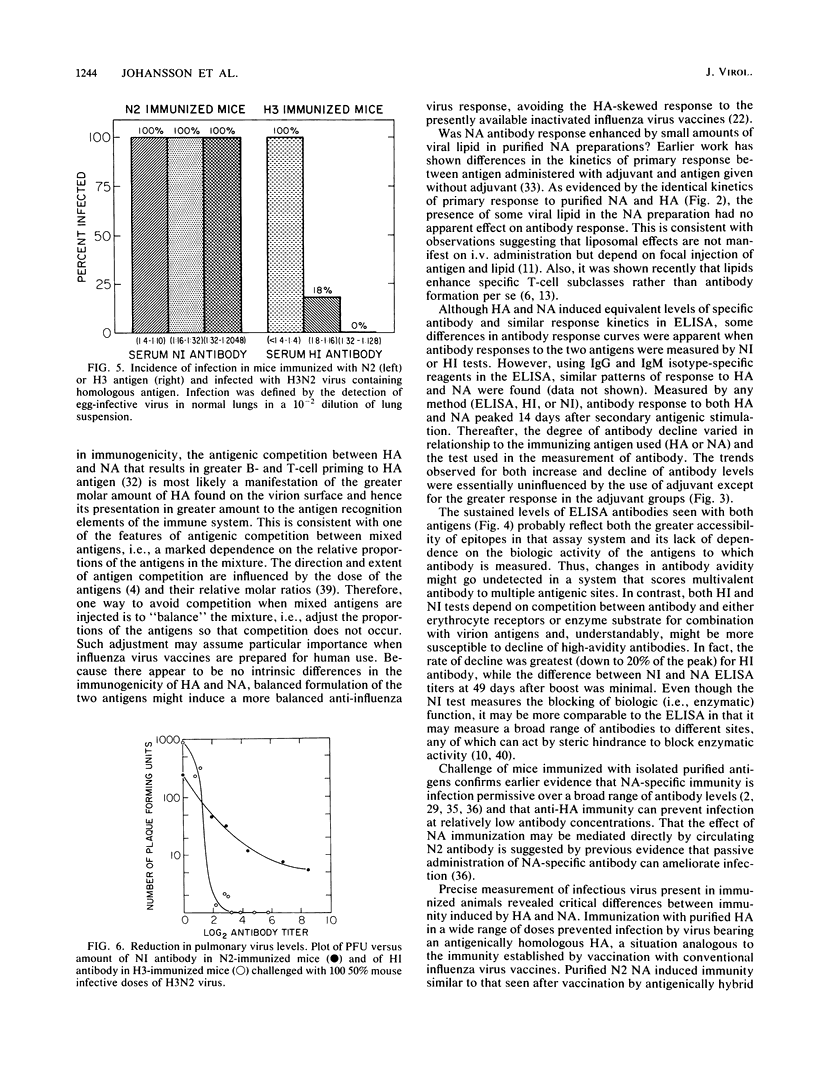
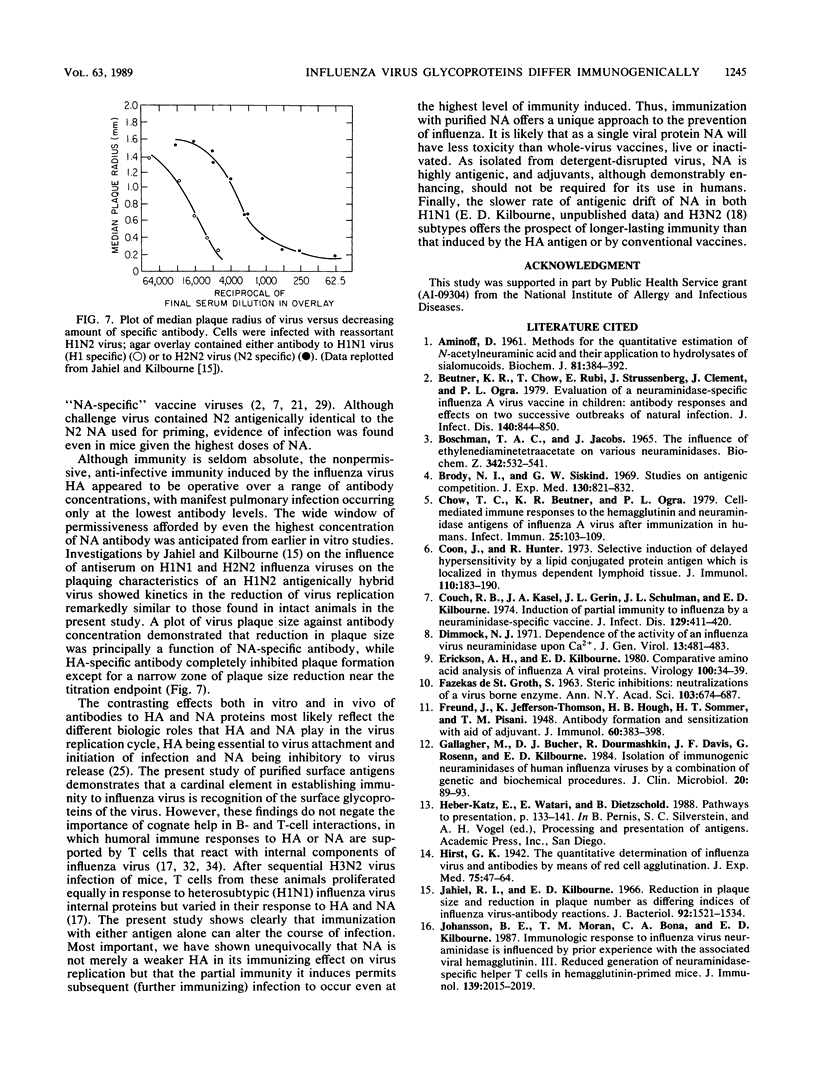
BALB/c mice immunized with graded doses of chromatographically purified hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) antigens derived from A/Hong Kong/1/68 (H3N2) influenza virus demonstrated equivalent responses when HA-specific and NA-specific serum antibodies were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Antibody responses measured by hemagglutination inhibition or neuraminidase inhibition titrations showed similar kinetic patterns, except for more rapid decline in hemagglutination inhibition antibody. Injection of mice with either purified HA or NA resulted in immunity manifested by reduction in pulmonary virus following challenge with virus containing homologous antigens. However, the nature of the immunity induced by the two antigens differed markedly. While HA immunization with all but the lowest doses of antigen prevented manifest infection, immunization with NA was infection-permissive at all antigen doses, although reduction in pulmonary virus was proportional to the amount of antigen administered. The immunizing but infection-permissive effect of NA immunization over a wide range of doses is in accord with results of earlier studies with mice in which single doses of NA and antigenically hybrid viruses were used. The demonstrable immunogenicity of highly purified NA as a single glycoprotein without adjuvant offers a novel infection-permissive approach with potentially low toxicity for human immunization against influenza virus.
Full text
PDF
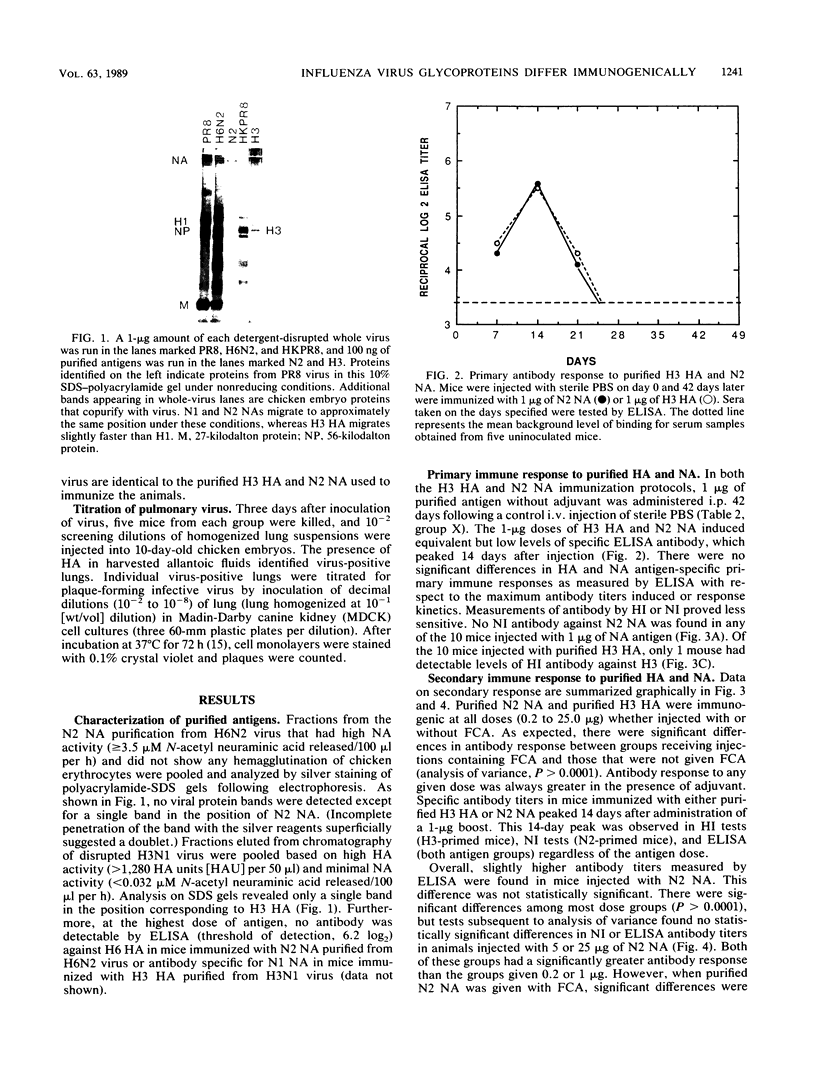
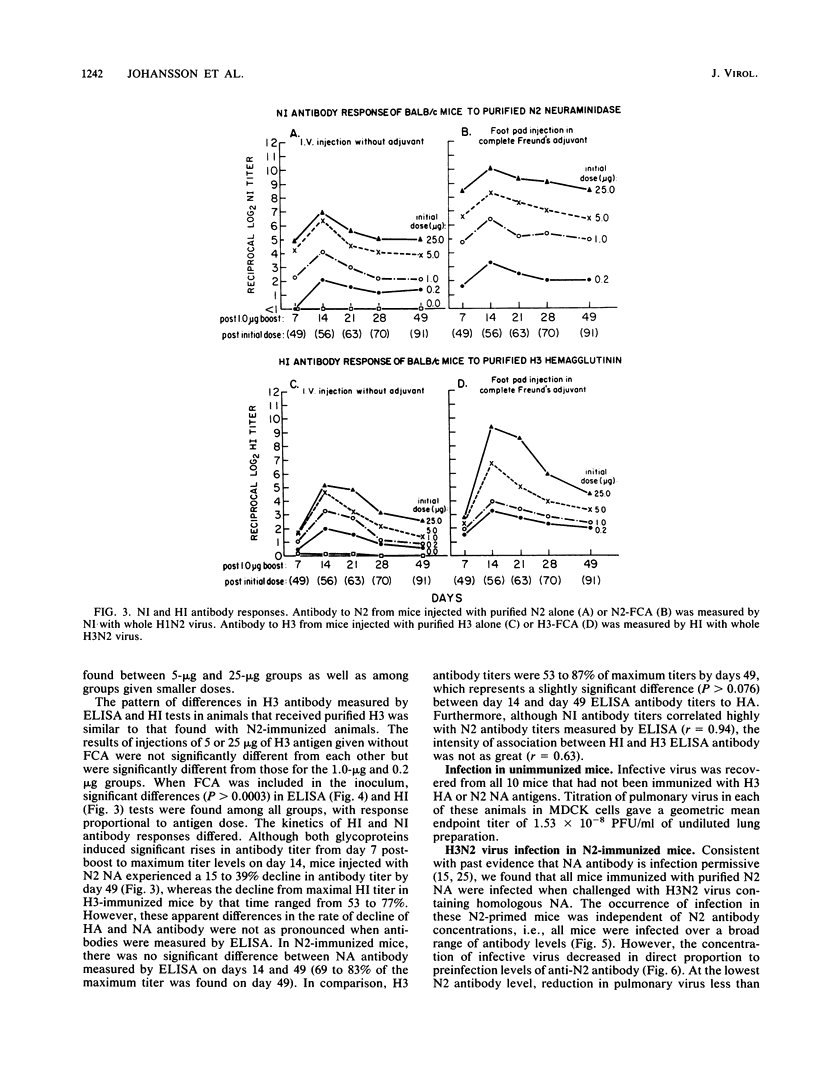

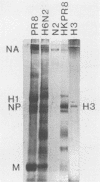
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutner K. R., Chow T., Rubi E., Strussenberg J., Clement J., Ogra P. L. Evaluation of a neuraminidase-specific influenza A virus vaccine in children: antibody responses and effects on two successive outbreaks of natural infection. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):844–850. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschman T. A., Jacobs J. The influence of ethylenediaminetetraacetate on various neuraminidases. Biochem Z. 1965 Sep 30;342(5):532–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody N. I., Siskind G. W. Studies on antigenic competition. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):821–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow T. C., Beutner K. R., Ogra P. L. Cell-mediated immune responses to the hemagglutinin and neuraminidase antigens of influenza A virus after immunization in humans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):103–109. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.103-109.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon J., Hunter R. Selective induction of delayed hypersensitivity by a lipid conjugated protein antigen which is localized in thymus dependent lymphoid tissue. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):183–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couch R. B., Kasel J. A., Gerin J. L., Schulman J. L., Kilbourne E. D. Induction of partial immunity to influenza by a neuraminidase-specific vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1974 Apr;129(4):411–420. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.4.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Dependence of the activity of an influenza virus neuraminidase upon Ca2+. J Gen Virol. 1971 Dec;13(3):481–483. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-3-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Kilbourne E. D. Comparative amino acid analysis of influenza A viral proteins. Virology. 1980 Jan 15;100(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90549-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher M., Bucher D. J., Dourmashkin R., Davis J. F., Rosenn G., Kilbourne E. D. Isolation of immunogenic neuraminidases of human influenza viruses by a combination of genetic and biochemical procedures. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jul;20(1):89–93. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.1.89-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahiel R. I., Kilbourne E. D. Reduction in plaque size and reduction in plaque number as differing indices of influenza virus-antibody reactions. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1521–1534. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1521-1534.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. E., Moran T. M., Bona C. A., Kilbourne E. D. Immunologic response to influenza virus neuraminidase is influenced by prior experience with the associated viral hemagglutinin. III. Reduced generation of neuraminidase-specific helper T cells in hemagglutinin-primed mice. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2015–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. E., Moran T. M., Bona C. A., Popple S. W., Kilbourne E. D. Immunologic response to influenza virus neuraminidase is influenced by prior experience with the associated viral hemagglutinin. II. Sequential infection of mice simulates human experience. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2010–2014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. E., Moran T. M., Kilbourne E. D. Antigen-presenting B cells and helper T cells cooperatively mediate intravirionic antigenic competition between influenza A virus surface glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6869–6873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. W., Gallagher M., Bucher D., Cerini C. P., Kilbourne E. D. Detection of influenza virus neuraminidase-specific antibodies by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):115–122. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.115-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kida H., Webster R. G., Yanagawa R. Inhibition of virus-induced hemolysis with monoclonal antibodies to different antigenic areas on the hemagglutinin molecule of A/seal/Massachusetts/1/80 (H7N7) influenza virus. Arch Virol. 1983;76(2):91–99. doi: 10.1007/BF01311693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. D., Cerini C. P., Khan M. W., Mitchell J. W., Jr, Ogra P. L. Immunologic response to the influenza virus neuraminidase is influenced by prior experience with the associated viral hemagglutinin. I. Studies in human vaccinees. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):3010–3013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. D., Christenson W. N., Sande M. Antibody response in man to influenza virus neuraminidase following influenza. J Virol. 1968 Jul;2(7):761–762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.7.761-762.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. D. Comparative efficacy of neuraminidase-specific and conventional influenza virus vaccines in induction of antibody to neuraminidase in humans. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):384–394. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourne E. D., Laver W. G., Schulman J. L., Webster R. G. Antiviral activity of antiserum specific for an influenza virus neuraminidase. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):281–288. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.281-288.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. R., Nelson D. L., Wright P. F., Tierney E. L., Phelan M. A., Chanock R. M. Secretory and systemic immunological response in children infected with live attenuated influenza A virus vaccines. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1102–1108. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1102-1108.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Chow T., Beutner K. R., Rubi E., Strussenberg J., DeMello S., Rizzone C. Clinical and immunologic evaluation of neuraminidase-specific influenza A virus vaccine in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):499–506. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa K., Ebata N. Silver stain for detecting 10-femtogram quantities of protein after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90703-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Liew F. Y. Cell cooperation in antibody responses to influenza virus. I. priming of helper t cells by internal components of virion. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Oct;10(10):791–796. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALK J. E., CONTAKOS M., LAURENT A. M., SORENSEN M., RAPALSKI A. J., SIMMONS I. H., SANDBERG H. Use of adjuvants in studies on influenza immunization. III. Degree of persistence of antibody in human subjects two years after vaccination. J Am Med Assoc. 1953 Apr 4;151(14):1169–1175. doi: 10.1001/jama.1953.02940140013005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherle P. A., Gerhard W. Functional analysis of influenza-specific helper T cell clones in vivo. T cells specific for internal viral proteins provide cognate help for B cell responses to hemagglutinin. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1114–1128. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman J. L., Khakpour M., Kilbourne E. D. Protective effects of specific immunity to viral neuraminidase on influenza virus infection of mice. J Virol. 1968 Aug;2(8):778–786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.8.778-786.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman J. L., Kilbourne E. D. Independent variation in nature of hemagglutinin and neuraminidase antigens of influenza virus: distinctiveness of hemagglutinin antigen of Hong Kong-68 virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):326–333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman J. L. The role of antineuraminidase antibody in immunity to influenza virus infection. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(3):647–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J. Studies on antigenic competition. 3. Is there a competitive step in tolerance induction? Eur J Immunol. 1972 Apr;2(2):118–122. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Reay P. A., Laver W. G. Protection against lethal influenza with neuraminidase. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):230–237. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90640-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoden S., Kida H., Kuwabara M., Yanagawa R., Webster R. G. Spin-labeling of influenza virus hemagglutinin permits analysis of the conformational change at low pH and its inhibition by antibody. Virus Res. 1986 May;4(3):251–261. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]