Abstract
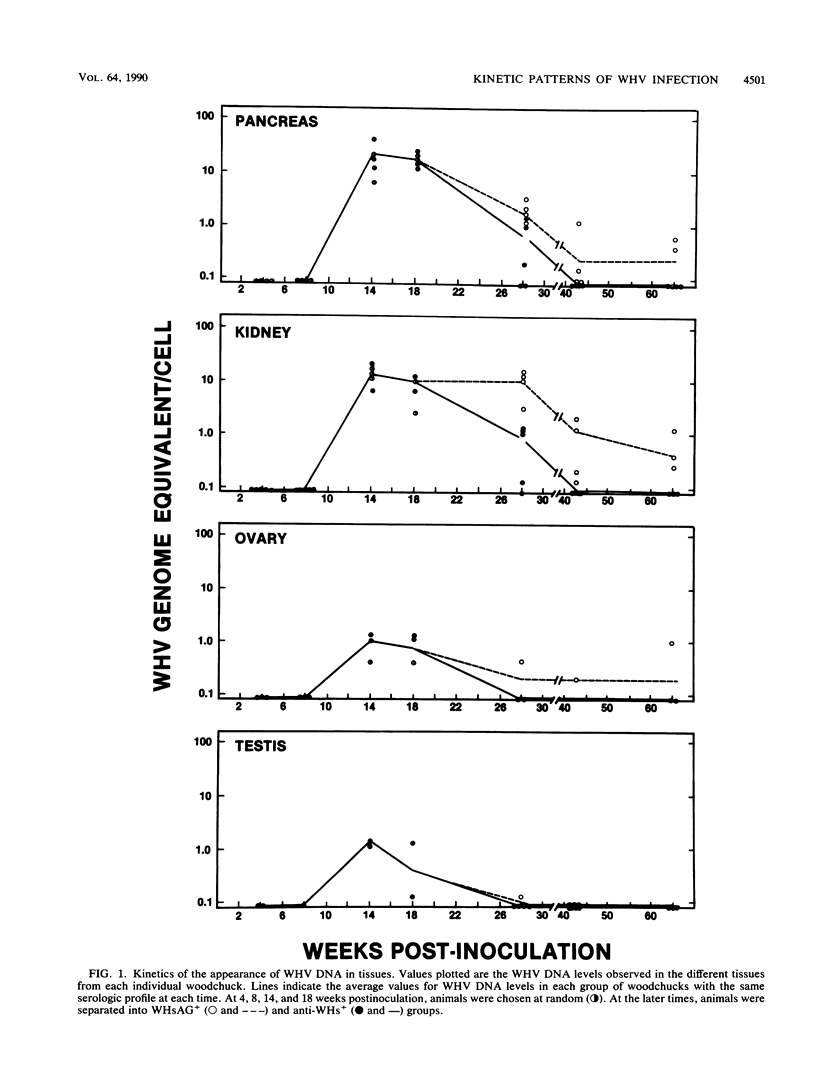
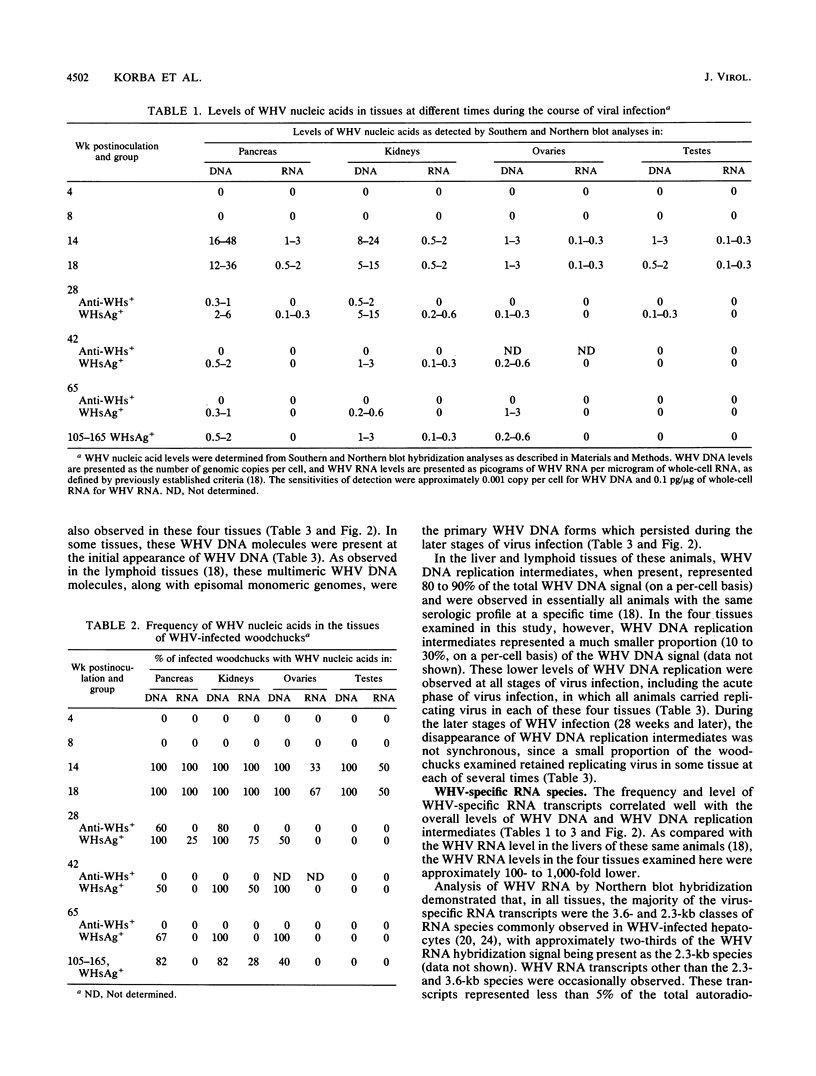
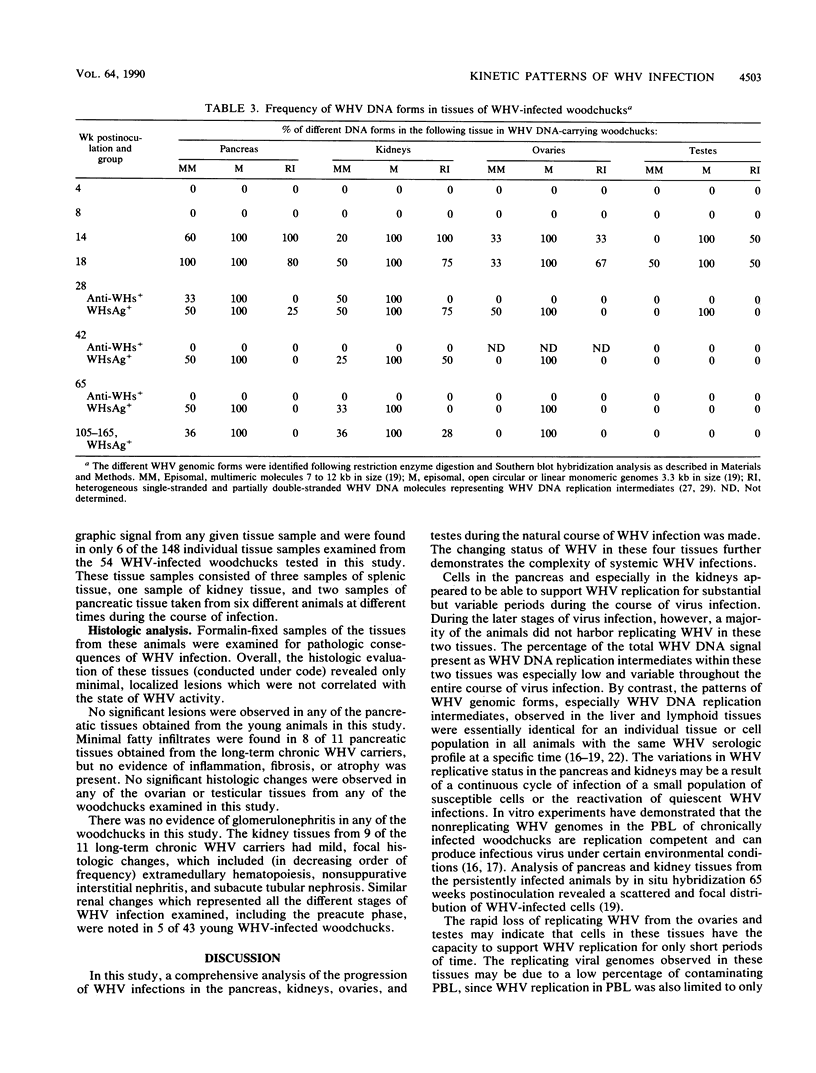
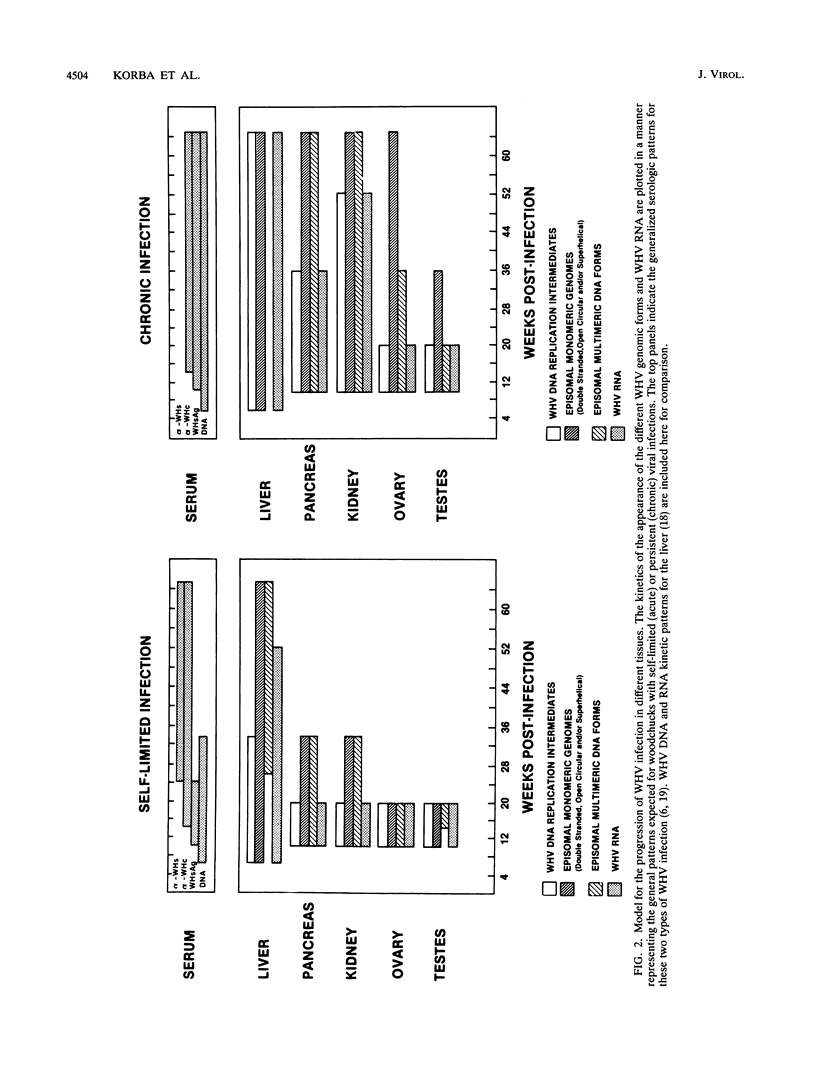
The kinetic patterns of woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) infection were monitored in the pancreas, kidneys, ovaries, and testes. Groups of woodchucks experimentally infected with a standardized inoculum of WHV were sacrificed at different times over a 65-week period beginning in the preacute phase of viral infection and continuing to the period of serologic recovery or the establishment of chronic infections and subsequent hepatocellular carcinoma (B. E. Korba, P. J. Cote, F. V. Wells, B. Baldwin, H. Popper, R. H. Purcell, B. C. Tennant, and J. L. Gerin, J. Virol. 63:1360-1370, 1989). Tissues from an additional group of long-term (2 to 3 years) chronic WHV carriers which had been infected with the same WHV inocula were also examined. Viral DNA replication intermediates were found in all four tissues during the acute phase of WHV infection. However, WHV DNA replication intermediates were observed only in the kidneys of a small proportion of the chronically infected animals. Following the acute phase of infection, WHV DNA was present only in the pancreas, kidneys, and ovaries of the chronically infected woodchucks. A progressive evolution of different WHV genomic forms related to the replicative state of WHV was observed in these tissues. Histologic evaluation of these four tissues revealed only minimal, localized lesions which were not correlated with the state of WHV activity. The observations compiled in this study further extend the tissue tropism of WHV.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L., London W. T., Kaplan P. M., McAuliffe V. J., Wagner J., Holland P. V. Transmission of hepatitis B to chimpanzees by hepatitis B surface antigen-positive saliva and semen. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):928–933. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.928-933.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babinet C., Farza H., Morello D., Hadchouel M., Pourcel C. Specific expression of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in transgenic mice. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1160–1163. doi: 10.1126/science.3865370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk R. D., DeLoia J. A., elAwady M. K., Gearhart J. D. Tissue preferential expression of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen gene in two lines of HBV transgenic mice. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):649–654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.649-654.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Miller R. H., Rosenblum B., Denniston K., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H. Sequence comparison of woodchuck hepatitis virus replicative forms shows conservation of the genome. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combes B., Shorey J., Barrera A., Stastny P., Eigenbrodt E. H., Hull A. R., Carter N. W. Glomerulonephritis with deposition of Australia antigen-antibody complexes in glomerular basement membrane. Lancet. 1971 Jul 31;2(7718):234–237. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92572-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote P. J., Shapiro M., Engle R. E., Popper H., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Protection of chimpanzees from type B hepatitis by immunization with woodchuck hepatitis virus surface antigen. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):895–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.895-901.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejean A., Lugassy C., Zafrani S., Tiollais P., Brechot C. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in pancreas, kidney and skin of two human carriers of the virus. J Gen Virol. 1984 Mar;65(Pt 3):651–655. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-3-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freiman J. S., Jilbert A. R., Dixon R. J., Holmes M., Gowans E. J., Burrell C. J., Wills E. J., Cossart Y. E. Experimental duck hepatitis B virus infection: pathology and evolution of hepatic and extrahepatic infection. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):507–513. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Cote P. J., Korba B. E., Tennant B. C. Hepadnavirus-induced liver cancer in woodchucks. Cancer Detect Prev. 1989;14(2):227–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Huret J. L., Molinie C., Villa E., Degos F., Brechot C. Presence of HBV DNA in spermatozoa: a possible vertical transmission of HBV via the germ line. J Med Virol. 1985 May;16(1):61–66. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890160109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. S., England J. M., Deery D. T., Petcu D. J., Mason W. S., Molnar-Kimber K. L. Viral nucleic acid synthesis and antigen accumulation in pancreas and kidney of Pekin ducks infected with duck hepatitis B virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4865–4869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameel S., Siddiqui A. The human hepatitis B virus enhancer requires trans-acting cellular factor(s) for activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):710–715. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilbert A. R., Freiman J. S., Gowans E. J., Holmes M., Cossart Y. E., Burrell C. J. Duck hepatitis B virus DNA in liver, spleen, and pancreas: analysis by in situ and Southern blot hybridization. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karayiannis P., Novick D. M., Lok A. S., Fowler M. J., Monjardino J., Thomas H. C. Hepatitis B virus DNA in saliva, urine, and seminal fluid of carriers of hepatitis B e antigen. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jun 22;290(6485):1853–1855. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6485.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Cote P. J., Gerin J. L. Mitogen-induced replication of woodchuck hepatitis virus in cultured peripheral blood lymphocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1213–1216. doi: 10.1126/science.3261887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Cote P. J., Shapiro M., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. In vitro production of infectious woodchuck hepatitis virus by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1989 Oct;160(4):572–576. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.4.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Cote P. J., Wells F. V., Baldwin B., Popper H., Purcell R. H., Tennant B. C., Gerin J. L. Natural history of woodchuck hepatitis virus infections during the course of experimental viral infection: molecular virologic features of the liver and lymphoid tissues. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1360–1370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1360-1370.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Gowans E. J., Wells F. V., Tennant B. C., Clarke R., Gerin J. L. Systemic distribution of woodchuck hepatitis virus in the tissues of experimentally infected woodchucks. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):172–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90670-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Wells F. V., Baldwin B., Cote P. J., Tennant B. C., Popper H., Gerin J. L. Hepatocellular carcinoma in woodchuck hepatitis virus-infected woodchucks: presence of viral DNA in tumor tissue from chronic carriers and animals serologically recovered from acute infections. Hepatology. 1989 Mar;9(3):461–470. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Wells F., Tennant B. C., Cote P. J., Gerin J. L. Lymphoid cells in the spleens of woodchuck hepatitis virus-infected woodchucks are a site of active viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1318–1324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1318-1324.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Wells F., Tennant B. C., Yoakum G. H., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Hepadnavirus infection of peripheral blood lymphocytes in vivo: woodchuck and chimpanzee models of viral hepatitis. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.1-8.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai K. N., Lai F. M., Chan K. W., Chow C. B., Tong K. L., Vallance-Owen J. The clinico-pathologic features of hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis. Q J Med. 1987 Apr;63(240):323–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman H. M., Tung W. W., Shafritz D. A. Splenic replication of hepatitis B virus in the chimpanzee chronic carrier. J Med Virol. 1987 Apr;21(4):347–359. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890210407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T., Etiemble J., Trépo C., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Transcription of woodchuck hepatitis virus in the chronically infected liver. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1507–1514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada K., Kamiyama I., Inomata M., Imai M., Miyakawa Y. e antigen and anti-e in the serum of asymptomatic carrier mothers as indicators of positive and negative transmission of hepatitis B virus to their infants. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):746–749. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto A., Cote P. J., Ford E. C., Purcell R. H., Gerin J. L. Core antigen and antibody in woodchucks after infection with woodchuck hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):70–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.70-76.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biochemical and genetic evidence for the hepatitis B virus replication strategy. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):477–484. doi: 10.1126/science.3961490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen H. D., Choo K. B., Wu T. C., Ng H. T., Han S. H. Hepatitis B virus infection of cord blood leukocytes. J Med Virol. 1987 Jul;22(3):211–216. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890220303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandau D. F., Lee C. H. trans-activation of viral enhancers by the hepatitis B virus X protein. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):427–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.427-434.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa M., Omata M., Yokosuka O., Uchiumi K., Imazeki F., Okuda K. Early events in duck hepatitis B virus infection. Sequential appearance of viral deoxyribonucleic acid in the liver, pancreas, kidney, and spleen. Gastroenterology. 1985 Dec;89(6):1224–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



