Abstract
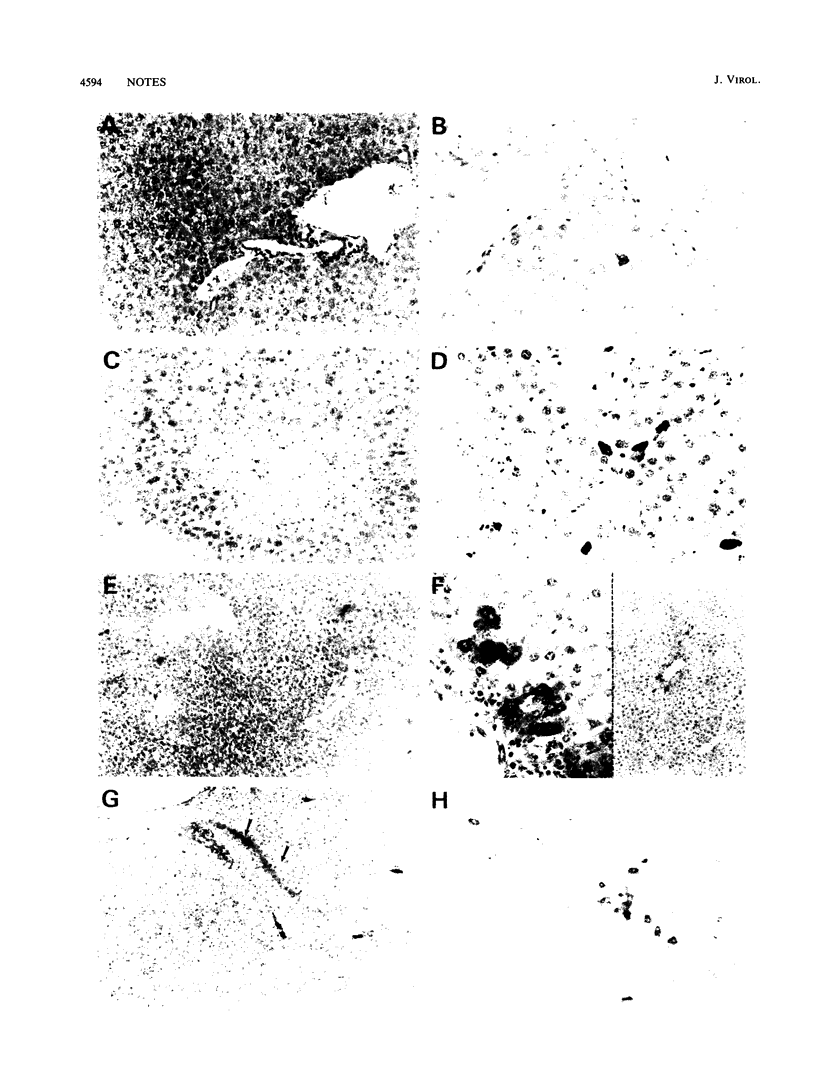
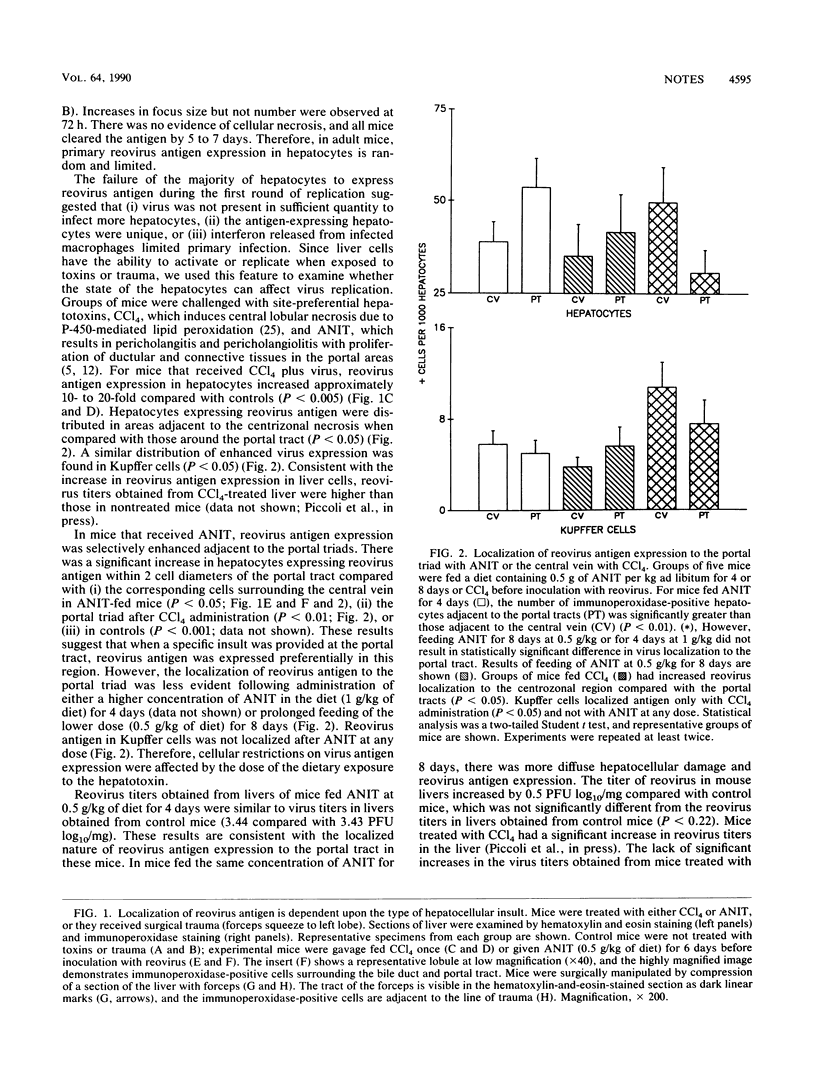
Reovirus type 1 strain Lang is restricted from replicating in adult murine livers. In noninjured livers, approximately 1% of hepatocytes express reovirus antigen during infection. However, hepatocytes can be induced to express reovirus antigen if challenged with either toxins or trauma. We used selective hepatotoxins or surgical trauma to demonstrate that reovirus antigen localization in liver is determined by the site of hepatocellular insult and the timing of the virus inoculum.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BODIAN D. Emerging concept of poliomyelitis infection. Science. 1955 Jul 15;122(3159):105–108. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3159.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangaru B., Morecki R., Glaser J. H., Gartner L. M., Horwitz M. S. Comparative studies of biliary atresia in the human newborn and reovirus-induced cholangitis in weanling mice. Lab Invest. 1980 Nov;43(5):456–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Co M. S., Gaulton G. N., Tominaga A., Homcy C. J., Fields B. N., Greene M. I. Structural similarities between the mammalian beta-adrenergic and reovirus type 3 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5315–5318. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonno R. J., Callahan P. L., Long W. J. Isolation of a monoclonal antibody that blocks attachment of the major group of human rhinoviruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.7-12.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly A. K., Price S. C., Connelly J. C., Hinton R. H. Early changes in bile duct lining cells and hepatocytes in rats treated with alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;93(2):208–219. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(88)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatmaitan B. G., Chason J. L., Lerner A. M. Augmentation of the virulence of murine coxsackie-virus B-3 myocardiopathy by exercise. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1121–1136. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORSTMANN D. M. Acute poliomyelitis relation of physical activity at the time of onset to the course of the disease. J Am Med Assoc. 1950 Jan 28;142(4):236–241. doi: 10.1001/jama.1950.02910220016004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reovirions. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson M. T., Villanove F., Greaves P. Histological demonstration of wheat germ lectin binding sites in the liver of normal and ANIT treated rats. Arch Toxicol. 1986 Jul;59(2):121–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00286735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Genome RNAs and polypeptides of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):726–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.726-733.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepenhoff-Talty M., Lee P. C., Carmody P. J., Barrett H. J., Ogra P. L. Age-dependent rotavirus-enterocyte interactions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Jun;170(2):146–154. doi: 10.3181/00379727-170-41410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Costello T., Witzleben C. L., Greene M. I. Transport of infectious reovirus into bile: class II major histocompatibility antigen-bearing cells determine reovirus transport. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3222–3226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3222-3226.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Eaton M. A., Costello T. Reovirus type 1 is secreted into the bile. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):726–728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.726-728.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Kornstein M. J., Anderson A. O. Reovirus serotype 1 intestinal infection: a novel replicative cycle with ileal disease. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):391–398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.391-398.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H. Reovirus serotype 1 binds to the basolateral membrane of intestinal epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1987 Sep;3(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Weiner H. L. Viral receptors on isolated murine and human ependymal cells. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):419–421. doi: 10.1126/science.6276976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdin E. M., Lynn S. P., Fields B. N., Maratos-Flier E. Uptake of reovirus serotype 1 by the lungs from the bloodstream is mediated by the viral hemagglutinin. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.545-551.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Girard K., Williams W. V., McPhillips T., Rubin D. H. Reovirus type 1 and type 3 differ in their binding to isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jul;5(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Drayna D., Averill D. R., Jr, Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence: role of the S1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]