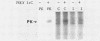Abstract
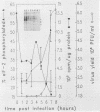
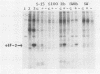
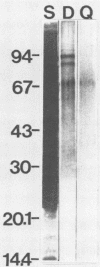
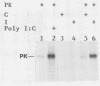
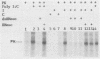
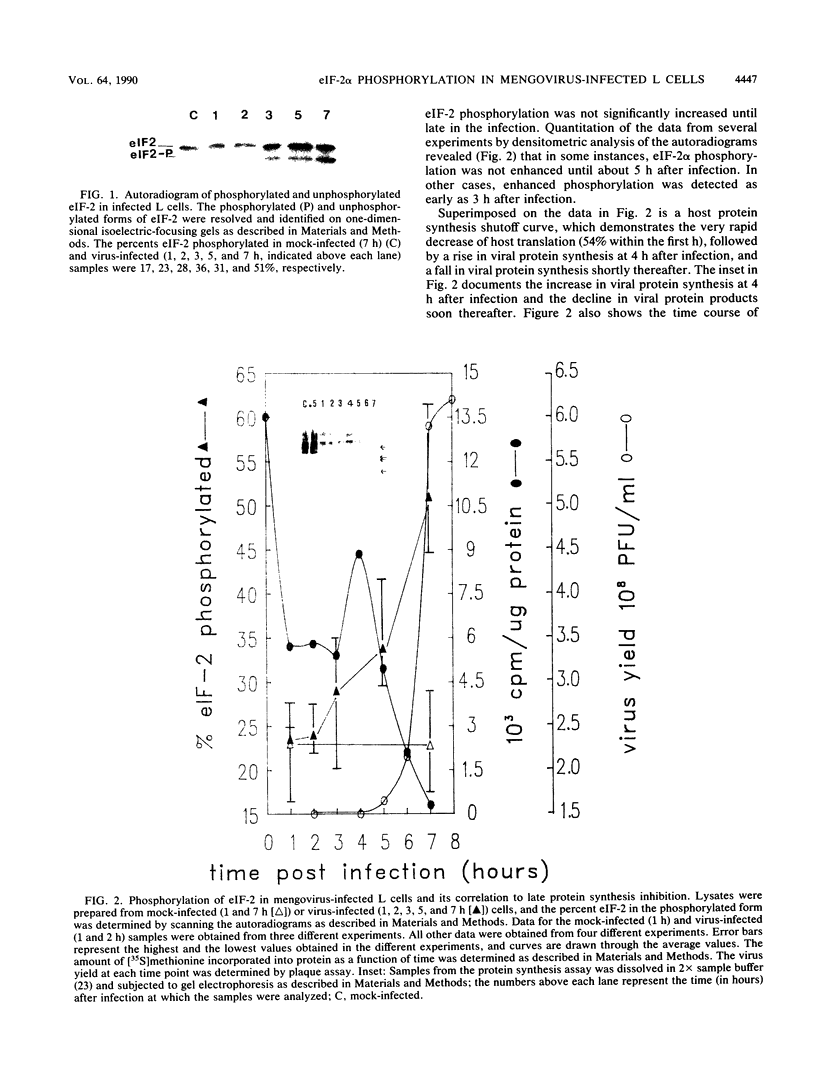
Infection of mouse L cells with mengovirus resulted in the activation of a protein kinase (PK) that selectively phosphorylated the small, 38,000-molecular-weight alpha subunit of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2) in vitro. The mengovirus-activated kinase was detected in vitro approximately 3 h after virus adsorption. The ratio of phosphorylated to unphosphorylated eIF-2 also increased in vivo between 3 and 7 h after adsorption. The virus-activated kinase fractionated with the ribosomal pellet and had a high affinity for DEAE-cellulose and Mono Q ion-exchange columns. Gel electrophoresis of the kinase activity eluting from the Mono Q column and silver staining of the gel revealed only one protein band with a molecular mass of 70 kilodaltons. The optimal assay conditions for the mengovirus-activated kinase paralleled those of the double-stranded RNA-activated PK (dsRNA-PK). Lysates from infected cells contained elements capable of activating partially purified dsRNA-PK. These elements were identified as double-stranded RNA by their sensitivity to double-stranded RNase. The phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eIF-2 coincided with the synthesis of dsRNA in infected cells, suggesting that the mengovirus-activated kinase is the dsRNA-PK. The phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eIF-2 correlated with the global inhibition of protein synthesis that occurs at late times after infection.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abreu S. L., Lucas-Lenard J. Cellular protein synthesis shutoff by mengovirus: translation of nonviral and viral mRNA's in extracts from uninfected and infected Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):182–194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.182-194.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Knutson G. S., Lasky S. R., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Purification and substrate specificities of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase from untreated and interferon-treated mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11240–11247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black T. L., Safer B., Hovanessian A., Katze M. G. The cellular 68,000-Mr protein kinase is highly autophosphorylated and activated yet significantly degraded during poliovirus infection: implications for translational regulation. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2244–2251. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2244-2251.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau A. M., Sonenberg N. Proteolysis of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex is not sufficient for complete inhibition of host cell protein synthesis after poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.986-991.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby D. S., Finnerty V., Lucas-Lenard J. Fate of mRNA of L-cells infected with mengovirus. J Virol. 1974 Apr;13(4):858–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.4.858-869.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetti A., Baglioni C. Phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2 alpha, binding of mRNA to 48 S complexes, and its reutilization in initiation of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14556–14562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Fout S. Human rhinovirus 14 infection of HeLa cells results in the proteolytic cleavage of the p220 cap-binding complex subunit and inactivates globin mRNA translation in vitro. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):634–638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.634-638.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. Autophosphorylation of the protein kinase dependent on double-stranded RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15538–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Katze M. G., Robert N., Hovanessian A. G. The binding of double-stranded RNA and adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):581–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Krust B., Hovanessian A. G. Interferon-mediated protein kinase activity in different fractions of mouse L-929 cells. J Interferon Res. 1984 Fall;4(4):469–480. doi: 10.1089/jir.1984.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L. Specific protein phosphorylation in interferon-treated uninfected and virus-infected mouse L929 cells: enhancement by double-stranded RNA. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):301–311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.301-311.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E. Inhibition of host cell protein synthesis by UV-inactivated poliovirus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):259–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.259-267.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G. The double stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon: dsRNA-PK. J Interferon Res. 1989 Dec;9(6):641–647. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imani F., Jacobs B. L. Inhibitory activity for the interferon-induced protein kinase is associated with the reovirus serotype 1 sigma 3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7887–7891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jen G., Birge C. H., Thach R. E. Comparison of initiation rates of encephalomyocarditis virus and host protein synthesis in infected cells. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):640–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.640-647.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Tomita J., Black T., Krug R. M., Safer B., Hovanessian A. Influenza virus regulates protein synthesis during infection by repressing autophosphorylation and activity of the cellular 68,000-Mr protein kinase. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3710–3717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3710-3717.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Safer B. Purification of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2-eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex and characterization of its guanine nucleotide exchange activity during protein synthesis initiation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Brayley A., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. The effect of cyclic AMP and related compounds on the control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesch W. T., Jr, Arlinghaus R. B. Polypeptides associated with the 250 S mengovirus-induced RNA polymerase structure. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;46(3-4):253–268. doi: 10.1007/BF01240068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Guidon P. T., Jr, Sekellick M. J. Interferon induction by viruses. VII. Mengovirus: "interferon-sensitive" mutant phenotype attributed to interferon-inducing particle activity. J Interferon Res. 1981;1(4):601–611. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meegan J. M., Marcus P. I. Double-stranded ribonuclease coinduced with interferon. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1089–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.2471268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Gibbons G. F., Dasgupta A. The host protein required for in vitro replication of poliovirus is a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor-2. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):913–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosenkis J., Daniels-McQueen S., Janovec S., Duncan R., Hershey J. W., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Shutoff of host translation by encephalomyocarditis virus infection does not involve cleavage of the eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide that accompanies poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):643–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.643-645.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. E., Racaniello V. R. Inhibition of translation in cells infected with a poliovirus 2Apro mutant correlates with phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eucaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5069–5075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5069-5075.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pani A., Julian M., Lucas-Lenard J. A kinase able to phosphorylate exogenous protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 alpha is present in lysates of mengovirus-infected L cells. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1012–1017. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1012-1017.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panniers R., Henshaw E. C. A GDP/GTP exchange factor essential for eukaryotic initiation factor 2 cycling in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells and its regulation by eukaryotic initiation factor 2 phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7928–7934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensiero M. N., Lucas-Lenard J. M. Evidence for the presence of an inhibitor on ribosomes in mouse L cells infected with mengovirus. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):161–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.161-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Bercoff R., Kaempfer R. Genomic RNA of mengovirus V. Recognition of common features by ribosomes and eucaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):30–41. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.30-41.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Duncan R., Hershey J. W., Kerr I. M. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase and 2-5A system are both activated in interferon-treated, encephalomyocarditis virus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):894–898. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.894-898.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Di Segni G., Kaempfer R. Translational control by messenger RNA competition for eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):946–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B. 2B or not 2B: regulation of the catalytic utilization of eIF-2. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Knutson G. S., Berry M. J., Atwater J. A., Lasky S. R. Purification of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase from mouse fibroblasts. Methods Enzymol. 1986;119:499–516. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)19070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Knutson G. S. Mechanism of interferon action: eIF-2 alpha phosphatase in interferon-treated mouse fibroblasts is double-stranded RNA independent. J Interferon Res. 1982;2(3):441–445. doi: 10.1089/jir.1982.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Impact of virus infection on host cell protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:317–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scorsone K. A., Panniers R., Rowlands A. G., Henshaw E. C. Phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 during physiological stresses which affect protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14538–14543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mariano T. M., Reichel P. A., Mathews M. B. Translational control by adenovirus: lack of virus-associated RNAI during adenovirus infection results in phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2 and inhibition of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. H., Kung S., Koh T. T., Brandman P. Interferon-sensitive mutants of mengovirus. I. Isolation and biological characterization. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):727–736. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90501-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker-Dowling P., Youngner J. S. Characterization of a specific kinase inhibitory factor produced by vaccinia virus which inhibits the interferon-induced protein kinase. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]