Abstract
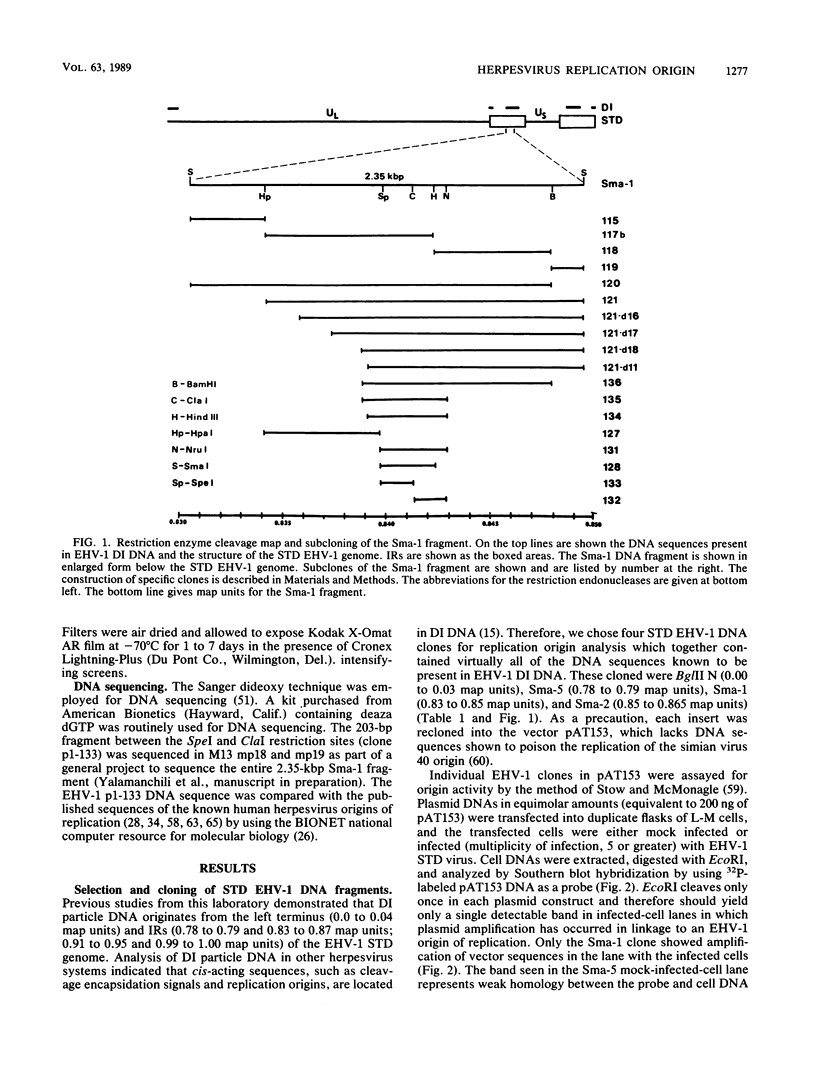
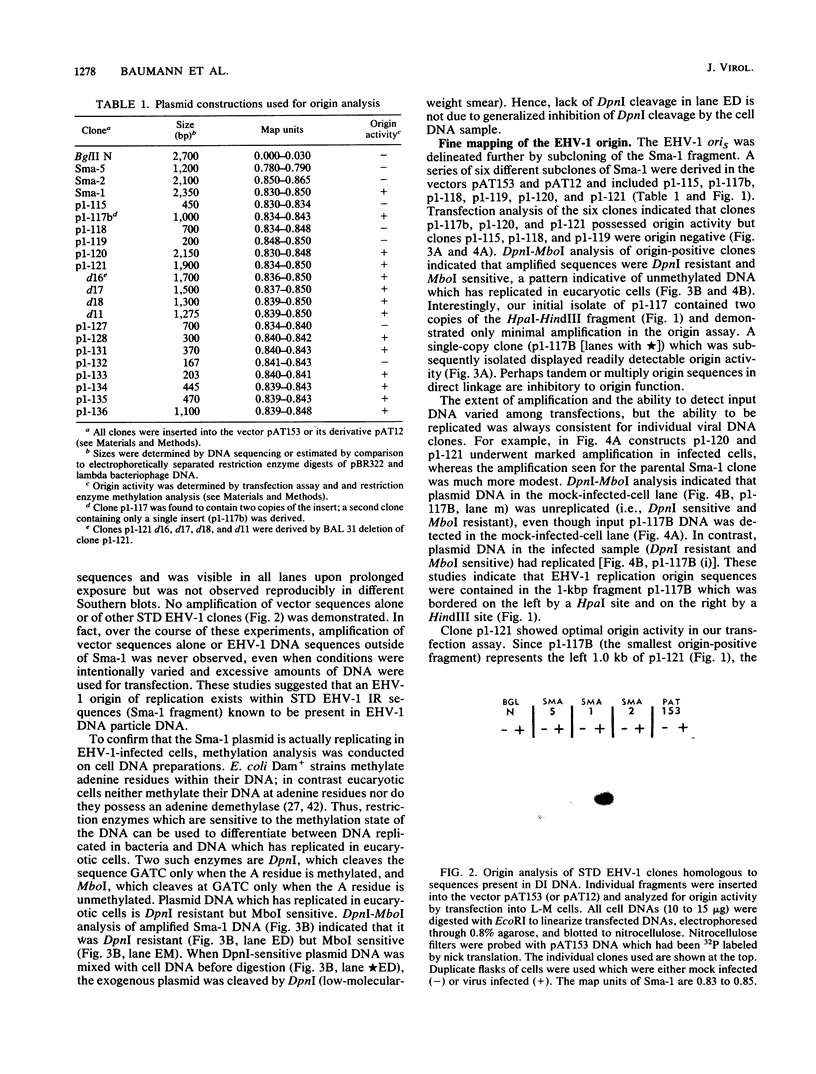
The genome of equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) defective interfering (DI) particle DNA originates from discrete regions within the standard (STD) EHV-1 genome: the left terminus (0.0 to 0.04 map units) and the inverted repeats (0.78 to 0.79 and 0.83 to 0.87 map units of the internal inverted repeat; 0.91 to 0.95 and 0.99 to 1.00 map units of the terminal inverted repeat). Since DI DNA must contain cis-acting DNA sequences, such as replication origins, which cannot be supplied in trans by the STD EHV-1 virus, regions of the EHV-1 genome shown to be in DI DNA were assayed for the presence of a viral origin of DNA replication. Specifically, STD EHV-1 DNA fragments encompassing the genomic regions present in DI particle DNA were inserted into the vector pAT153, and individual clones were tested by transfection assays for the ability to support the amplification and replication of plasmid DNA in EHV-1-infected cells. The Sma-1 subfragment of the internal inverted repeat sequence (0.83 to 0.85 map units) was shown to contain origin of replication activity. Subcloning and BAL 31 deletion analysis of the 2.35-kilobase-pair (kbp) Sma-1 fragment delineated a 200-bp fragment that contained origin activity. The origin activities of all EHV-1 clones which were positive by the transfection assay were confirmed by methylation analysis by using the methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes DpnI and MboI. DNA sequencing of the 200-bp fragment which contained an EHV-1 origin of replication indicated that this region has significant homology to previously characterized origins of replication of human herpesviruses. Furthermore, comparison of known origin sequences demonstrated that a 9-bp sequence, CGTTCGCAC, which is conserved among all origins of replication of human lytic herpesviruses and which is contained within the 18-bp region in herpes simplex virus type 1 origins shown by others to be protected by an origin-binding protein (P. Elias, M. E. O'Donnell, E. S. Mocarski, and I. R. Lehman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:6322-6326) is also conserved across species in the EHV-1 origin of replication.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann R. P., Dauenhauer S. A., Caughman G. B., Staczek J., O'Callaghan D. J. Structure and genetic complexity of the genomes of herpesvirus defective-interfering particles associated with oncogenic transformation and persistent infection. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):13–21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.13-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann R. P., Staczek J., O'Callaghan D. J. Cloning and fine mapping the DNA of equine herpesvirus type one defective interfering particles. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):188–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann R. P., Staczek J., O'Callaghan D. J. Equine herpesvirus type 1 defective-interfering (DI) particle DNA structure: the central region of the inverted repeat is deleted from DI DNA. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90356-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann R. P., Sullivan D. C., Staczek J., O'Callaghan D. J. Genetic relatedness and colinearity of genomes of equine herpesvirus types 1 and 3. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):816–825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.816-825.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. E., Kemp M. C., Perdue M. L., Randall C. C., Gentry G. A. Equine herpesvirus in vivo: cyclic production of a DNA density variant with repetitive sequences. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90502-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. L. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:733–771. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughman G. B., Robertson A. T., Gray W. L., Sullivan D. C., O'Callaghan D. J. Characterization of equine herpesvirus type 1 immediate early proteins. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauenhauer S. A., Robinson R. A., O'Callaghan D. J. Chronic production of defective-interfering particles by hamster embryo cultures of herpesvirus persistently infected and oncogenically transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):1–14. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., Doelberg M. A 67-base-pair segment from the Ori-S region of herpes simplex virus type 1 encodes origin function. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2516–2519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2516-2519.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., O'Donnell M. E., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA binding protein specific for an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6322–6326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann A., Shlomai J., Becker Y. Electron microscopy of herpes simplex virus DNA molecules isolated from infected cells by centrifugation in CsCl density gradients. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):507–522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C. P., Kaerner H. C. Sequence of the putative origin of replication in the UL region of herpes simplex virus type 1 ANG DNA. J Gen Virol. 1984 Dec;65(Pt 12):2109–2119. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-12-2109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray W. L., Baumann R. P., Robertson A. T., O'Callaghan D. J., Staczek J. Characterization and mapping of equine herpesvirus type 1 immediate early, early, and late transcripts. Virus Res. 1987 Sep;8(3):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry B. E., Newcomb W. W., O'Callaghan D. J. Alterations in virus protein synthesis and capsid production in infection with DI particles of herpesvirus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Apr;47(2):343–353. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-47-2-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry B. E., Newcomb W. W., O'Callaghan D. J. Biological and biochemical properties of defective interfering particles of equine herpesvirus type 1. Virology. 1979 Jan 30;92(2):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry B. E., Robinson R. A., Dauenhauer S. A., Atherton S. S., Hayward G. S., O'Callaghan D. J. Structure of the genome of equine herpesvirus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):97–114. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch I., Cabral G., Patterson M., Biswal N. Studies on the intracellular replicating DNA of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):48–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubenthal-Voss J., Starr L., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus origins of DNA synthesis in the S component are each contained in a transcribed open reading frame. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3349–3355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3349-3355.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf C. W., Spies B., Kaerner H. C. The DNA replication origins of herpes simplex virus type 1 strain Angelotti. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8655–8667. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B. Complementary specificity of restriction endonucleases of Diplococcus pneumoniae with respect to DNA methylation. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):153–168. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockshon D., Galloway D. A. Cloning and characterization of oriL2, a large palindromic DNA replication origin of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):513–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.513-521.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Herpesvirus-dependent amplification and inversion of cell-associated viral thymidine kinase gene flanked by viral a sequences and linked to an origin of viral DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5626–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D. J., Cheevers W. P., Gentry G. A., Randall C. C. Kinetics of cellular and viral DNA synthesis in equine abortion (herpes) virus infection of L-M cells. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):104–114. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan D. J., Hyde J. M., Gentry G. A., Randall C. C. Kinetics of viral deoxyribonucleic acid, protein, and infectious particle production and alterations in host macromolecular syntheses in equine abortion (herpes) virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1968 Aug;2(8):793–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.8.793-804.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdue M. L., Kemp M. C., Randall C. C., O'Callaghan D. J. Studies of the molecular anatomy of the L-M cell strain of equine herpes virus type 1: proteins of the nucleocapsid and intact virion. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):201–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90216-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polvino-Bodnar M., Orberg P. K., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 oriL is not required for virus replication or for the establishment and reactivation of latent infection in mice. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3528–3535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3528-3535.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson A. T., Caughman G. B., Gray W. L., Baumann R. P., Staczek J., O'Callaghan D. J. Analysis of the in vitro translation products of the equine herpesvirus type 1 immediate early mRNA. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):451–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. A., Henry B. E., Duff R. G., O'Callaghan D. J. Oncogenic transformation by equine herpesviruses (EHV). I. Properties of hamster embryo cells transformed by ultraviolet-irradiated EHV-1. Virology. 1980 Mar;101(2):335–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. A., O'Callaghan D. J. A specific viral DNA sequence is stably integrated in herpesvirus oncogenically transformed cells. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90476-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. A., Tucker P. W., Dauenhauer S. A., O'Callaghan D. J. Molecular cloning of equine herpesvirus type 1 DNA: analysis of standard and defective viral genomes and viral sequences in oncogenically transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6684–6688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. A., Vance R. B., O'Callaghan D. J. Oncogenic transformation by by equine herpesviruses. II. Coestablishment of persistent infection and oncogenic transformation of hamster embryo cells by equine herpesvirus type 1 preparations enriched for defective interfering particles. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):204–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.204-219.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Dauenhauer S. A., O'Callaghan D. J. Electron microscopic study of equine herpesvirus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):297–300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.297-300.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: analyses of cis-acting replication functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):694–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Davison A. J. Identification of a varicella-zoster virus origin of DNA replication and its activation by herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1613–1623. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Mutagenesis of a herpes simplex virus origin of DNA replication and its effect on viral interference. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jan;66(Pt 1):31–42. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley J. M., Robertson G. R., Davison A. J. Analysis of the genome of equine herpesvirus type 1: arrangement of cleavage sites for restriction endonucleases EcoRI, BglII and BamHI. J Gen Virol. 1981 Dec;57(Pt 2):307–323. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. Replication origins and a sequence involved in coordinate induction of the immediate-early gene family are conserved in an intergenic region of herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2061–2079. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Harper L., Ben-Porat T. cis Functions involved in replication and cleavage-encapsidation of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):318–327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.318-327.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]