Abstract
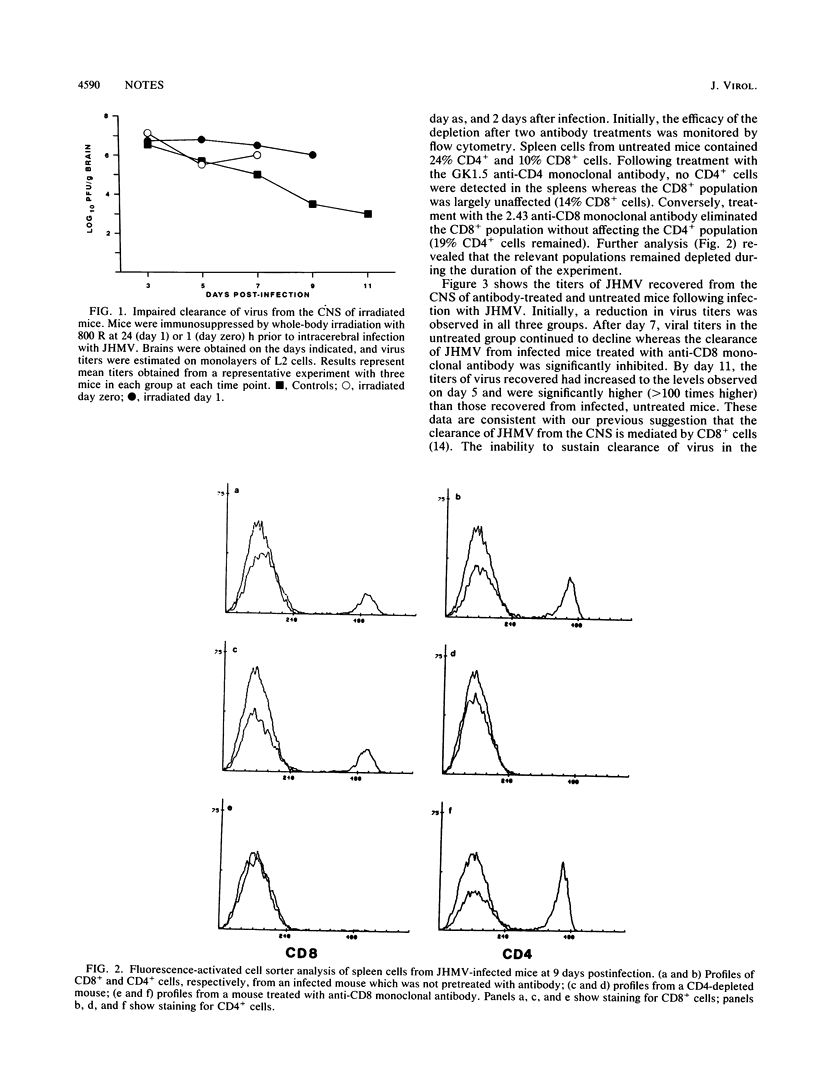
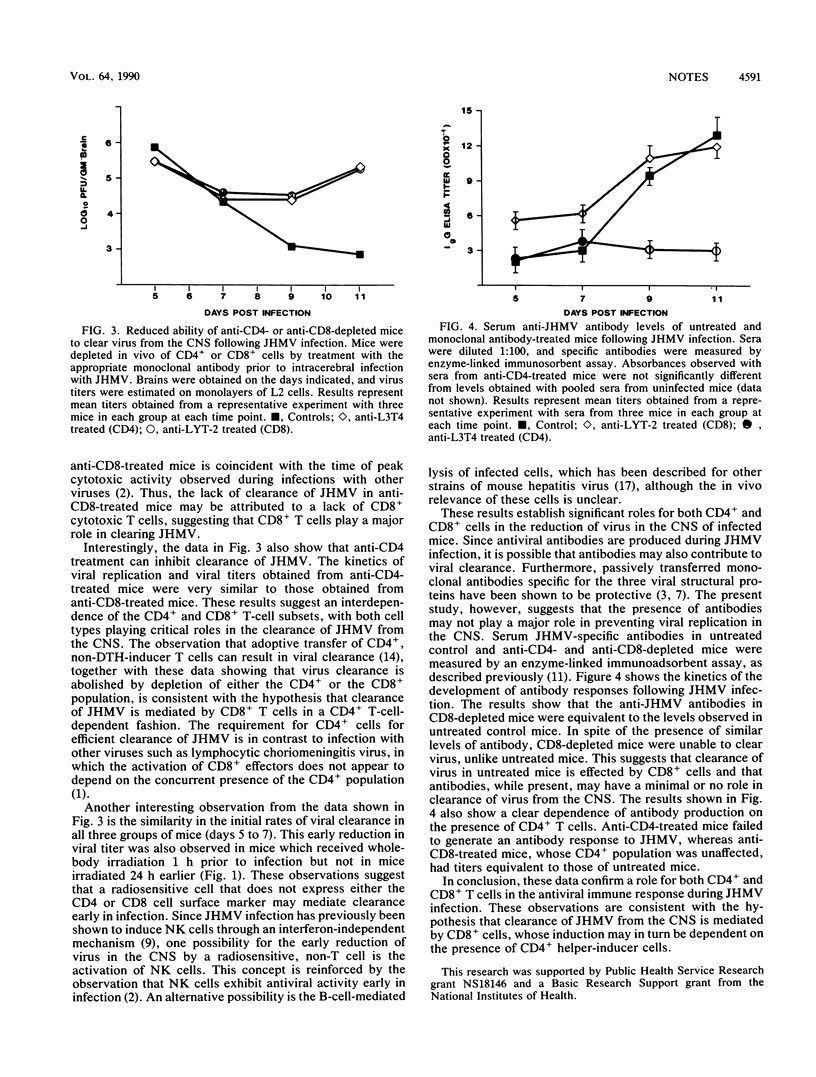
Both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are required for the clearance of virus from the central nervous system following infection with the JHM strain of mouse hepatitis virus. Development of antiviral antibodies requires the presence of CD4+ T cells but appears to play a minimal role in the reduction of virus. The data presented are consistent with the hypothesis that clearance of JHM virus is mediated by virus-specific CD8+ T cells, which appear to require the presence of CD4+ T cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Butler L. D., Bhatti L. T4+ T helper cell function in vivo: differential requirement for induction of antiviral cytotoxic T-cell and antibody responses. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2102–2106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2102-2106.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron C. A., Natuk R. J., Welsh R. M. Generation of large granular T lymphocytes in vivo during viral infection. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2280–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Lewicki H. A., Talbot P. J., Knobler R. L. Murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM)-induced neurologic disease is modulated in vivo by monoclonal antibody. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90033-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich S. S., Matsushima G. K., Stohlman S. A. Studies on the mechanism of protection from acute viral encephalomyelitis by delayed-type hypersensitivity inducer T cell clones. J Neurol Sci. 1989 Apr;90(2):203–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-510X(89)90102-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Dubois-Dalcq M., Haspel M. V., Claysmith A. P., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Selective localization of wild type and mutant mouse hepatitis virus (JHM strain) antigens in CNS tissue by fluorescence, light and electron microscopy. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Mar;1(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Sims J. K., Kniazeff A. J. Mechanism of demyelination in JHM virus encephalomyelitis. Electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1973 Mar 30;24(1):76–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00691421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanaga K., Yamanouchi K., Fujiwara K. Protective effect of monoclonal antibodies on lethal mouse hepatitis virus infection in mice. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):168–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.168-171.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen O., Dugre R., Percy D., Dales S. In vivo and in vitro models of demyelinating disease: endogenous factors influencing demyelinating disease caused by mouse hepatitis virus in rats and mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1248–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1248-1260.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Brayton P. R., Fleming J. O., Weiner L. P., Lai M. M. Murine coronaviruses: isolation and characterization of two plaque morphology variants of the JHM neurotropic strain. J Gen Virol. 1982 Dec;63(2):265–275. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Brayton P. R., Harmon R. C., Stevenson D., Ganges R. G., Matsushima G. K. Natural killer cell activity during mouse hepatitis virus infection: response in the absence of interferon. Int J Cancer. 1983 Mar 15;31(3):309–314. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Matsushima G. K., Casteel N., Weiner L. P. In vivo effects of coronavirus-specific T cell clones: DTH inducer cells prevent a lethal infection but do not inhibit virus replication. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3052–3056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Weiner L. P. Chronic central nervous system demyelination in mice after JHM virus infection. Neurology. 1981 Jan;31(1):38–44. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. A., Fleming J. O., Allen H., Stohlman S. A. Immune mediated clearance of JHM virus from the central nervous system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;218:399–410. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-1280-2_49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman M. A., Shubin R. A., Kyuwa S., Stohlman S. A. T-cell-mediated clearance of mouse hepatitis virus strain JHM from the central nervous system. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3051–3056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3051-3056.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Dörries R., Wege H. Hybridoma antibodies to the murine coronavirus JHM: characterization of epitopes on the peplomer protein (E2). J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):1931–1942. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-1931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P. Pathogenesis of demyelination induced by a mouse hepatitis. Arch Neurol. 1973 May;28(5):298–303. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490230034003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Haspel M. V., Parker D. C., Holmes K. V. Natural cytotoxicity against mouse hepatitis virus-infected cells. II. A cytotoxic effector cell with a B lymphocyte phenotype. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1454–1460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



