Abstract
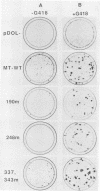
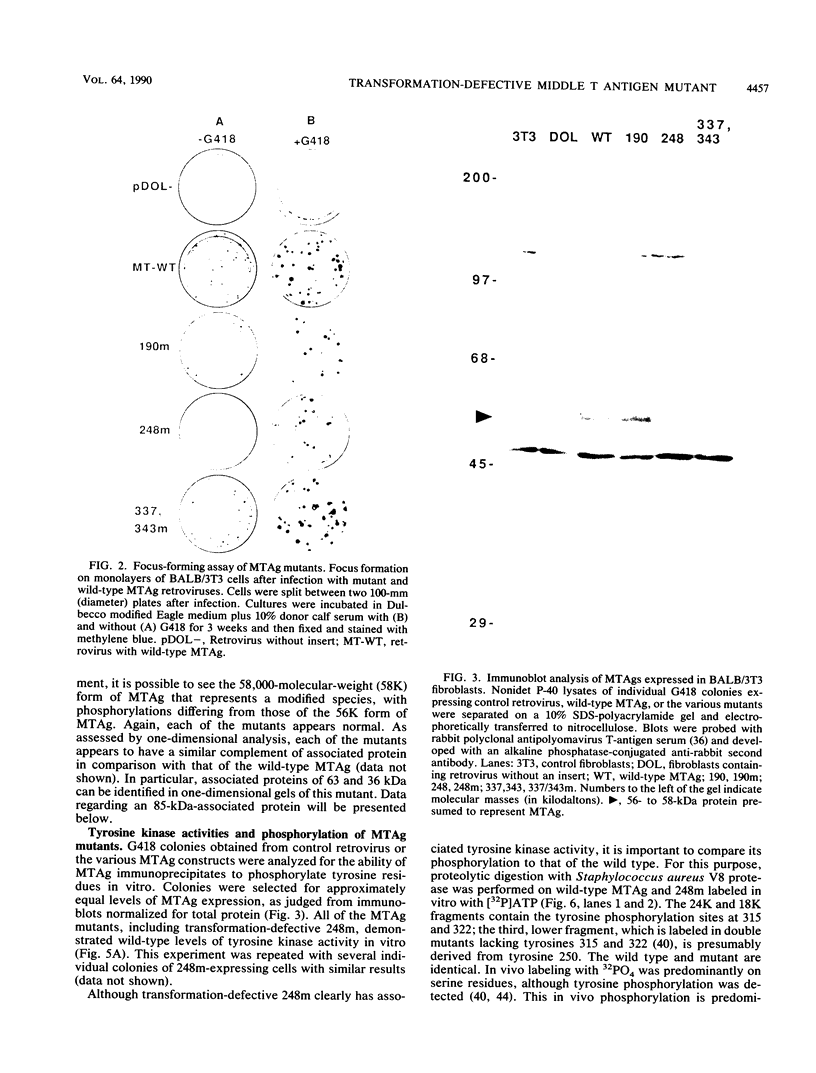
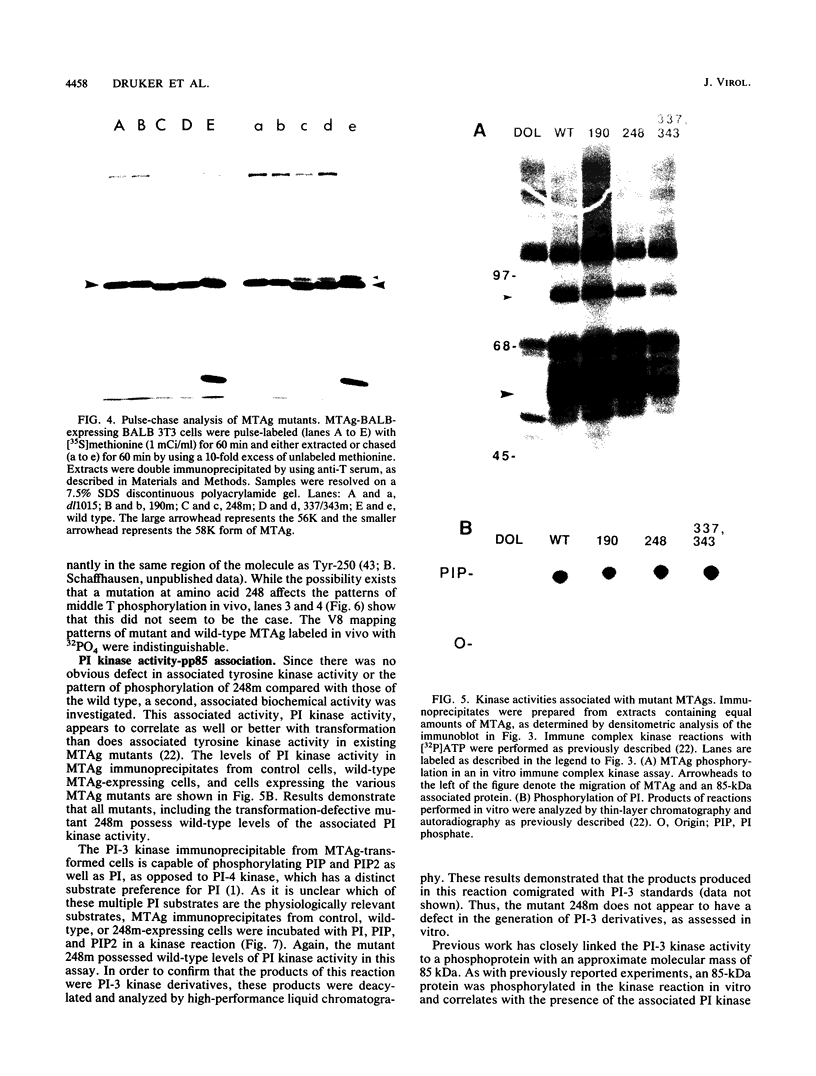
By using a random mutagenesis procedure combined with a recombinant retrovirus vector, mutants of polyomavirus middle T antigen (MTAg) were generated. Three new MTAg mutants with various degrees of transformation competence were more thoroughly characterized. All of the mutants produced a stable MTAg, as assessed by metabolic labeling or immunoblotting, and each mutant possessed wild-type levels of associated tyrosine kinase activity and associated phosphatidylinositol-3 (PI-3) kinase activity. One of these mutants, with a substitution of leucine for proline at amino acid 248 of MTAg (248m) was completely transformation defective, as measured in a focus-forming assay. Furthermore, the pattern of phosphorylation of 248m in vivo was identical to that of wild-type MTAg, and the kinetics of association of MTAg with an 85-kilodalton protein, the putative PI kinase, was not altered. Similarly, the pattern of PI derivatives obtained in an in vitro kinase assay was not altered by the substitution at amino acid 248. Since the single base pair mutation at amino acid 248 resulted in an MTAg that was completely transformation defective despite possessing wild-type levels of kinase activities, this suggests that neither tyrosine kinase nor PI-3 kinase activity nor the combination of both are sufficient for transformation by MTAg.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):394–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., DeSeau V., O'Shaughnessy J., Amini S. Analysis of middle tumor antigen and pp60c-src interactions in polyomavirus-transformed rat cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3299–3305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3299-3305.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., Schaffhausen B. S., Dorsky D. I., Oliver D. B., Benjamin T. L. Carboxy terminus of polyoma middle-sized tumor antigen is required for attachment to membranes, associated protein kinase activities, and cell transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3579–3583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. NPXY, a sequence often found in cytoplasmic tails, is required for coated pit-mediated internalization of the low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3116–3123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Harvey R., Espino P. C., Semba K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Smith A. E. Peptide antibodies to the human c-fyn gene product demonstrate pp59c-fyn is capable of complex formation with the middle-T antigen of polyomavirus. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3845–3855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherington V., Morgan B., Spiegelman B. M., Roberts T. M. Recombinant retroviruses that transduce individual polyoma tumor antigens: effects on growth and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4307–4311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B., Liu Y. X., Druker B., Roberts T. M., Schaffhausen B. S. Characterization of pp85, a target of oncogenes and growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2909–2915. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Heber A. An 81 kd protein complexed with middle T antigen and pp60c-src: a possible phosphatidylinositol kinase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus transforming protein associates with the product of the c-src cellular gene. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):435–439. doi: 10.1038/303435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. The complex of polyoma virus middle-T antigen and pp60c-src. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):585–591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoghue D. J., Anderson C., Hunter T., Kaplan P. L. Transmission of the polyoma virus middle T gene as the oncogene of a murine retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):748–750. doi: 10.1038/308748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin B. E., Ito Y., Novak U., Spurr N., Dilworth S., Smolar N., Pollack R., Smith K., Rifkin D. B. Early mutants of polyoma virus (dl8 and dl23) with altered transformation properties: is polyoma virus middle T antigen a transforming gene product? Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):271–283. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grussenmeyer T., Scheidtmann K. H., Hutchinson M. A., Eckhart W., Walter G. Complexes of polyoma virus medium T antigen and cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7952–7954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Spurr N., Griffin B. E. Middle T antigen as primary inducer of full expression of the phenotype of transformation by polyoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):219–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.219-232.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Raptis L., Garcea R. L., Pallas D., Roberts T. M., Cantley L. Phosphatidylinositol metabolism and polyoma-mediated transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Simon S., Eckhart W. Polyomavirus middle T protein encoded by a retrovirus transforms nonestablished chicken embryo cells. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):1023–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.1023-1026.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Frantz J. D., Strominger J. L., Mulligan R. C. Expression of human class II major histocompatibility complex antigens using retrovirus vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2150–2154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Cross F. R., Harbison M., Hanafusa H. Transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts and tumor induction by the middle T antigen of polyomavirus carried in an avian retroviral vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1545–1551. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Sudol M., Hanafusa H. Association of the polyomavirus middle-T antigen with c-yes protein. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):171–173. doi: 10.1038/325171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T. J., Carmichael G. G., Benjamin T. L. A polyoma mutant that encodes small T antigen but not middle T antigen demonstrates uncoupling of cell surface and cytoskeletal changes associated with cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2774–2783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie R. R., King C. S., MacAuley A., Marth J. D., Perlmutter R. M., Eckhart W., Cooper J. A. p56lck protein-tyrosine kinase is cytoskeletal and does not bind to polyomavirus middle T antigen. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4673–4679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4673-4679.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson G., Berg P. Construction and analysis of viable deletion mutants of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):523–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.523-529.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland W., Oostra B. A., Harvey R., Markham A. F., Colledge W. H., Smith A. E. Site-directed mutagenesis of polyomavirus middle-T antigen sequences encoding tyrosine 315 and tyrosine 250. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):384–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.384-391.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland W., Smith A. E. Mutants of polyomavirus middle-T antigen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 25;907(3):299–321. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. C., Kaplan D. R., Pallas D. C., Roberts T. M. Recombinant retroviruses that transduce middle T antigen cDNAs derived from polyomavirus mutants: separation of focus formation and soft-agar growth in transformation assays and correlations with kinase activities in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3407–3414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3407-3414.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Browning P. J., White M. F., Roberts T. M. Tyrosine phosphorylations in vivo associated with v-fms transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):176–185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Cherington V., Morgan W., DeAnda J., Kaplan D., Schaffhausen B., Roberts T. M. Cellular proteins that associate with the middle and small T antigens of polyomavirus. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3934–3940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3934-3940.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Schley C., Mahoney M., Harlow E., Schaffhausen B. S., Roberts T. M. Polyomavirus small t antigen: overproduction in bacteria, purification, and utilization for monoclonal and polyclonal antibody production. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1075–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1075-1084.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Shahrik L. K., Martin B. L., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Brautigan D. L., Roberts T. M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90726-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raptis L., Lamfrom H., Benjamin T. L. Regulation of cellular phenotype and expression of polyomavirus middle T antigen in rat fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2476–2486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Cowie A., Carr A., Glaichenhaus N., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The roles of individual polyoma virus early proteins in oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):713–718. doi: 10.1038/300713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Bockus B. J., Berkner K. L., Kaplan D., Roberts T. M. Characterization of middle T antigen expressed by using an adenovirus expression system. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1221–1225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1221-1225.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Liang T. J., Carmichael G. G., Benjamin T. L. Residual transforming activity of PY1178T, a mutant lacking the principal in vitro tyrosine phosphorylation site, is not affected by removal of the secondary tyrosine phosphorylation site at residue 322. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):671–675. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90410-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B., Benjamin T. L. Comparison of phosphorylation of two polyoma virus middle T antigens in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):184–196. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.184-196.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa K., Ito Y. Differential subcellular localization of in vivo-phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated middle-sized tumor antigen of polyoma virus and its relationship to middle-sized tumor antigen phosphorylating activity in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6812–6816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolar N., Griffin B. E. DNA sequences of polyoma virus early deletion mutants. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):958–967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.958-967.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton D., Eckhart W. Mutation causing premature termination of the polyoma virus medium T antigen blocks cell transformation. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1014–1024. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1014-1024.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Novak U., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Transformation of rat cells by an altered polyoma virus genome expressing only the middle-T protein. Nature. 1981 Aug 13;292(5824):595–600. doi: 10.1038/292595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D., Roberts T., Cantley L. Evidence for two distinct phosphatidylinositol kinases in fibroblasts. Implications for cellular regulation. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):165–174. doi: 10.1042/bj2470165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]