Abstract
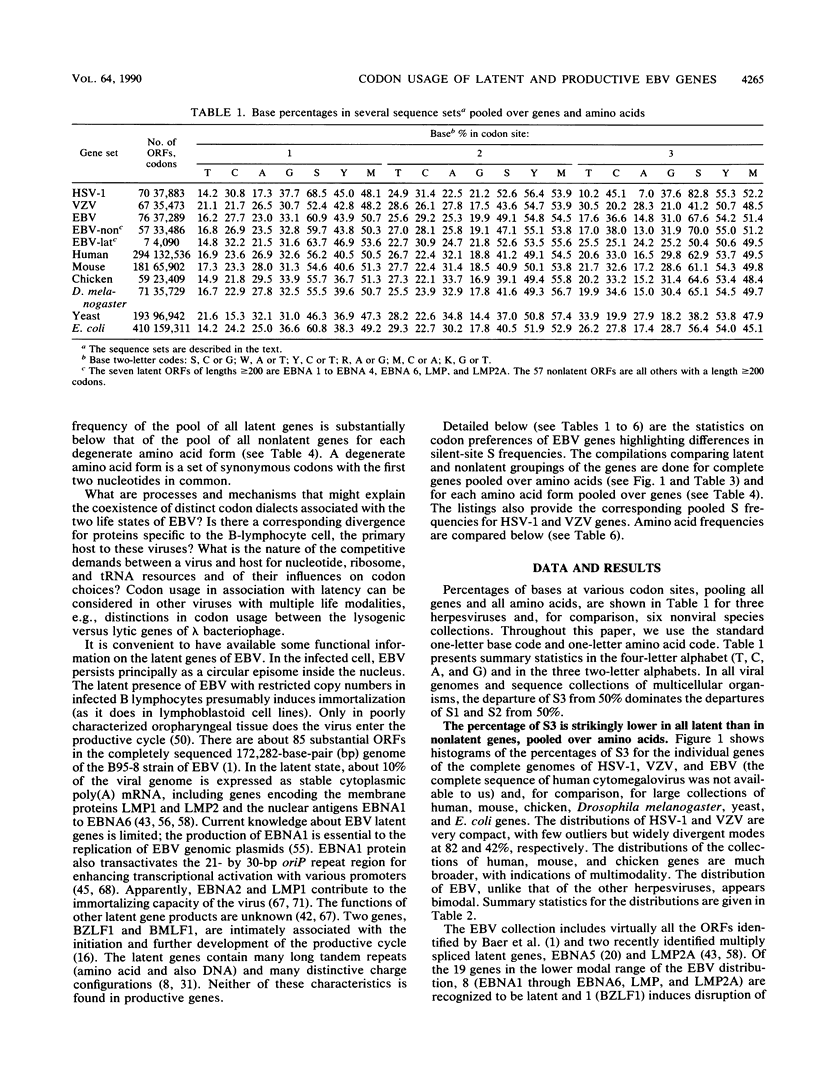
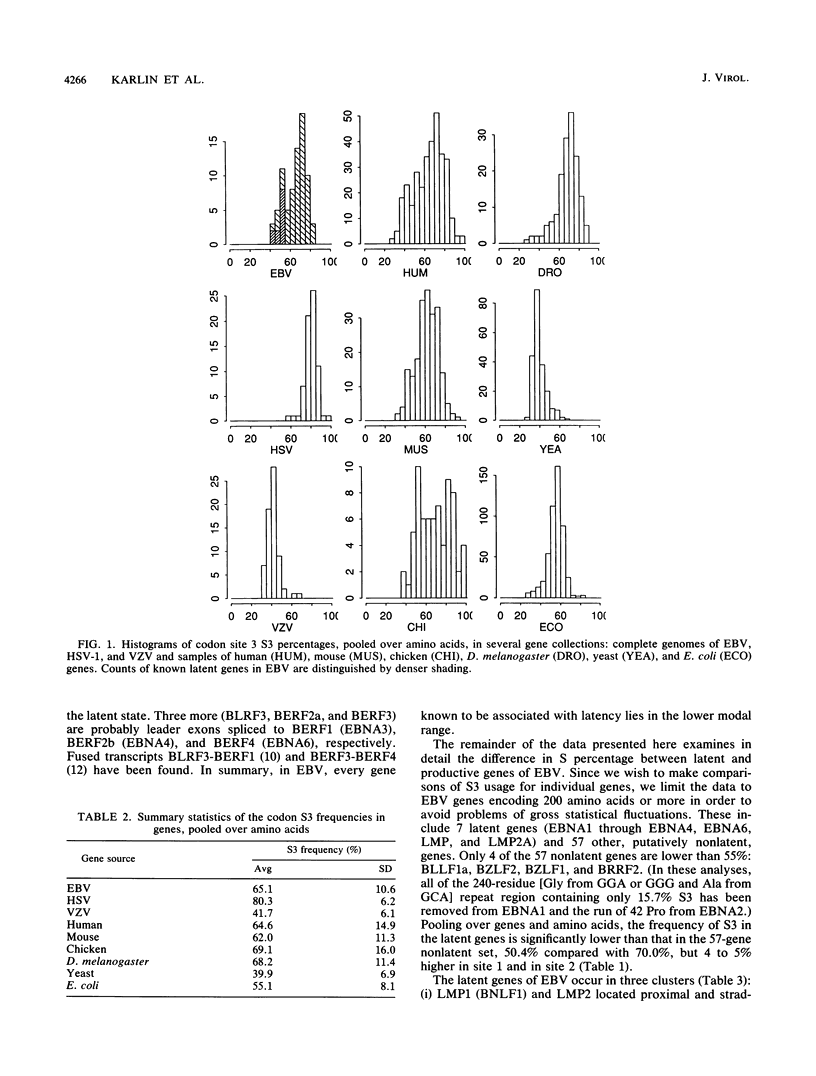
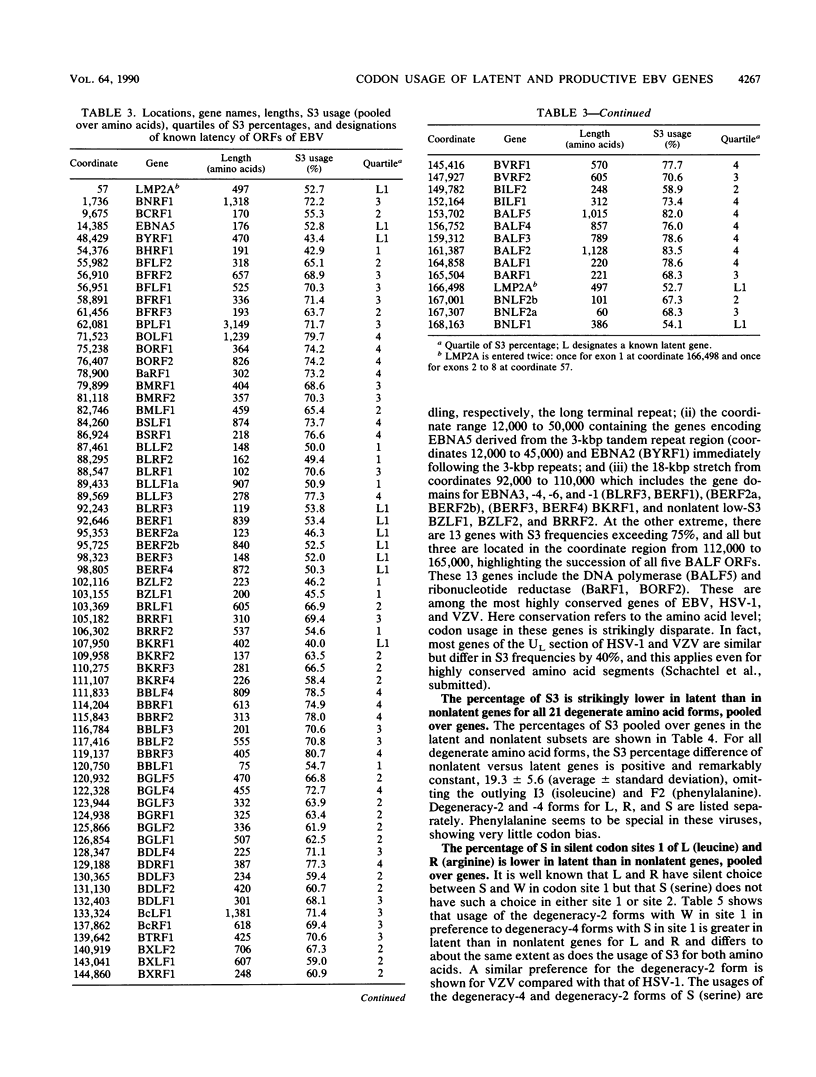
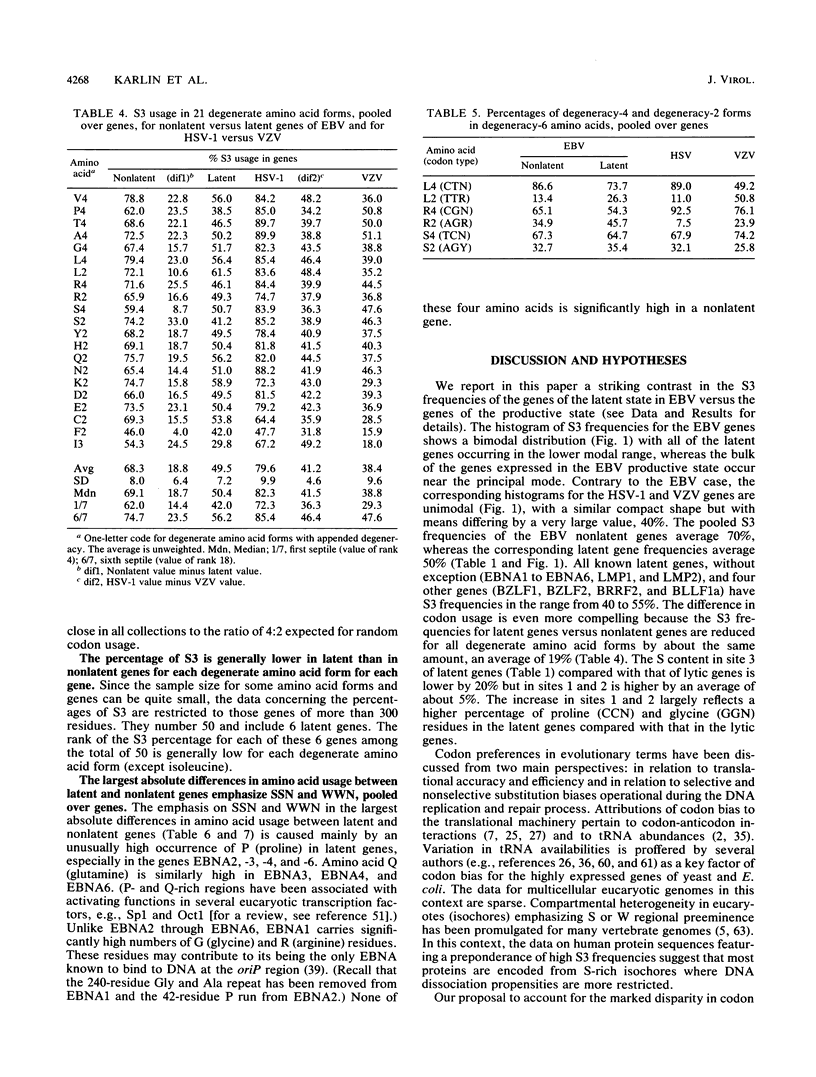
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) has two different modes of existence: latent and productive. There are eight known genes expressed during latency (and hardly at all during the productive phase) and about 70 other ("productive") genes. It is shown that the EBV genes known to be expressed during latency display codon usage strikingly different from that of genes that are expressed during lytic growth. In particular, the percentage of S3 (G or C in codon site 3) is persistently lower (about 20%) in all latent genes than in nonlatent genes. Moreover, S3 is lower in each multicodon amino acid form. Also, the percentage of S in silent codon sites 1 of leucine and arginine is lower in latent than in nonlatent genes. The largest absolute differences in amino acid usage between latent and nonlatent genes emphasize codon types SSN and WWN (W means nucleotide A or T and N is any nucleotide). Two principal explanations to account for the EBV latent versus productive gene codon disparity are proposed. Latent genes have codon usage substantially different from that of host cell genes to minimize the deleterious consequences to the host of viral gene expression during latency. (Productive genes are not so constrained.) It is also proposed that the latency genes of EBV were acquired recently by the viral genome. Evidence and arguments for these proposals are presented.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Bernardi G. Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF02099946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Mouchiroud D., Gautier C., Bernardi G. Compositional patterns in vertebrate genomes: conservation and change in evolution. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/BF02143493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaisdell B. E. Choice of base at silent codon site 3 is not selectively neutral in eucaryotic structural genes: it maintains excess short runs of weak and strong hydrogen bonding bases. J Mol Evol. 1983;19(3-4):226–236. doi: 10.1007/BF02099970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaisdell B. E., Karlin S. Distinctive charge configurations in proteins of the Epstein-Barr virus and possible functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6637–6641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake R. D., Hinds P. W. Analysis of the codon bias in E. coli sequences. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Dec;2(3):593–606. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M. Epstein-Barr virus mRNAs produced by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7103–7114. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Benne R., Tabak H. F. A fused chimeric protein made in human cells. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):421–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90419-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Taylor P. Genetic relations between varicella-zoster virus and Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Apr;68(Pt 4):1067–1079. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-4-1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Physical and functional domains of the herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):732–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.732-743.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ernberg I., Uno M., Ono Y., Klein G., Lerner R. A. An Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA5) partly encoded by the transformation-associated Bam WYH region of EBV DNA: preferential expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Tang P., Hsia H. C., Leong P. M., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):379–387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J. Correlation between molecular clock ticking, codon usage fidelity of DNA repair, chromosome banding and chromatin compactness in germline cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):184–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80660-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Salinas J., Rodier F. Two distinct compositional classes of vertebrate gene-bearing DNA stretches, their structures and possible evolutionary origin. DNA. 1987 Apr;6(2):109–118. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Jacobzone M., Mercier R. Codon catalog usage is a genome strategy modulated for gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r43–r74. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R., Gautier C., Gouy M., Mercier R., Pavé A. Codon catalog usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r49–r62. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman G. A., Hatfield G. W. Nonrandom utilization of codon pairs in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3699–3703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Flemington E., Kieff E., Deininger P. Repeat arrays in cellular DNA related to the Epstein-Barr virus IR3 repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):457–465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highton P. J., Whitfield M. Similarities between the DNA molecules of bacteriophages 424, lambda, and 21, determined by denaturation and electron microscopy. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):438–446. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. Y., Mocarski E. S. Herpes simplex virus latent RNA (LAT) is not required for latent infection in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7596–7600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmquist G. P. Evolution of chromosome bands: molecular ecology of noncoding DNA. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jun;28(6):469–486. doi: 10.1007/BF02602928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INMAN R. B., BALDWIN R. L. HELIX--RANDOM COIL TRANSITIONS IN DNA HOMOPOLYMER PAIRS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:452–469. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukes T. H., Bhushan V. Silent nucleotide substitutions and G + C content of some mitochondrial and bacterial genes. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):39–44. doi: 10.1007/BF02099949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Blaisdell B. E. A model for the development of the tandem repeat units in the EBV ori-P region and a discussion of their possible function. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(3):215–229. doi: 10.1007/BF02100015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Blaisdell B. E., Mocarski E. S., Brendel V. A method to identify distinctive charge configurations in protein sequences, with application to human herpesvirus polypeptides. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin S., Ghandour G. Comparative statistics for DNA and protein sequences: single sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5800–5804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Viral latency and transformation: the strategy of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90394-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Wilbur W. J. Contextual constraints on synonymous codon choice. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 25;163(3):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Kreofsky T., Pearson G. R., Hennessy K., Kieff E. Identification and characterization of a cellular protein that cross-reacts with the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):833–838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.833-838.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Lindahl T., Klein G. Purification of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen from Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human lymphoid cell lines. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.604-611.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama T., Gojobori T., Aota S., Ikemura T. Codon usage tabulated from the GenBank genetic sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14 (Suppl):r151–r197. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Kieff E. A sixth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3B) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2173–2178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2173-2178.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Sample J., Wang F., Kieff E. A fifth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3C) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1330–1338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1330-1338.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Kallin B., Alexander H., Dillner J., Fåhraeus R., Klein G., Lerner R., Rymo L. BamHI E region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome encodes three transformation-associated nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):995–999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.933-937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. An evolutionary perspective on synonymous codon usage in unicellular organisms. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):28–38. doi: 10.1007/BF02099948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields D. C., Sharp P. M. Synonymous codon usage in Bacillus subtilis reflects both translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):8023–8040. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.8023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shpaer E. G. Constraints on codon context in Escherichia coli genes. Their possible role in modulating the efficiency of translation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):555–564. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. Approaches to physical mapping of the human genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):115–122. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. F., Ralph W. W., Goodman M., Czelusniak J. Codon usage in the vertebrate hemoglobins and its implications. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Sep;2(5):390–398. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N. Directional mutation pressure and neutral molecular evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B. An intricate route to immortality. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Warren N. A promoter of Epstein-Barr virus that can function during latent infection can be transactivated by EBNA-1, a viral protein required for viral DNA replication during latent infection. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2644–2649. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2644-2649.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A., Suyama A. Local stability of DNA and RNA secondary structure and its relation to biological functions. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1986;47(2):113–157. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(86)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Nussinov R., Brown R. J., Sussman J. L. Preferential codon usage in genes. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Folley L. S. Sense codons are found in specific contexts. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):529–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


