Abstract
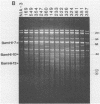
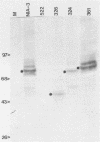
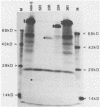
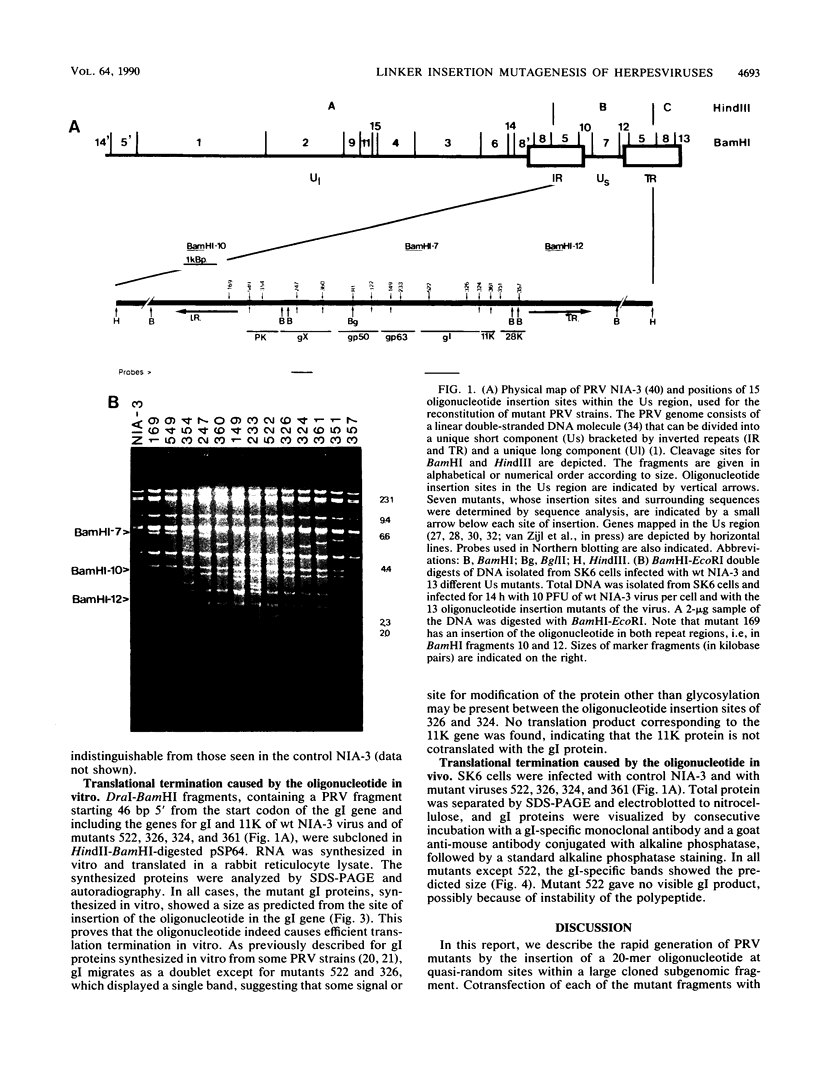
We describe a technique for the systematic inactivation of nonessential genes within the genome of a herpesvirus without the requirement for phenotypic selection. This technique is based on the insertion of an oligonucleotide containing translational stop codons at a random site within a large cloned viral DNA fragment. Mutant virus is then reconstituted by cotransfection with overlapping viral clones, together comprising the entire viral genome, as described previously (M. van Zijl, W. Quint, J. Briaire, T. de Rover, A. Gielkens, and A. Berns, J. Virol. 62:2191-2195, 1988). This technique was used to construct, in a single experiment, a set of 13 viable pseudorabies virus strains with oligonucleotide insertions within all known genes of the Us region except for the gp50 gene, which proved essential for virus growth in cell culture. The growth rate in porcine kidney cells of mutants of all nonessential Us genes was similar to that of the parental virus, with the exception of a mutant of the recently identified protein kinase gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., DeMarchi J., Pendrys J., Veach R. A., Kaplan A. S. Proteins specified by the short unique region of the genome of pseudorabies virus play a role in the release of virions from certain cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):191–196. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.191-196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Porat T., Rixon F. J., Blankenship M. L. Analysis of the structure of the genome of pseudorabies virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90484-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Z., Person S., DebRoy C., Gu B. H. Functional regions and structural features of the gB glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1. An analysis of linker insertion mutants. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):575–588. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90639-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activities of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) ICP4 genes specifying nonsense peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4491–4511. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Purves F. C., McGeoch D. J., Marsden H. S., Leader D. P. Identification of the herpes simplex virus protein kinase as the product of viral gene US3. J Gen Virol. 1987 Oct;68(Pt 10):2699–2704. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-10-2699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gielkens A. L., Van Oirschot J. T., Berns A. J. Genome differences among field isolates and vaccine strains of pseudorabies virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jan;66(Pt 1):69–82. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. An ICP6::lacZ insertional mutagen is used to demonstrate that the UL52 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 is required for virus growth and DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2970–2977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2970-2977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland J., Brown S. M. Generation of a herpes simplex virus type 2 variant devoid of XbaI sites: removal of the 0.91 map coordinate site results in impaired synthesis of glycoprotein G-2. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):113–124. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander S. L., Sutherland S. L., Gage P. J., Johnson D. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies specific for herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D inhibit virus penetration. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3356–3364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3356-3364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Ligas M. W. Herpes simplex viruses lacking glycoprotein D are unable to inhibit virus penetration: quantitative evidence for virus-specific cell surface receptors. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4605–4612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4605-4612.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. M., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D mediates interference with herpes simplex virus infection. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):819–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.819-827.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor Q. S., Chinnadurai G. Method for introducing site-specific mutations into adenovirus 2 genome: construction of a small deletion mutant in VA-RNAI gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2184–2188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligas M. W., Johnson D. C. A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1486–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1486-1494.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Kaplan A. S., Ben-Porat T. Multiple defects in the genome of pseudorabies virus can affect virulence without detectably affecting replication in cell culture. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Clustering of genes dispensable for growth in culture in the S component of the HSV-1 genome. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.3033823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S., Easterday B. C., Kaplan A. S., Ben-Porat T. Vaccination of swine with thymidine kinase-deficient mutants of pseudorabies virus. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jul;46(7):1494–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Lomniczi B., Sugg N., Schreurs C., Ben-Porat T. Host cell-specific growth advantage of pseudorabies virus with a deletion in the genome sequences encoding a structural glycoprotein. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):12–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.12-19.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Thiel H. J., Rziha H. J. Variability of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein I expression. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Zuckermann F., Ben-Porat T., Kaplan A. S. Role of glycoprotein gIII of pseudorabies virus in virulence. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2712–2717. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2712-2717.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Zuckermann F., Ben-Porat T. Role of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gI in virus release from infected cells. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2764–2769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2764-2769.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Zsak L., Kaplan A. S., Ben-Porat T., Lomniczi B. Role of a structural glycoprotein of pseudorabies in virus virulence. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):4030–4032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.4030-4032.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C. Conversion of circular DNA to linear strands for mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):415–426. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Meyer A. L., Post L. E. Reduced yield of infectious pseudorabies virus and herpes simplex virus from cell lines producing viral glycoprotein gp50. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2196–2199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2196-2199.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Post L. E. A small open reading frame in pseudorabies virus and implications for evolutionary relationships between herpesviruses. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):193–195. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90368-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Armentrout M. A., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. DNA sequence of the gene for pseudorabies virus gp50, a glycoprotein without N-linked glycosylation. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):216–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.216-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Gierman T. M., Post L. E. Deletions in vaccine strains of pseudorabies virus and their effect on synthesis of glycoprotein gp63. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1166–1169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1166-1169.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrovskis E. A., Timmins J. G., Post L. E. Use of lambda gt11 to isolate genes for two pseudorabies virus glycoproteins with homology to herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):185–193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.185-193.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Longnecker R. M., Leader D. P., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 protein kinase is encoded by open reading frame US3 which is not essential for virus growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2896–2901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2896-2901.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea T. J., Timmins J. G., Long G. W., Post L. E. Mapping and sequence of the gene for the pseudorabies virus glycoprotein which accumulates in the medium of infected cells. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):21–29. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.21-29.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Jenkins F. J. Genetic engineering of novel genomes of large DNA viruses. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1208–1214. doi: 10.1126/science.2994215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Kaplan A. S. Electron microscopic studies of the DNA of defective and standard pseudorabies virions. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90211-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Analysis of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein gIII localization and modification by using novel infectious viral mutants carrying unique EcoRI sites. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2962–2972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2962-2972.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Berns A. Proviral activation of the putative oncogene Pim-1 in MuLV induced T-cell lymphomas. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1793–1798. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. C., Atkinson T., Smith M., Pawson T. Identification of functional regions in the transforming protein of Fujinami sarcoma virus by in-phase insertion mutagenesis. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. Replication and virulence of pseudorabies virus mutants lacking glycoprotein gX. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):229–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.229-232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Wathen L. M. Isolation, characterization, and physical mapping of a pseudorabies virus mutant containing antigenically altered gp50. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):57–62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.57-62.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Rapid identification of nonessential genes of herpes simplex virus type 1 by Tn5 mutagenesis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):576–579. doi: 10.1126/science.3033824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann F. A., Mettenleiter T. C., Schreurs C., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Complex between glycoproteins gI and gp63 of pseudorabies virus: its effect on virus replication. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4622–4626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4622-4626.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zijl M., Quint W., Briaire J., de Rover T., Gielkens A., Berns A. Regeneration of herpesviruses from molecularly cloned subgenomic fragments. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2191–2195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2191-2195.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]