Abstract
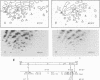
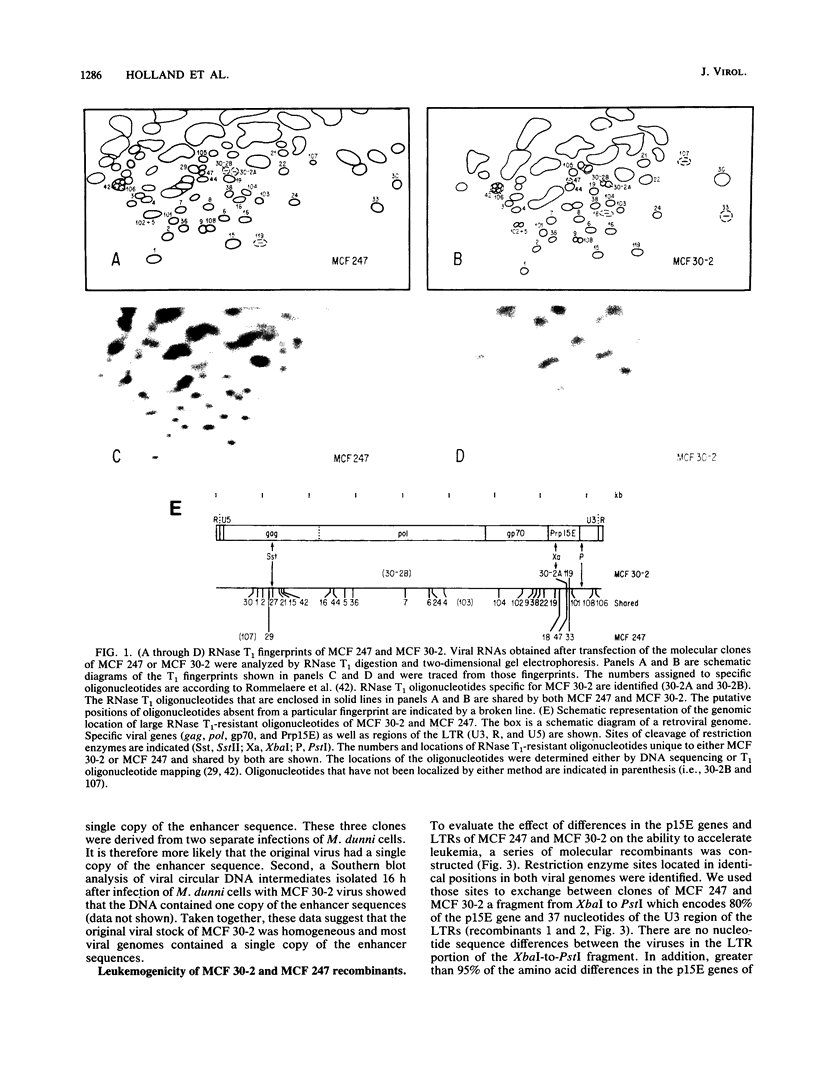
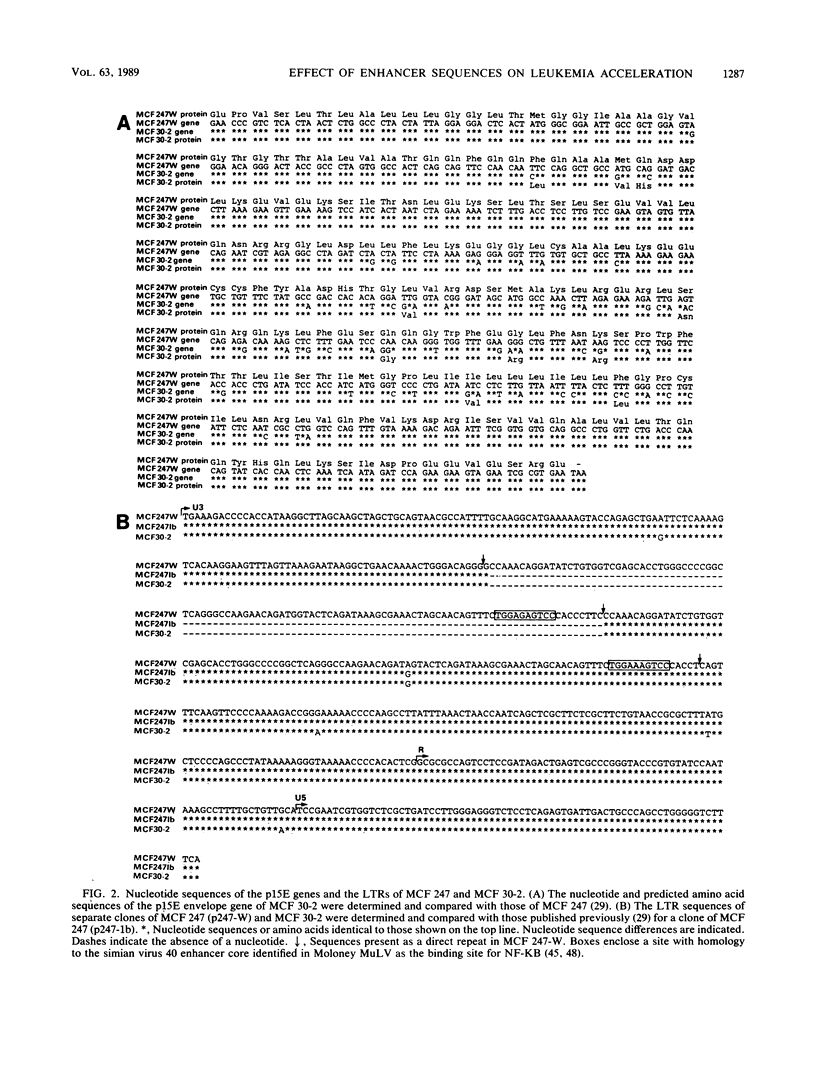
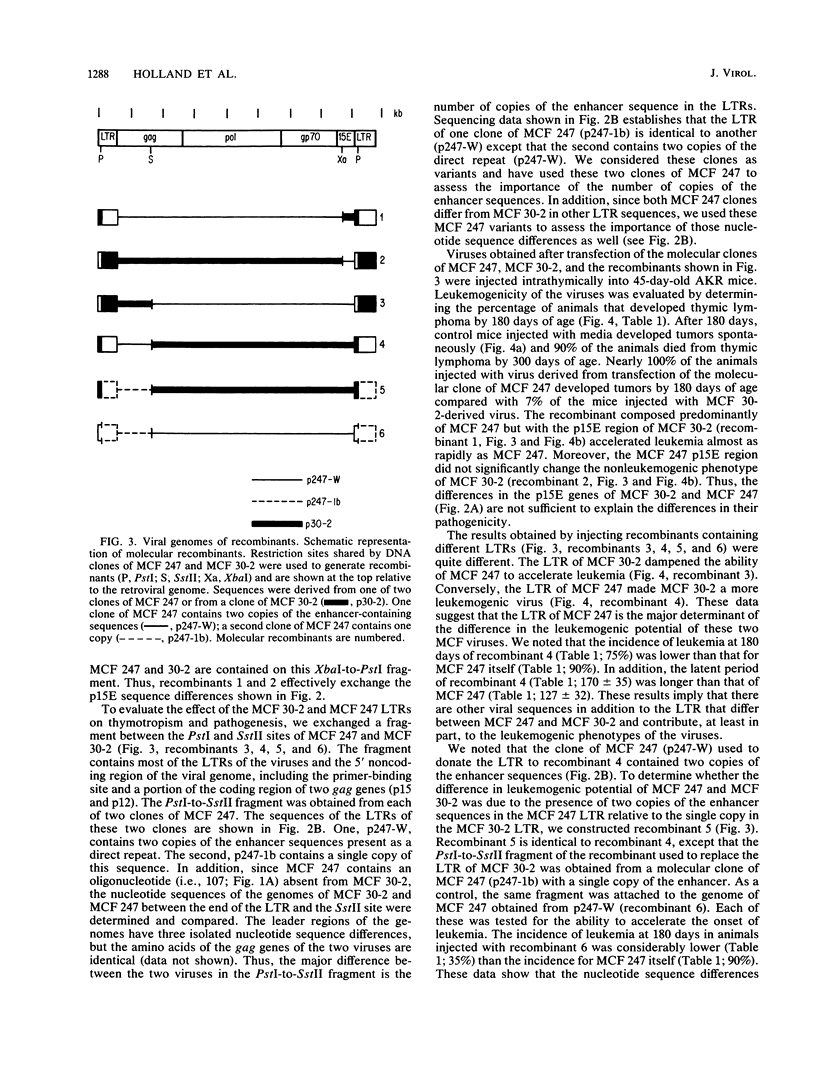
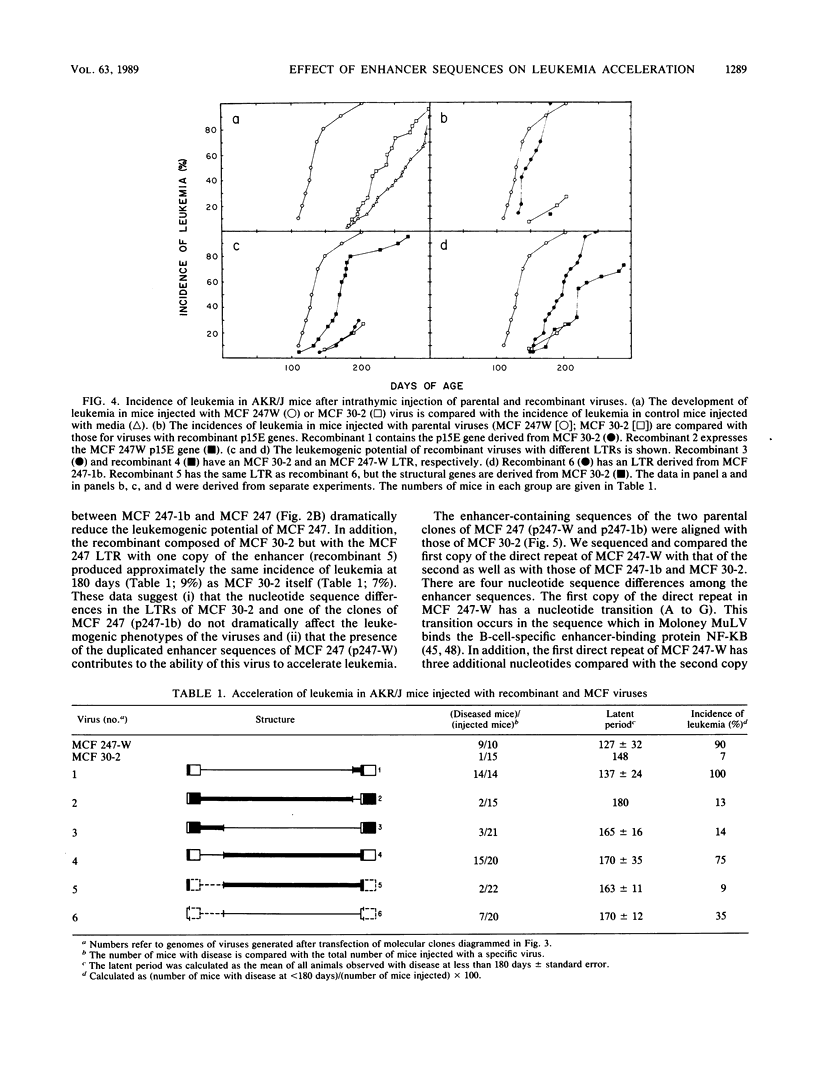
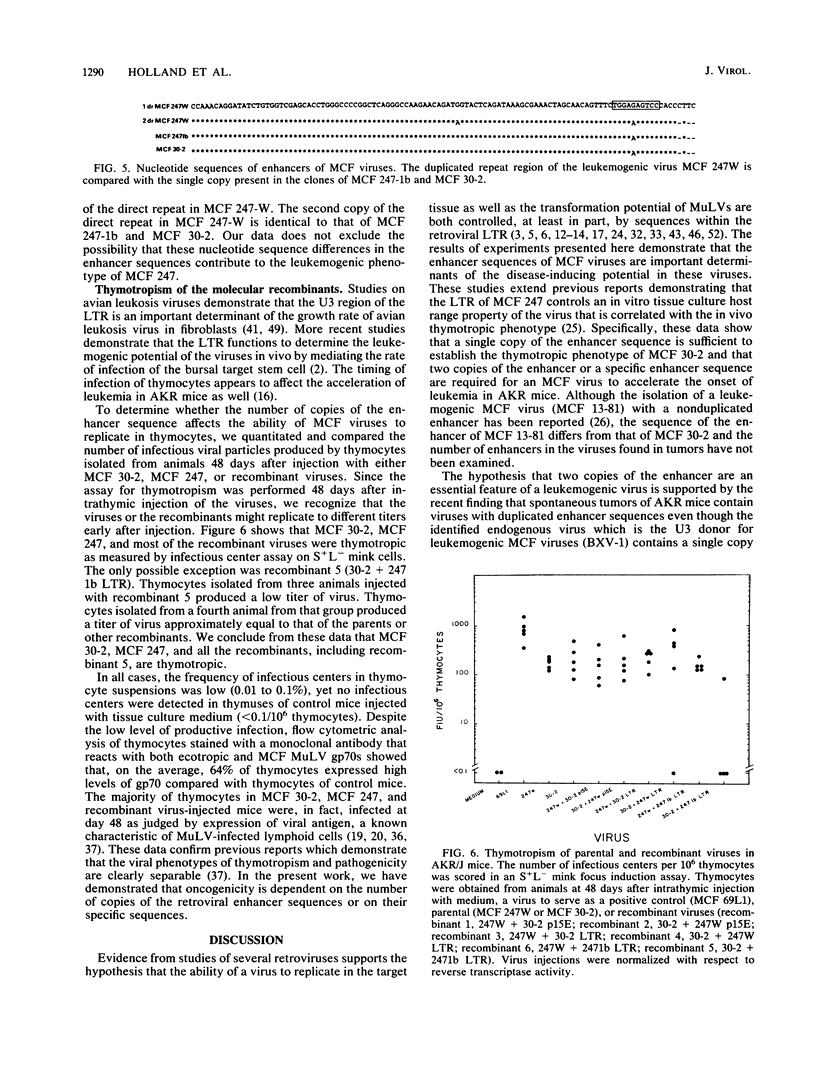
Oncogenic mink cell focus-forming (MCF) viruses, such as MCF 247, show a positive correlation between the ability to replicate efficiently in the thymus and a leukemogenic phenotype. Other MCF viruses, such as MCF 30-2, replicate to high titers in thymocytes and do not accelerate the onset of leukemia. We used these two MCF viruses with different biological phenotypes to distinguish the effect of specific viral genes and genetic determinants on thymotropism and leukemogenicity. Our goal was to identify the viral sequences that distinguish thymotropic, nonleukemogenic viruses such as MCF 30-2 from thymotropic, leukemogenic viruses such as MCF 247. We cloned MCF 30-2, compared the genetic hallmarks of MCF 30-2 with those of MCF 247, constructed a series of recombinants, and tested the ability of recombinant viruses to replicate in the thymus and to induce leukemia. The results established that (i) MCF 30-2 and MCF 247 differ in the numbers of copies of the enhancer sequences in the long terminal repeats. (ii) The thymotropic phenotype of both viruses is independent of the number of copies of the enhancer sequences. (iii) The oncogenic phenotype of MCF 247 is correlated with the presence in the virus of duplicated enhancer sequences or with the presence of an enhancer with a specific sequence. These results show that the pathogenic phenotypes of MCF viruses are dissociable from the thymotropic phenotype and depend, at least in part, upon the enhancer sequences. On the basis of these results, we suggest that the molecular mechanisms by which the enhancer sequences determine thymotropism are different from those that determine oncogenicity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. W., Blais B. P., Robinson H. L. Long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences, env, and a region near the 5' LTR influence the pathogenic potential of recombinants between Rous-associated virus types 0 and 1. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3431–3437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3431-3437.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Haseltine W. A. Tissue-specific transcription preference as a determinant of cell tropism and leukaemogenic potential of murine retroviruses. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):159–162. doi: 10.1038/312159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Hsu B. L., Haseltine W. A. Regulatory elements within the murine leukemia virus enhancer regions mediate glucocorticoid responsiveness. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1314–1322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1314-1322.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Silver J. E., Frederickson T. N., Hopkins N., Hartley J. W. A 3' end fragment encompassing the transcriptional enhancers of nondefective Friend virus confers erythroleukemogenicity on Moloney leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W. Characterization of target cells for MCF viruses in AKR mice. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90512-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declève A., Lieberman M., Ihle J. N., Kaplan H. S. Biological and serological characterization of radiation leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4675–4679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. The tandem direct repeats within the long terminal repeat of murine leukemia viruses are the primary determinant of their leukemogenic potential. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):945–952. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.945-952.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Villemur R., Jolicoeur P. The high leukemogenic potential of Gross passage A murine leukemia virus maps in the region of the genome corresponding to the long terminal repeat and to the 3' end of env. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.24-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H. Characterization of polytropic MuLVs from three-week-old AKR/J mice. Virology. 1986 Aug;153(1):122–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Malik F. G. Class II polytropic murine leukemia viruses (MuLVs) of AKR/J mice: possible role in the generation of class I oncogenic polytropic MuLVs. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1882–1892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1882-1892.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Morrey J. D. Tissue-specific replication of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses in infected mice. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1350–1357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1350-1357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller D. V., Hopkins N. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of B-tropic murine leukemia virus from BALB/c and five of its NB-tropic derivatives. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):188–195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.188-195.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G., Cieplensky D. A time-course study of MuLV env gene expression in the AKR thymus: qualitative and quantitative analysis of ecotropic and recombinant virus gene products. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):282–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famulari N. G. Murine leukemia viruses with recombinant env genes: a discussion of their role in leukemogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;103:75–108. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68943-7_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Nomura S., Bolognesi D. P. A novel murine oncornavirus with dual eco- and xenotropic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5150–5155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. At least four viral genes contribute to the leukemogenicity of murine retrovirus MCF 247 in AKR mice. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):158–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.158-165.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN H. S. Influence of thymectomy, splenectomy, and gonadectomy on incidence of radiation-induced lymphoid tumors in strain C57 black mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1950 Aug;11(1):83–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima K., Ikeda H., Hartley J. W., Stockert E., Rowe W. P., Old L. J. Changes in expression of murine leukemia virus antigens and production of xenotropic virus in the late preleukemic period in AKR mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. A Mus dunni cell line that lacks sequences closely related to endogenous murine leukemia viruses and can be infected by ectropic, amphotropic, xenotropic, and mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):695–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.695-698.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Golemis E., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Disease specificity of nondefective Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses is controlled by a small number of nucleotides. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.693-700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Nowinski R. C., Stockert E. Amplified expression of murine leukemia virus (MuLV)-coded antigens on thymocytes and leukemia cells of AKR mice after infection by dualtropic (MCF) MuLV. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):450–464. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E., Obata Y., Old L. J. Leukemogenic properties of AKR dualtropic (MCF) viruses: amplification of murine leukemia virus-related antigens on thymocytes and acceleration of leukemia development in AKR mice. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):548–563. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Woller R., Chu A. Stages in development of mink cell focus-inducing (MCF) virus-accelerated leukemia in AKR mice. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):914–934. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Blais B. M., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. At least two regions of the viral genome determine the oncogenic potential of avian leukosis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1225–1229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of Akv-1 and Akv-2 type C viruses of AKR mice. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):690–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.690-694.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lenz J., Ruprecht R., Cloyd M. W. Tissue selectivity of murine leukemia virus infection is determined by long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):862–866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.862-866.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E., Fried M. Sequence repeats in a polyoma virus DNA region important for gene expression. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):233–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.233-237.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short M. K., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Correlation of leukemogenic potential of murine retroviruses with transcriptional tissue preference of the viral long terminal repeats. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1067-1072.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Sola B., Evans L., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Nathanson K., Garon C. F., Chesebro B. Hemolytic anemia and erythroleukemia, two distinct pathogenic effects of Friend MuLV: mapping of the effects to different regions of the viral genome. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodore T. S., Khan A. S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of long terminal repeats of leukemogenic and non-leukemogenic MCF MuLVs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5898–5898. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Recombinants between endogenous and exogenous avian tumor viruses: role of the C region and other portions of the genome in the control of replication and transformation. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):238–249. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.238-249.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Ruscetti S. Tissue tropism of a leukemogenic murine retrovirus is determined by sequences outside of the long terminal repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3376–3380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Davison B., Chaffin K. Murine leukemia virus long terminal repeat sequences can enhance gene activity in a cell-type-specific manner. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2832–2835. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]