Abstract
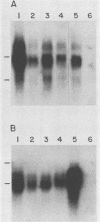
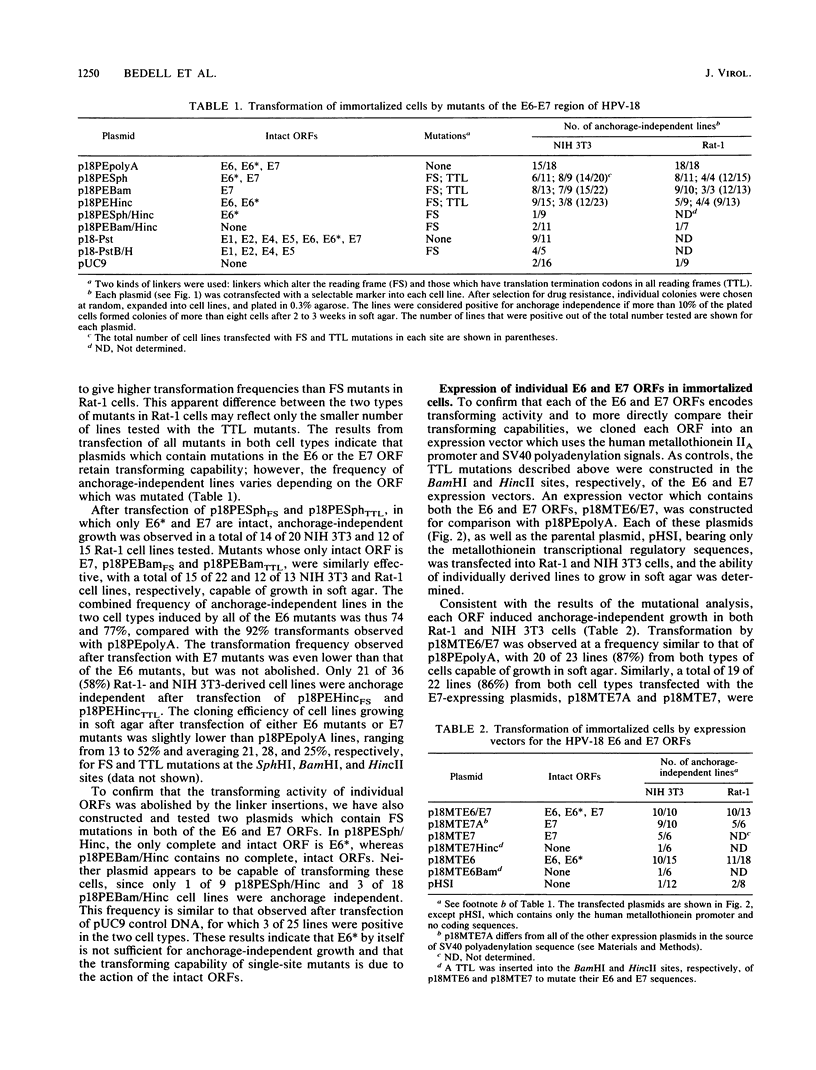
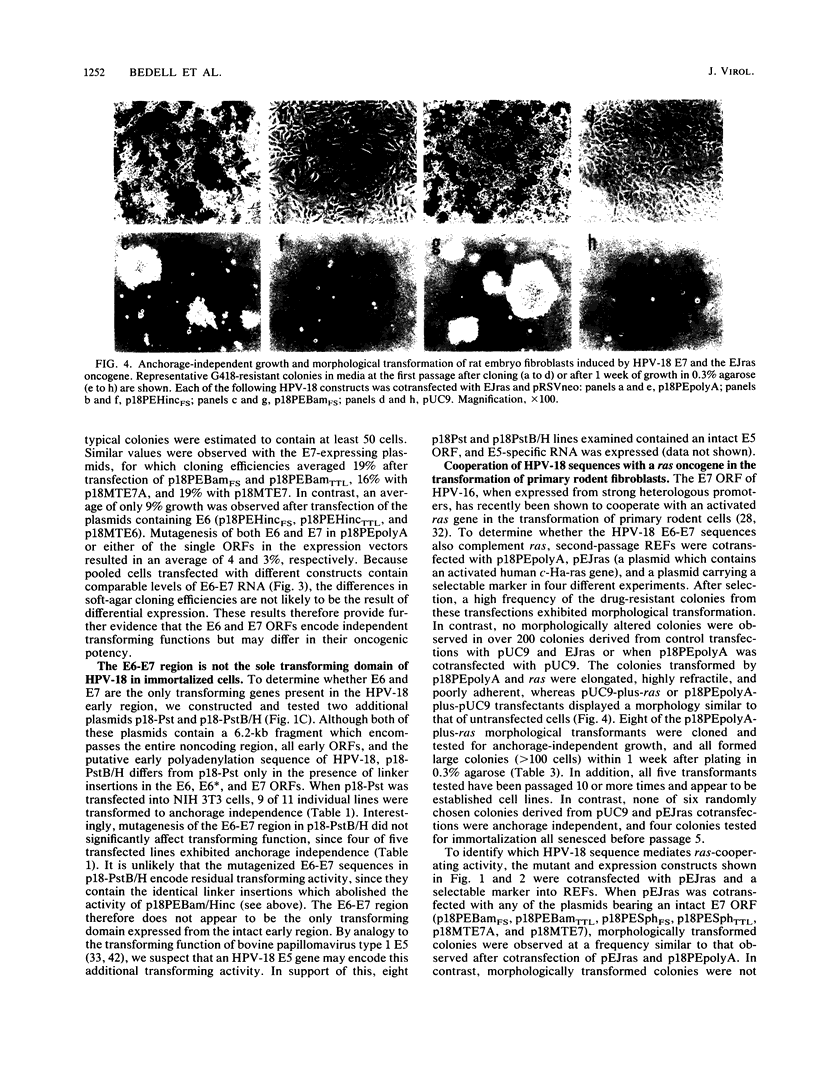
The selective retention and expression of the E6-E7 region of human papillomavirus (HPV) types 16 and 18 in cervical carcinomas suggests that these viral sequences play a role in the development of genital neoplasia. Each of three possible gene products, E6, E6*, and E7, from this region of HPV-18 were examined for transforming properties in several types of rodent cells. We have found that in immortalized fibroblasts, both E6 and E7 (but not E6*) are capable of inducing anchorage-independent growth. In rat embryo cells, the HPV-18 E7 open reading frame was an effective immortalizing agent and complemented an activated ras oncogene for transformation. In both immortalized and primary cells, transformation was observed when the HPV-18 sequences were expressed from either the HPV-18 promoter or a heterologous promoter. The E6-E7 region is not, however, the sole transforming domain of HPV-18, since another portion of the early region, possibly E5, also exhibited transforming capability in immortalized fibroblasts. The development of human cervical carcinomas may therefore involve a series of steps involving multiple viral and cellular gene products.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Androphy E. J., Hubbert N. L., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the HPV-16 E6 protein from transformed mouse cells and human cervical carcinoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):989–992. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the protein encoded by the E6 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2996134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Spence P., Androphy E., Hubbert N., Matlashewski G., Murray A., Crawford L. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 polypeptide in cells derived from human cervical carcinomas. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1351–1359. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Laimins L. A. The E6-E7 region of human papillomavirus type 18 is sufficient for transformation of NIH 3T3 and rat-1 cells. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3635–3640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3635-3640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin M. T., Hirochika R., Hirochika H., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Regulation of human papillomavirus type 11 enhancer and E6 promoter by activating and repressing proteins from the E2 open reading frame: functional and biochemical studies. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2994–3002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2994-3002.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Nasseri M., Wolinsky S. M., Broker T. R. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 mRNAs from genital condylomata acuminata. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2581–2588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2581-2588.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Danos O. Nucleotide sequence and comparative analysis of the human papillomavirus type 18 genome. Phylogeny of papillomaviruses and repeated structure of the E6 and E7 gene products. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):599–608. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe T. P., Haugen T. H., Turk J. P., Tabatabai F., Schmid P. G., 3rd, Dürst M., Gissmann L., Roman A., Turek L. P. Transcriptional regulation of the human papillomavirus-16 E6-E7 promoter by a keratinocyte-dependent enhancer, and by viral E2 trans-activator and repressor gene products: implications for cervical carcinogenesis. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3745–3753. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02709.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Kleinheinz A., Hotz M., Gissmann L. The physical state of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA in benign and malignant genital tumours. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1515–1522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge J., Smith T. F. Cell-division sequence motif. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):109–109. doi: 10.1038/334109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri I., Yaniv M. Study of the E2 gene product of the cottontail rabbit papillomavirus reveals a common mechanism of transactivation among papillomaviruses. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1573–1581. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1573-1581.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gius D., Grossman S., Bedell M. A., Laimins L. A. Inducible and constitutive enhancer domains in the noncoding region of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):665–672. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.665-672.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. R., Mora R., Laimins L. A. Intracellular localization and DNA-binding properties of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 protein expressed with a baculovirus vector. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.366-374.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslinger A., Karin M. Upstream promoter element of the human metallothionein-IIA gene can act like an enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8572–8576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Enhancers and trans-acting E2 transcriptional factors of papillomaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2599–2606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2599-2606.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Hirochika R., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Functional mapping of the human papillomavirus type 11 transcriptional enhancer and its interaction with the trans-acting E2 proteins. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):54–67. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frame E7 encodes a transforming gene for rat 3Y1 cells. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):610–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.610-613.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Watanabe S., Yoshiike K. Immortalization of primary rat cells by human papillomavirus type 16 subgenomic DNA fragments controlled by the SV40 promoter. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90694-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. The approaching era of the tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1539–1545. doi: 10.1126/science.3317834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. A transcriptional repressor encoded by BPV-1 shares a common carboxy-terminal domain with the E2 transactivator. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab J. C., Walkinshaw S. A., Cordiner J. W., Clements J. B. Human papillomavirus in clinically and histologically normal tissue of patients with genital cancer. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 23;315(17):1052–1058. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610233151703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Schneider J., Banks L., Jones N., Murray A., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA cooperates with activated ras in transforming primary cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1741–1746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J. Human papillomaviruses and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;823(3):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(86)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Howley P. M. Transcriptional trans-activation by the human papillomavirus type 16 E2 gene product. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1630-1638.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Identification of a second transforming region in bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7880–7884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Freese U. K., Gissmann L., Mayer W., Roggenbuck B., Stremlau A., zur Hausen H. Structure and transcription of human papillomavirus sequences in cervical carcinoma cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):111–114. doi: 10.1038/314111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Oltersdorf T., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. The major human papillomavirus protein in cervical cancers is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1686–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1686-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry F., Yaniv M. The BPV1-E2 trans-acting protein can be either an activator or a repressor of the HPV18 regulatory region. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3391–3397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02662.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunokawa Y., Takebe N., Kasamatsu T., Terada M., Sugimura T. Transforming activity of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence in a cervical cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2200–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Okayama H., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus contains multiple transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto S., Burkhardt A. L., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA-induced malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):572–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.572-577.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Genital papillomavirus infections. Prog Med Virol. 1985;32:15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]