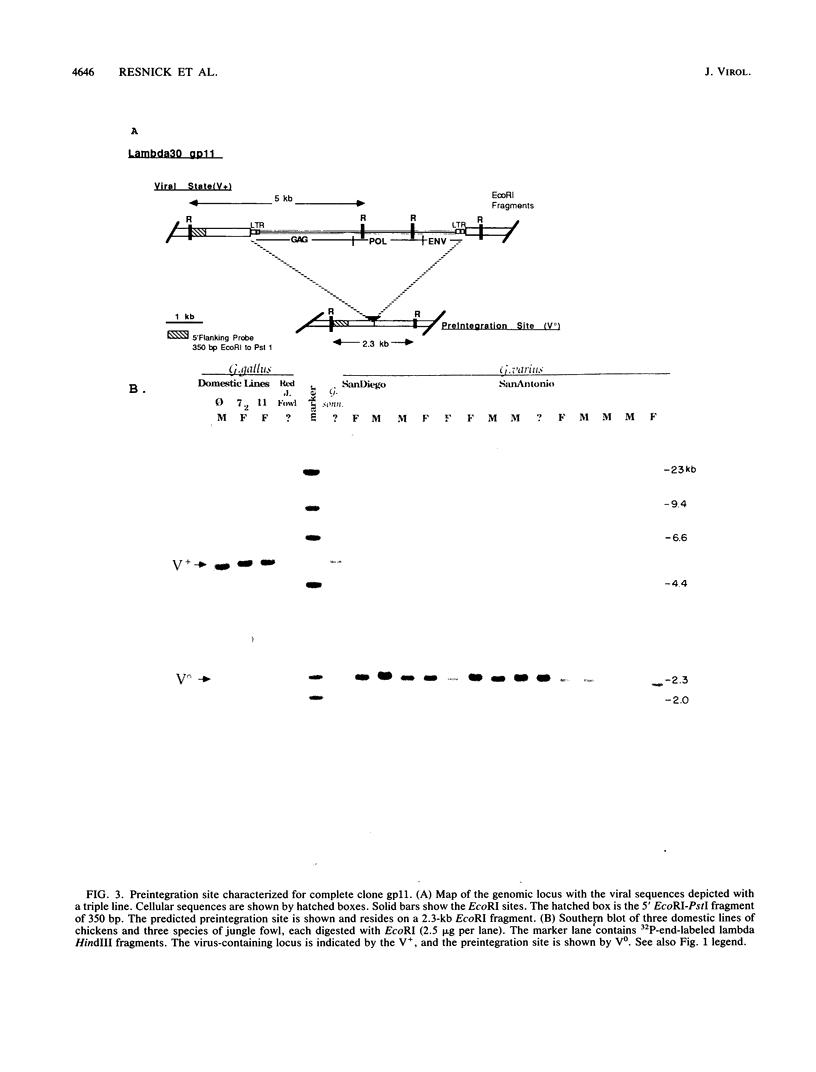
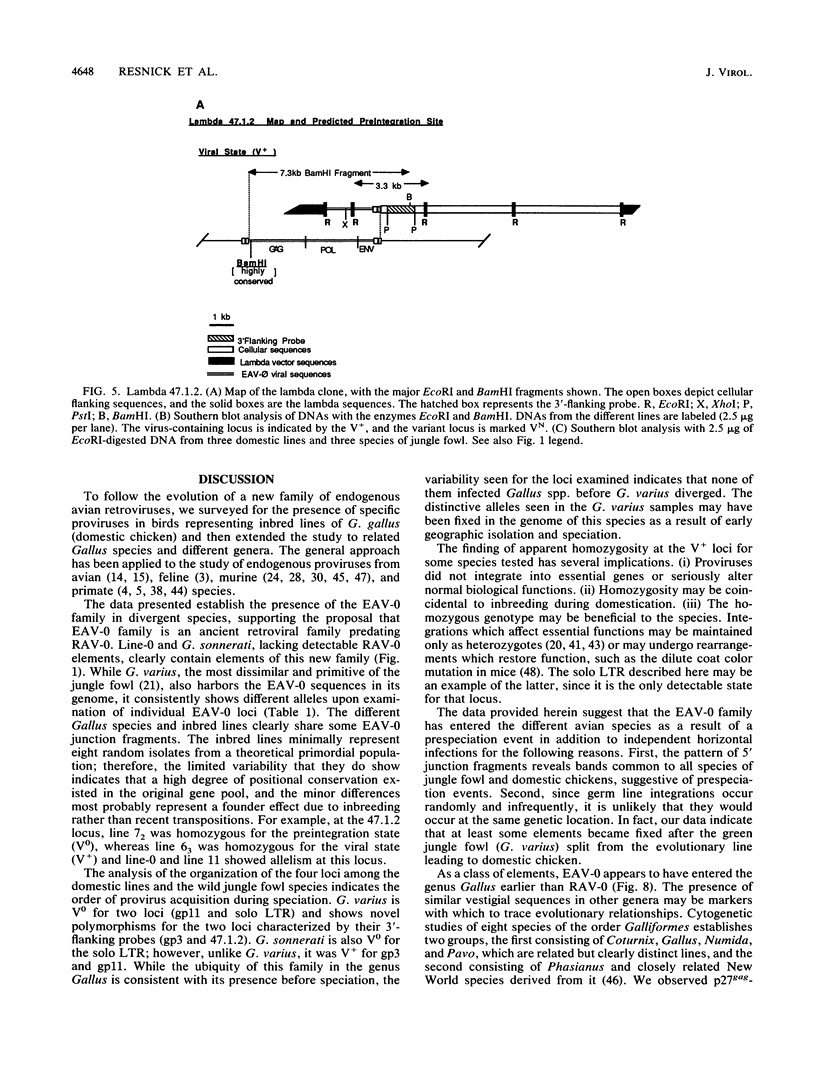
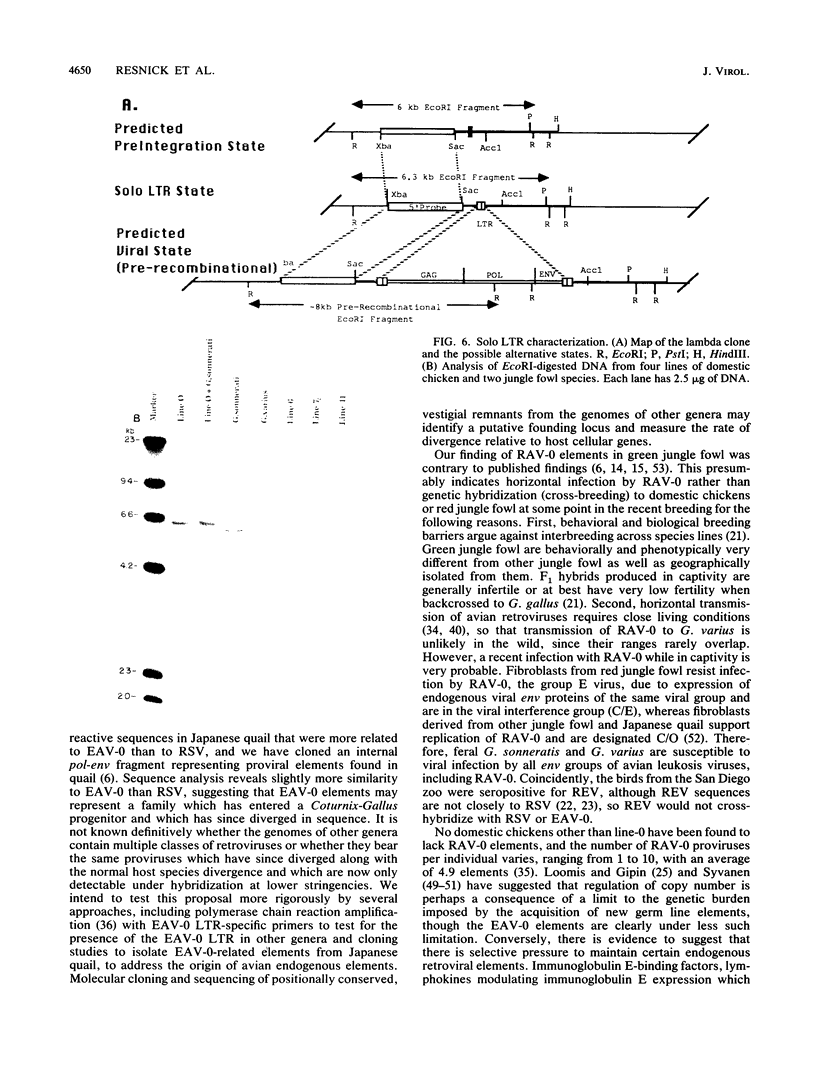
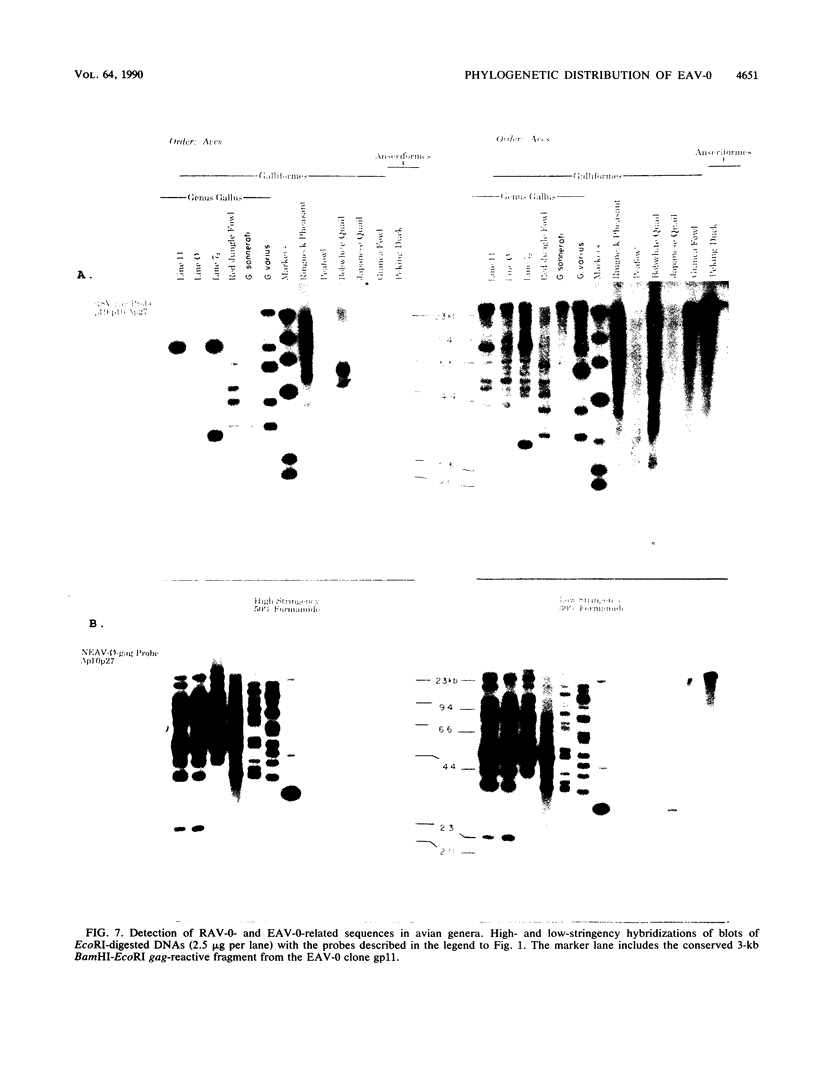
Abstract
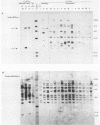
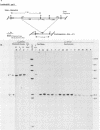
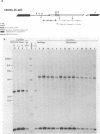
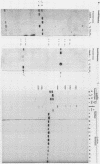
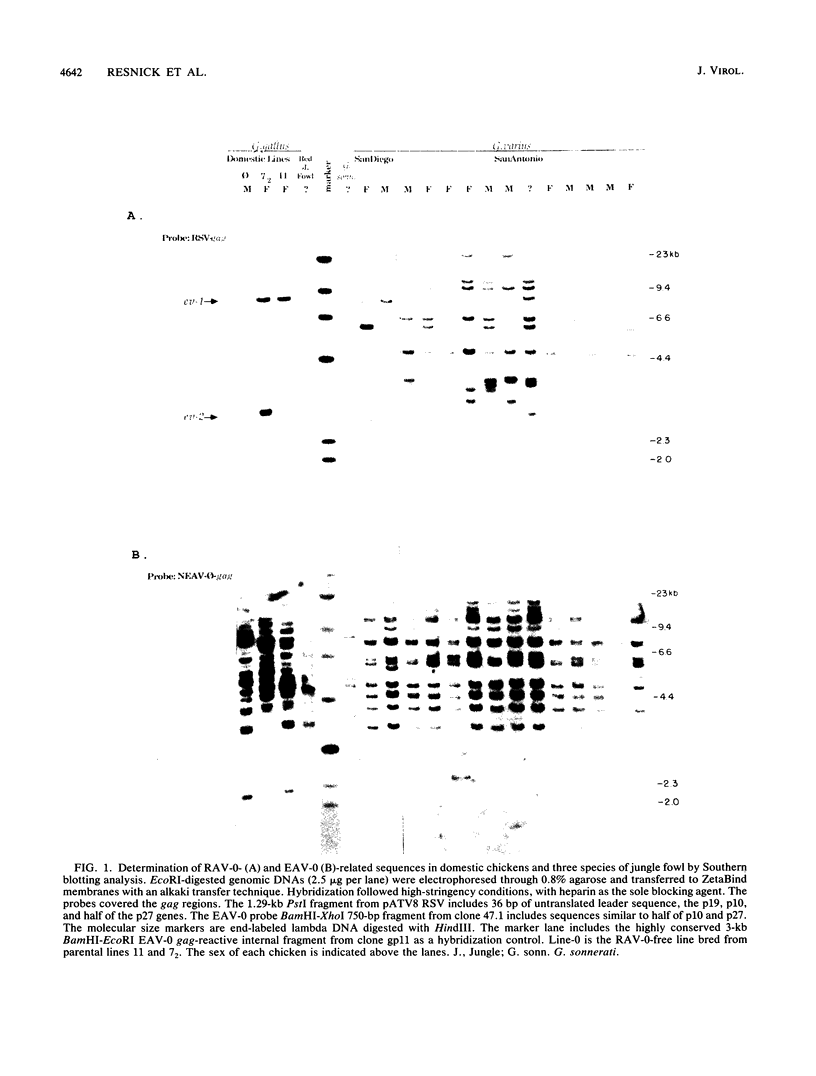
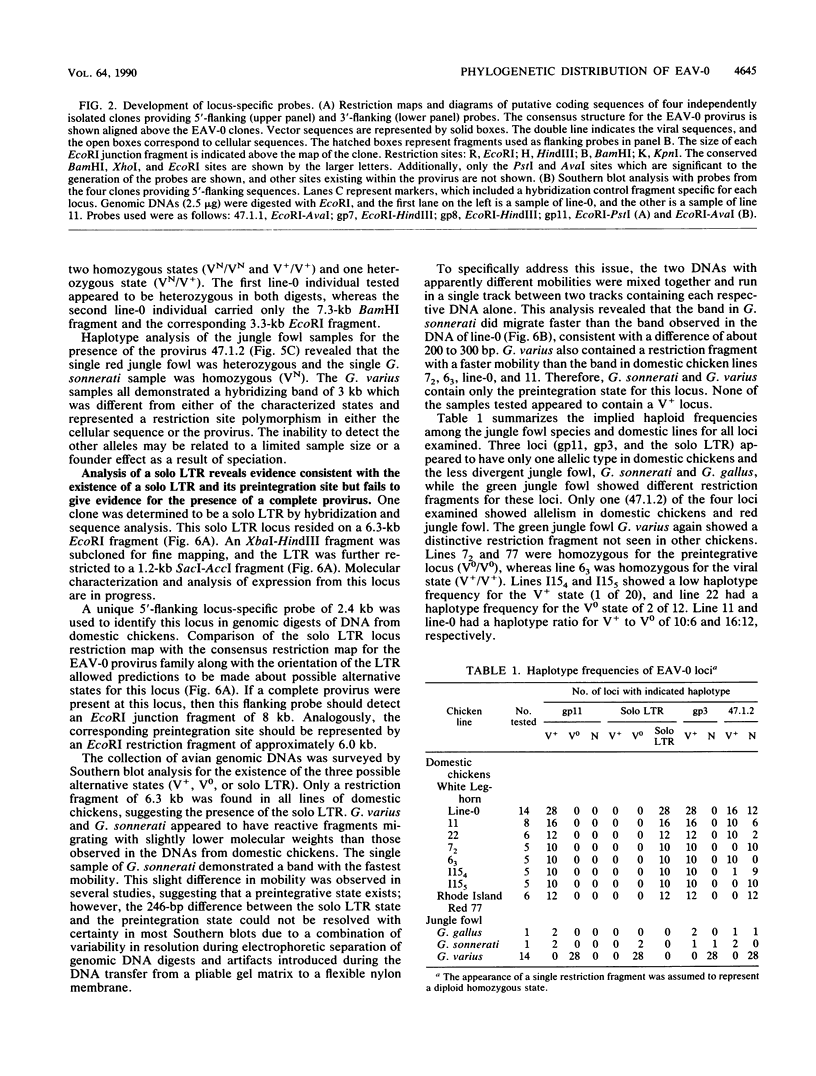
A new family of related endogenous proviruses, existing at 50 to 100 copies per haploid genome and distinguishable by remarkably short long terminal repeats, has been described for domestic chickens (Gallus gallus subsp domesticus). In this communication, by using Southern blot analysis and probes derived from both internal viral sequences and locus-specific, cellular flanking sequences, we studied the genetic distribution of this family of moderately repetitive avian endogenous retroviruses within the genomes of four Gallus species. Eight inbred lines of domestic chickens, the evolutionary progenitor to the domestic chicken (red jungle fowl), and two more distantly related species (grey and green jungle fowl) were studied. All Gallus species harbored this class of elements, although the different lines of domestic chickens and different species of jungle fowl bore distinguishable complements of the proviral loci. Jungle fowl appeared to have fewer copies than domestic chickens. For three randomly isolated proviral loci, domestic chickens (G. gallus subsp. domesticus) and red jungle fowl (G. gallus subsp. gallus) showed only a proviral state, whereas the most primitive and divergent of the jungle fowl, the green jungle fowl (G. varius), consistently demonstrated only preintegration states or disparate alleles. The presence of this family in all Gallus species and of related sequences in other genera suggests that a primordial founding integration event occurred prior to the evolutionary separation of Gallus species and possibly related genera. Additionally, at least one proviral locus has been acquired subsequent to speciation, indicating that this family was actively infectious after the primary founding event. This conserved, repetitive proviral family appears to represent the vestigial remnant of an avian retrovirus class related to and evolutionarily more ancient than the Rous-associated virus-0 family of avian endogenous retroviruses.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astrin S. M., Buss E. G., Haywards W. S. Endogenous viral genes are non-essential in the chicken. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):339–341. doi: 10.1038/282339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon L. D., Smith E., Crittenden L. B., Havenstein G. B. Association of the slow feathering (K) and an endogenous viral (ev21) gene on the Z chromosome of chickens. Poult Sci. 1988 Feb;67(2):191–197. doi: 10.3382/ps.0670191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Evolution of type C viral genes: origin of feline leukemia virus. Science. 1975 Nov 28;190(4217):886–888. doi: 10.1126/science.52892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of C-type viral genes: inheritance of exogenously acquired viral genes. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):456–459. doi: 10.1038/252456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of type C viral genes: evidence for an Asian origin of man. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):101–108. doi: 10.1038/261101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce-Jacino M. T., Resnick R., Faras A. J. Structural and functional characterization of the unusually short long terminal repeats and their adjacent regions of a novel endogenous avian retrovirus. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. A., Cywinski A., Chen P. J., Taylor J. M. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus-related sequences in the Japanese quail. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.354-362.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernov M. V., Gudkov A. V., Obukh I. B. Variations of endogenous chicken proviruses: characterization of new loci of endogenous proviruses in the genome of Italian partridge chickens. Folia Biol (Praha) 1984;30(5):342–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernov M. V., Tikhonenko A. T., Zaitsevskaia T. E., Denisova R. A., Obukh I. B. V genome kur, svobodnykh ot éndogennykh provirusov leikozo-sarkomnogo kompleksa ptits, prisutstvuiu posledovatel'nosti, otdalenno rodstvennye virusu sarcomy Rausa. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1987 Mar;(3):6–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., McMahon S., Halpern M. S., Fadly A. M. Embryonic infection with the endogenous avian leukosis virus Rous-associated virus-0 alters responses to exogenous avian leukosis virus infection. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):722–725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.722-725.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden L. B., Witter R. L., Fadly A. M. Low incidence of lymphoid tumors in chickens continuously producing endogenous virus. Avian Dis. 1979 Jul-Sep;23(3):646–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie C. T., Resnick R., Boyce-Jacino M., Alegre J. N., Faras A. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of gag-, pol-, and env-related gene sequences in the ev- chicken. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):669–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.669-675.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie C., Faras A. J. Presence of retrovirus reverse transcriptase-related gene sequences in avian cells lacking endogenous avian leukosis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5097–5101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisby D. P., Weiss R. A., Roussel M., Stehelin D. The distribution of endogenous chicken retrovirus sequences in the DNA of galliform birds does not coincide with avian phylogenetic relationships. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Israel M. A., Law M. F., Martin M. A. A rapid method for detecting and mapping homology between heterologous DNAs. Evaluation of polyomavirus genomes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4876–4883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Payvar F., Spector D., Schimke R. T., Robinson H. L., Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Heterogeneity of genetic loci in chickens: analysis of endogenous viral and nonviral genes by cleavage of DNA with restriction endonucleases. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):347–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Toyoshima K., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Organization of the endogenous proviruses of chickens: implications for origin and expression. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):189–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90538-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Vogt P. K., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Endogenous proviruses of random-bred chickens and ring-necked pheasants: analysis with restriction endonucleases. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90540-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Harbers K., Schnieke A., Löhler J., Chumakov I., Jähner D., Grotkopp D., Hoffmann E. Germline integration of moloney murine leukemia virus at the Mov13 locus leads to recessive lethal mutation and early embryonic death. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90511-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Temin H. M. Lack of sequence homology among RNAs of avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses, reticuloendotheliosis viruses, and chicken endogenous RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1314–1324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1314-1324.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Temin H. M. Reticuloendotheliosis virus nucleic acid sequences in cellular DNA. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1179–1188. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1179-1188.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. R., Horowitz J. M., Risser R. Nucleotide conservation of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia proviruses in inbred mice: implications for viral origin and dispersal. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90298-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Gilpin M. E. Multigene families and vestigial sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2143–2147. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., Jardieu P., Mietz J. A., Trounstine M. L., Kuff E. L., Ishizaka K., Martens C. L. Rodent IgE-binding factor genes are members of an endogenous, retrovirus-like gene family. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4283–4290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris V. L., Medeiros E., Ringold G. M., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Comparison of mouse mammary tumor virus-specific DNA in inbred, wild and Asian mice, and in tumors and normal organs from inbred mice. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):73–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motta J. V., Crittenden L. B., Purchase H. G., Stone H. A., Witter R. L. Low oncogenic potential of avian endogenous RNA tumor virus infection or expression. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Sep;55(3):685–689. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.3.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata M. M., Khan A. S. Structure, distribution, and expression of an ancient murine endogenous retroviruslike DNA family. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4381–4386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4381-4386.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Astrin S. M., Senior A. M., Salazar F. H. Host Susceptibility to endogenous viruses: defective, glycoprotein-expressing proviruses interfere with infections. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):745–751. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.745-751.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Eisenman R. N. New findings on the congenital transmission of avian leukosis viruses. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):417–419. doi: 10.1126/science.6330893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovigatti U. G., Astrin S. M. Avian endogenous viral genes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;103:1–21. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68943-7_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Hughes S. H., Varmus H. E. Restriction endonuclease mapping of the DNA of Rous-associated virus O reveals extensive homology in structure and sequence with avian sarcoma virus DNA. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90537-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih A., Misra R., Rush M. G. Detection of multiple, novel reverse transcriptase coding sequences in human nucleic acids: relation to primate retroviruses. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):64–75. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.64-75.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Jones K. W. The use of heparin as a simple cost-effective means of controlling background in nucleic acid hybridization procedures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5627–5638. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. J., Salter D. W., Silva R. F., Crittenden L. B. Selective shedding and congenital transmission of endogenous avian leukosis viruses. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1050–1054. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1050-1054.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Gridley T., Jaenisch R. Retroviruses and insertional mutagenesis in mice: proviral integration at the Mov 34 locus leads to early embryonic death. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):366–375. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence S. E., Gilbert D. J., Swing D. A., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Spontaneous germ line virus infection and retroviral insertional mutagenesis in eighteen transgenic Srev lines of mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):177–184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele P. E., Martin M. A., Rabson A. B., Bryan T., O'Brien S. J. Amplification and chromosomal dispersion of human endogenous retroviral sequences. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):545–550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.545-550.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Bird S., Weinberg R. A. Evidence for the Asiatic origin of endogenous AKR-type murine leukemia proviruses. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):824–835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.824-835.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A. D., Bunch T. D. The evolutionary implications of chromosome banding pattern homologies in the bird order Galliformes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1982;34(1-2):136–148. doi: 10.1159/000131802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. The four classes of endogenous murine leukemia virus: structural relationships and potential for recombination. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2659–2669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2659-2669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Fenner S., Greenoak G. E., Moran C., Coffin J. M. Role of endogenous retroviruses as mutagens: the hairless mutation of mice. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90201-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen M. Cross-species gene transfer; implications for a new theory of evolution. J Theor Biol. 1985 Jan 21;112(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(85)80291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen M. Molecular clocks and evolutionary relationships: possible distortions due to horizontal gene flow. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(1-2):16–23. doi: 10.1007/BF02111278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen M. The evolutionary implications of mobile genetic elements. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:271–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Biggs P. M. Leukosis and Marek's disease viruses of feral red jungle flow and domestic fowl in Malaya. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Dec;49(6):1713–1725. doi: 10.1093/jnci/49.6.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L. A simple method to recover intact high molecular weight RNA and DNA after electrophoretic separation in low gelling temperature agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemiecki A., Krömer G., Mueller R. G., Hàla K., Wick G. ev 22, a new endogenous avian leukosis virus locus found in chickens with spontaneous autoimmune thyroiditis. Arch Virol. 1988;100(3-4):267–271. doi: 10.1007/BF01487689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]