Abstract
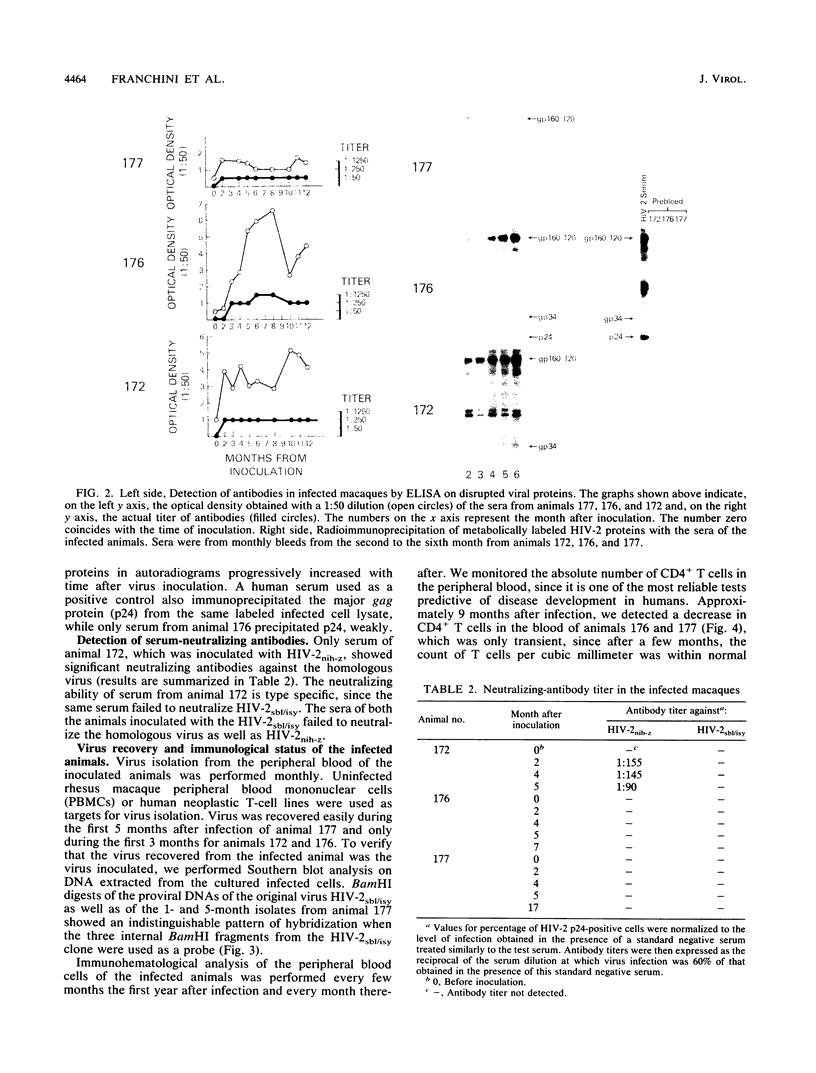
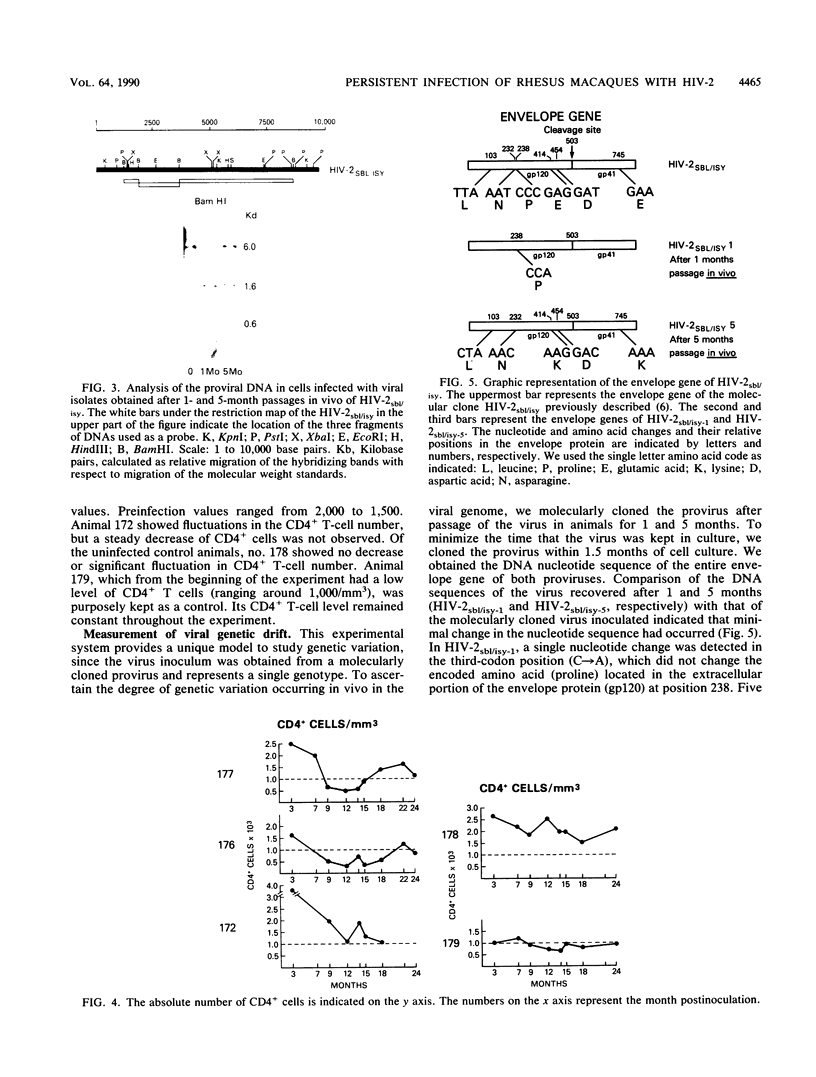
In an attempt to generate a suitable animal model to study the infectivity and possible pathogenicity of human immunodeficiency viruses, we intravenously inoculated juvenile rhesus macaques and African green monkeys with a molecularly cloned virus, human immunodeficiency virus type 2 HIV-2sbl/isy, as well as with the uncloned HIV-2nih-z virus. Infection was monitored by virus recovery from the peripheral blood cells and by seroconversion against HIV-2 antigens measured by Western immunoblot, radioimmunoprecipitation, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. We successfully infected two out of two macaques with the molecularly cloned virus and one macaque out of two with the HIV-2nih-z. No evidence of infection was seen in the African green monkeys with either virus. We followed the infected animals for 2 years. The animals remained healthy, although we observed intermittent lymphadenopathy and a transient decrease in the absolute number of circulating CD4+ T lymphocytes in both animals infected with the molecularly cloned virus. Virus isolation from the peripheral blood cells of the infected animals was successful only within the first few months after inoculation. Evidence of persistent infection was provided by the detection of proviral DNA by polymerase chain reaction analysis of the blood cells of the inoculated animals and by the stability of antiviral antibody titers. To evaluate the genetic drift of the proviral DNA, we molecularly cloned viruses which were reisolated 1 and 5 months postinoculation from one of these animals. Comparison of the DNA sequences of the envelope genes of both these isolates indicated that a low degree of variation (0.2%) in the envelope protein had occurred in vivo during the 5-month period. These data suggest that the use of HIV-2sbl/isy in rhesus macaques may represent a good animal model system to study prevention of viral infection. In particular, molecularly cloned virus can be manipulated for functional studies of viral genes in the pathogenesis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome and provides a reproducible source of virus for vaccine studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Eichberg J. W., Masur H., Saxinger W. C., Gallo R., Macher A. M., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Transmission of HTLV-III infection from human plasma to chimpanzees: an animal model for AIDS. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):549–552. doi: 10.1126/science.6093251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Guétard D., Brun-Vézinet F., Chamaret S., Rey M. A., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Laurent A. G., Dauguet C., Katlama C., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a new human retrovirus from West African patients with AIDS. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2425430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dormont D., Livartowski J., Chamaret S., Guetard D., Henin D., Levagueresse R., van de Moortelle P. F., Larke B., Gourmelon P., Vazeux R. HIV-2 in rhesus monkeys: serological, virological and clinical results. Intervirology. 1989;30 (Suppl 1):59–65. doi: 10.1159/000150125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Fargnoli K. A., Giombini F., Jagodzinski L., De Rossi A., Bosch M., Biberfeld G., Fenyo E. M., Albert J., Gallo R. C. Molecular and biological characterization of a replication competent human immunodeficiency type 2 (HIV-2) proviral clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2433–2437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Gurgo C., Guo H. G., Gallo R. C., Collalti E., Fargnoli K. A., Hall L. F., Wong-Staal F., Reitz M. S., Jr Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus and its relationship to the human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):539–543. doi: 10.1038/328539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. P., Feorino P. M., Broderson J. R., McClure H. M., Getchell J. P., McGrath C. R., Swenson B., McDougal J. S., Palmer E. L., Harrison A. K. Infection of chimpanzees with lymphadenopathy-associated virus. Lancet. 1984 Dec 1;2(8414):1276–1277. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92824-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa M., Miura T., Hasegawa A., Morikawa S., Tsujimoto H., Miki K., Kitamura T., Hayami M. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from African green monkey, a new member of the HIV/SIV group. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):457–461. doi: 10.1038/333457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C., Amyx H. L., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Asher D. M., Rodgers-Johnson P., Epstein L. G., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C., Maluish A., Arthur L. O. Infection of chimpanzees by human T-lymphotropic retroviruses in brain and other tissues from AIDS patients. Lancet. 1985 Jan 5;1(8419):55–56. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C. The AIDS virus. Sci Am. 1987 Jan;256(1):46–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Taylor M. E., Redfield R. R., Markham P. D., Salahuddin S. Z., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Parks E. S., Parks W. P. Genetic variation in HTLV-III/LAV over time in patients with AIDS or at risk for AIDS. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1548–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.3012778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V., Riedel N., Mullins J. I. The genome organization of STLV-3 is similar to that of the AIDS virus except for a truncated transmembrane protein. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):307–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90283-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney D. J., Fisher A. G., Putney S. D., Rusche J. R., Redfield R. R., Burke D. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Type-restricted neutralization of molecular clones of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):357–359. doi: 10.1126/science.3388046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlink R. G., Ricard D., M'Boup S., Kanki P. J., Romet-Lemonne J. L., N'Doye I., Diop K., Simpson M. A., Greco F., Chou M. J. Clinical, hematologic, and immunologic cross-sectional evaluation of individuals exposed to human immunodeficiency virus type-2 (HIV-2). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Apr;4(2):137–148. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhans A., Cheynier R., Albert J., Seth M., Kwok S., Sninsky J., Morfeldt-Månson L., Asjö B., Wain-Hobson S. Temporal fluctuations in HIV quasispecies in vivo are not reflected by sequential HIV isolations. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):901–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90942-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Hatch W. C., Dunlop N. M., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Gonda M. A., Fischinger P. J. Simple, rapid, quantitative, syncytium-forming microassay for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus neutralizing antibody. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Fall;3(3):283–302. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Robey W. G., Arthur L. O., Gonda M. A., Asher D. M., Yanagihara R., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C., Fischinger P. J. Simultaneous isolation of simian foamy virus and HTLV-III/LAV from chimpanzee lymphocytes following HTLV-III or LAV inoculation. Arch Virol. 1987;92(1-2):183–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01310072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicol I., Flamminio-Zola G., Dubouch P., Bernard J., Snart R., Jouffre R., Reveil B., Fouchard M., Desportes I., Nara P. Persistent HIV-2 infection of rhesus macaque, baboon, and mangabeys. Intervirology. 1989;30(5):258–267. doi: 10.1159/000150101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkonen P., Böttiger B., Warstedt K., Thorstensson R., Albert J., Biberfeld G. Experimental infection of cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with HIV-2. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(4):366–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Guroff M., Brown M., Gallo R. C. HTLV-III-neutralizing antibodies in patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):72–74. doi: 10.1038/316072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagury J. F., Franchini G., Reitz M., Collalti E., Starcich B., Hall L., Fargnoli K., Jagodzinski L., Guo H. G., Laure F. Genetic variability between isolates of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 2 is comparable to the variability among HIV type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5941–5945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






