Abstract
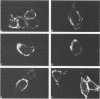
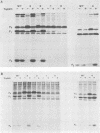
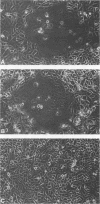
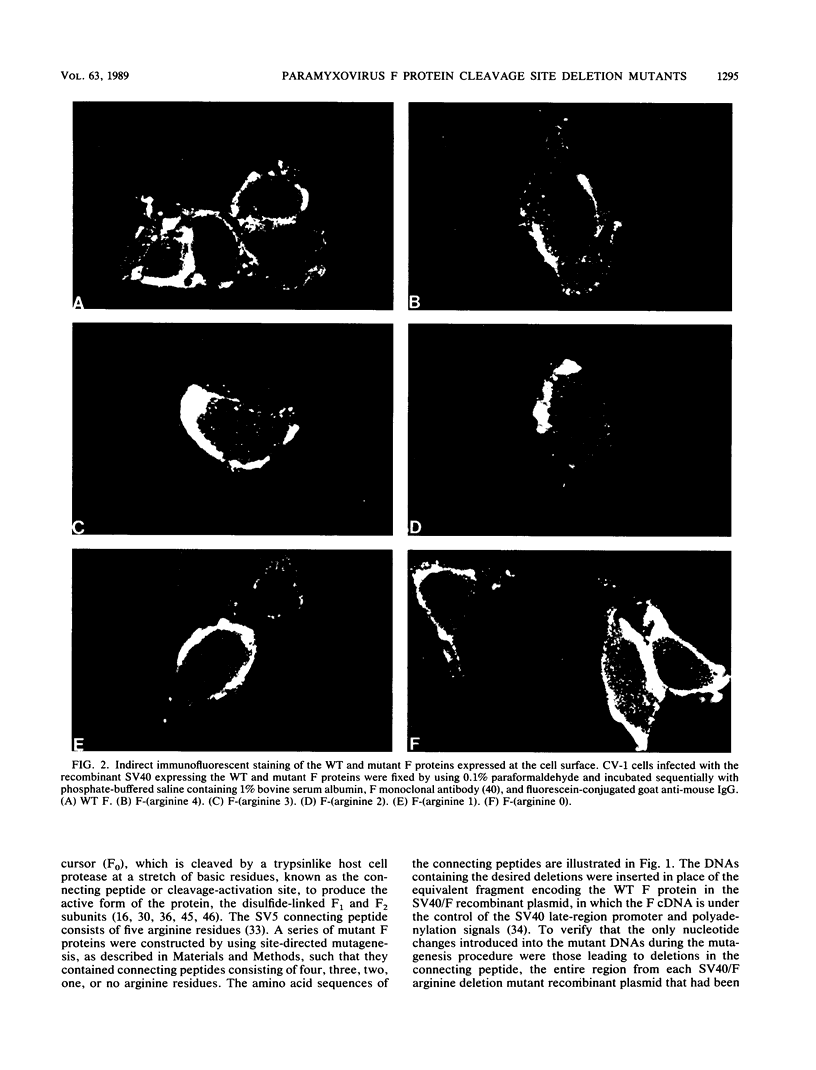
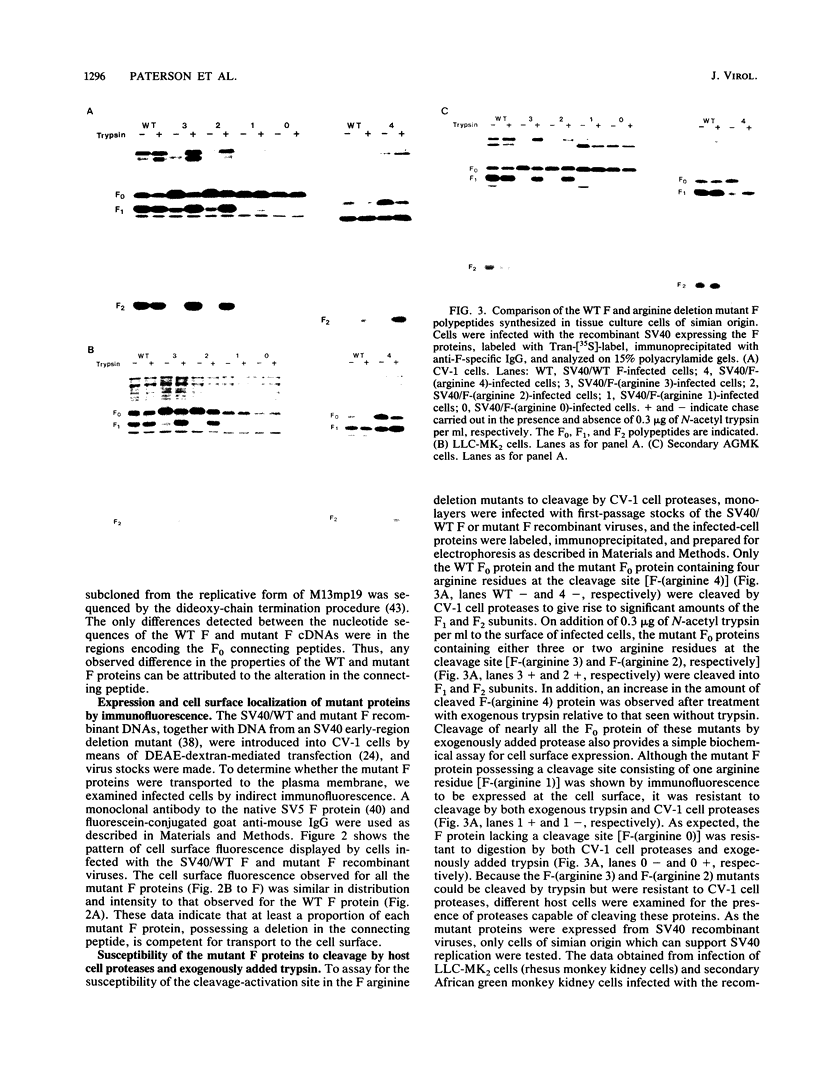
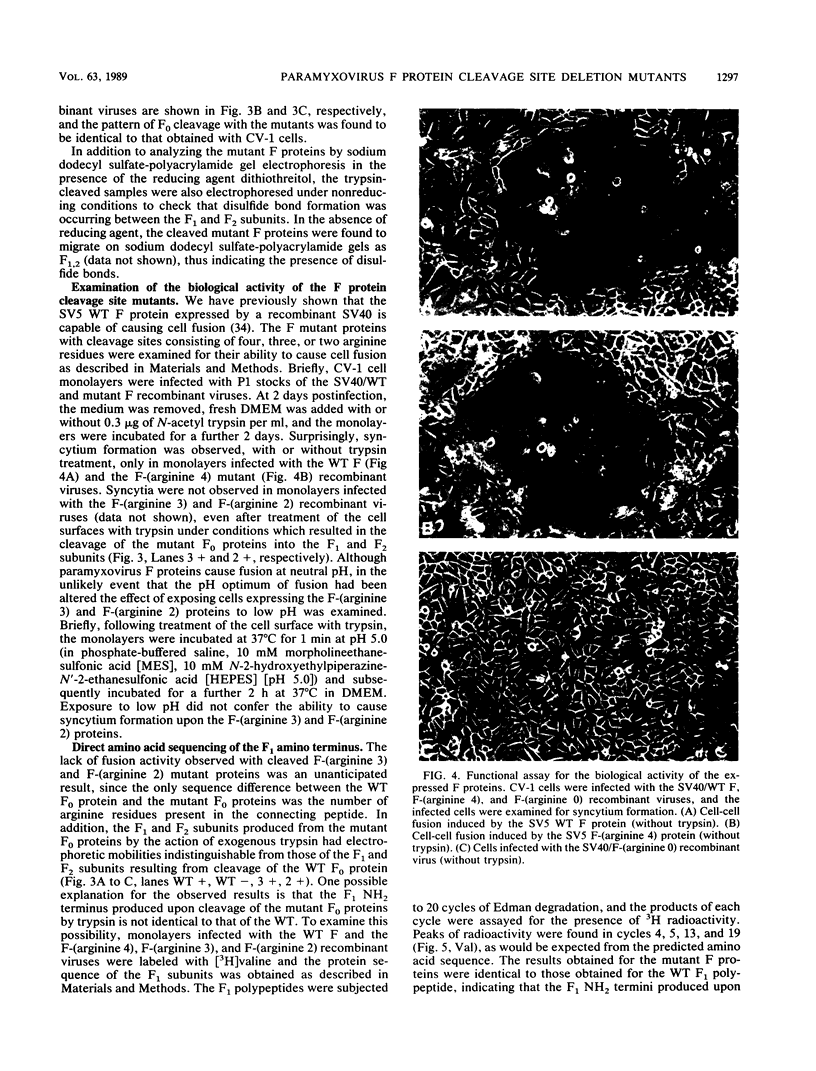
The relationship between the length of the connecting peptide in a paramyxovirus F0 protein and cleavage of F0 into the F1 and F2 subunits has been examined by constructing a series of mutant F proteins via site-directed mutagenesis of a cDNA clone encoding the simian virus 5 F protein. The mutant F proteins had one to five arginine residues deleted from the connecting peptide. The minimum number of arginine residues required for cleavage-activation of the simian virus 5 F0 protein by host cell proteases was found to be four. F proteins with two or three arginine residues in the connecting peptide were not cleaved by host cell proteases but could be cleaved by exogenously added trypsin. The mutant F protein possessing a connecting peptide consisting of one arginine residue was not cleaved by trypsin. The altered F proteins were all transported to the infected-cell plasma membrane as shown by cell surface immunofluorescence or cell surface trypsinization. However, the only mutant F protein found to be biologically active as detected by syncytium formation was the F protein which has four arginine residues at the cleavage site. The results presented here suggest that in the paramyxovirus F protein the number of basic amino acid residues in the connecting peptide is important for cleavage of the precursor protein by host cell proteases but is not the only structural feature involved. In addition, the data indicate that cleavage of F0 into F1 and F2 does not necessarily result in biological activity and that the connecting peptide may affect the local conformation of the F polypeptide.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett T., Clarke D. K., Evans S. A., Rima B. K. The nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the F protein of canine distemper virus: a comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence with other paramyxoviruses. Virus Res. 1987 Nov;8(4):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Giorgi C., Rose K., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus fusion protein gene. J Gen Virol. 1985 Feb;66(Pt 2):317–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Garten W., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of influenza virus hemagglutinins: primary structure of the connecting peptide between HA1 and HA2 determines proteolytic cleavability and pathogenicity of Avian influenza viruses. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Orlich M., Klenk H. D., Rott R. The structure of the hemagglutinin, a determinant for the pathogenicity of influenza viruses. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers P., Millar N. S., Emmerson P. T. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the fusion glycoprotein of Newcastle disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2685–2694. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choppin P. W., Scheid A. Role of cellular proteases in viral pathogenicity. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 1979;90:56–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Huang Y. T., Wertz G. W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the fusion (F) glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7683–7687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Zimmer K. P., Wagner K. R., Healey G. A., Mellman I., Helenius A. Folding, trimerization, and transport are sequential events in the biogenesis of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Choi Y. D., Adam S. A. Characterization of heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein complexes in vivo with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elango N., Satake M., Coligan J. E., Norrby E., Camargo E., Venkatesan S. Respiratory syncytial virus fusion glycoprotein: nucleotide sequence of mRNA, identification of cleavage activation site and amino acid sequence of N-terminus of F1 subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1559–1574. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., White J. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification of the fusion protein of Sendai virus: analysis of the NH2-terminal sequence generated during precursor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2737–2740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluschankof P., Morel A., Gomez S., Nicolas P., Fahy C., Cohen P. Enzymes processing somatostatin precursors: an Arg-Lys esteropeptidase from the rat brain cortex converting somatostatin-28 into somatostatin-14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6662–6666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka Y., Kanda T., Iwasaki K., Nomoto A., Shioda T., Shibuta H. Nucleotide sequence of a Sendai virus genome region covering the entire M gene and the 3' proximal 1013 nucleotides of the F gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):7965–7973. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Ouchi M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. 3. Structural difference of Sendai viruses grown in eggs and tissue culture cells. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1457-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Tamagawa S. Restoration of the fusion activity of L cell-borne Sendai virus by trypsin. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;19(3):423–426. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Choppin P. W. Analysis of Sendai virus mRNAs with cDNA clones of viral genes and sequences of biologically important regions of the fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7732–7736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Activation of the Sendai virus fusion protein (f) involves a conformational change with exposure of a new hydrophobic region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3557–3563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Brake A., Blair L., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Nestorowicz A., Alexander D. J., Webster R. G. Molecular analyses of the hemagglutinin genes of H5 influenza viruses: origin of a virulent turkey strain. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):218–227. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaoka Y., Webster R. G. Sequence requirements for cleavage activation of influenza virus hemagglutinin expressed in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):324–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Etkind P. R., Choppin P. W. Evidence for a ninth influenza viral polypeptide. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):60–78. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnes L. W., Morrison T. G. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the Newcastle disease virus fusion protein and comparisons of paramyxovirus fusion protein sequences. Virus Res. 1986 Sep;5(4):343–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Immunological studies of the functions of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Virology. 1981 Feb;109(1):94–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz D. C., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Importance of antibodies to the fusion glycoprotein of paramyxoviruses in the prevention of spread of infection. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):275–288. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Homma M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. V. An activating enzyme for Sendai virus in the chorioallantoic fluid of the embryonated chicken egg. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(2):113–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb00569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeve C. W., Webster R. G. Sequence of the hemagglutinin gene from influenza virus A/Seal/Mass/1/80. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):298–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Proteolytic cleavage of the viral glycoproteins and its significance for the virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):494–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Shimokata K., Yoshida T., Hamaguchi M., Iinuma M., Maeno K., Matsumoto T., Klenk H. D., Rott R. The spread of a pathogenic and an apathogenic strain of Newcastle disease virus in the chick embryo as depending on the protease sensitivity of the virus glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1979 Nov;45(2):263–272. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Harris T. J., Lamb R. A. Analysis and gene assignment of mRNAs of a paramyxovirus, simian virus 5. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):310–323. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90354-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Harris T. J., Lamb R. A. Fusion protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of mRNA predicts a highly hydrophobic glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6706–6710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Hiebert S. W., Lamb R. A. Expression at the cell surface of biologically active fusion and hemagglutinin/neuraminidase proteins of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5 from cloned cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7520–7524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Ability of the hydrophobic fusion-related external domain of a paramyxovirus F protein to act as a membrane anchor. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Polypeptide synthesis in simian virus 5-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):177–187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.177-187.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Hunter E. Mutations within the proteolytic cleavage site of the Rous sarcoma virus glycoprotein that block processing to gp85 and gp37. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1609–1614. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1609-1614.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G., Barber C., Carey N. H., Hallewell R. A., Threlfall G., Emtage J. S. Complete nucleotide sequence of an influenza virus haemagglutinin gene from cloned DNA. Nature. 1979 Nov 29;282(5738):471–477. doi: 10.1038/282471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall R. E., Young D. F., Goswami K. K., Russell W. C. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to simian virus 5 and their use in revealing antigenic differences between human, canine and simian isolates. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2769–2780. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. D., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Specific inhibition of paramyxovirus and myxovirus replication by oligopeptides with amino acid sequences similar to those at the N-termini of the F1 or HA2 viral polypeptides. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):205–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Hull D., Greer P., Hasel K., Berkovich A., Englund G., Bellini W., Rima B., Lazzarini R. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the fusion protein of measles virus (Edmonston strain): a comparison of fusion proteins from several different paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):508–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Isolation of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Association of both hemagglutinating and neuraminidase activities with the larger SV5 glycoprotein. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):640–652. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. The hemagglutinating and neuraminidase protein of a paramyxovirus: interaction with neuraminic acid in affinity chromatography. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90308-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Two disulfide-linked polypeptide chains constitute the active F protein of paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1977 Jul 1;80(1):54–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90380-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Olmsted R. A., Venkatesan S., Coligan J. E., Collins P. L. Fusion glycoprotein of human parainfluenza virus type 3: nucleotide sequence of the gene, direct identification of the cleavage-activation site, and comparison with other paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Docherty K., Carroll R. Golgi/granule processing of peptide hormone and neuropeptide precursors: a minireview. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(2):121–130. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzu S., Sakai Y., Shioda T., Shibuta H. Nucleotide sequence of the bovine parainfluenza 3 virus genome: the genes of the F and HN glycoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2945–2958. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda T., Sakaguchi T., Imai K., Inocencio N. M., Gotoh B., Hamaguchi M., Nagai Y. Structural comparison of the cleavage-activation site of the fusion glycoprotein between virulent and avirulent strains of Newcastle disease virus. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukiyama K., Yoshikawa Y., Yamanouchi K. Fusion glycoprotein (F) of rinderpest virus: entire nucleotide sequence of the F mRNA, and several features of the F protein. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxham M. N., Server A. C., Goodman H. M., Wolinsky J. S. Cloning and sequencing of the mumps virus fusion protein gene. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90477-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]