Abstract
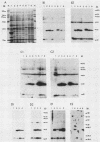
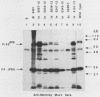
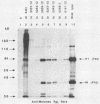
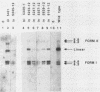
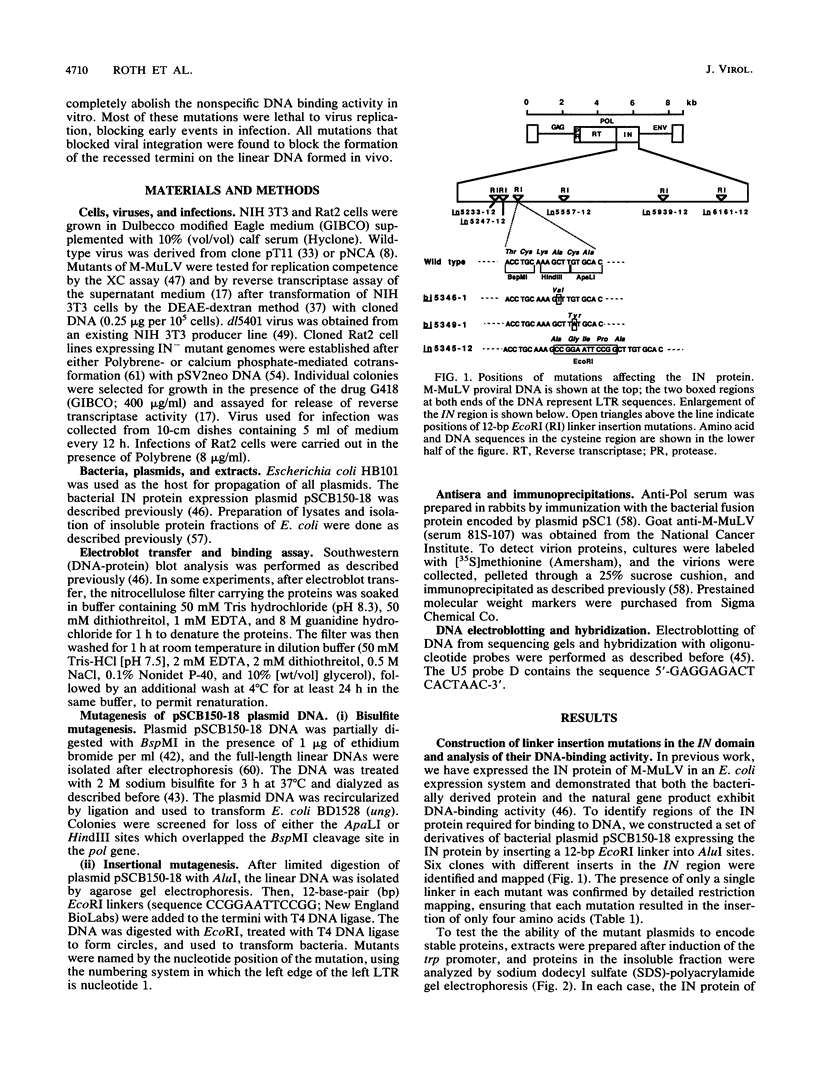
The 3' terminus of the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus encodes the integration (IN) protein, required for the establishment of the integrated provirus. A series of six linker insertion mutations and two single-base substitutions were generated within the region encoding the IN protein. Mutations were initially generated within an Escherichia coli plasmid expressing the IN protein, and the resulting variants were assayed for DNA-binding activity. Mutations which altered conserved cysteine residues within a potential DNA finger-binding motif resulted in lower or variable DNA binding, which appeared to be the result of variable protein folding. Upon renaturation, these proteins were able to nonspecifically bind DNA in a manner similar to that of the other mutant IN proteins and the parent. When reconstructed back into full-length virus, seven of the eight mutations were lethal. All mutants produced a stable IN protein in virions and mediated normal conversion of the retroviral RNA to its three DNA forms. Fine-structure analysis of the linear double-stranded viral DNA indicated that all seven lethal alterations within the IN protein blocked the formation of the 3' recessed termini that normally precedes integration.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. M. Zinc fingers and other metal-binding domains. Elements for interactions between macromolecules. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6513–6516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowerman B., Brown P. O., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. A nucleoprotein complex mediates the integration of retroviral DNA. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):469–478. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Horwitz M. S. Dissection of functional domains of adenovirus DNA polymerase by linker-insertion mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6116–6120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobrinik D., Katz R., Terry R., Skalka A. M., Leis J. Avian sarcoma and leukosis virus pol-endonuclease recognition of the tandem long terminal repeat junction: minimum site required for cleavage is also required for viral growth. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1999–2008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1999-2008.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Mutants and pseudorevertants of Moloney murine leukemia virus with alterations at the integration site. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):573–580. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90114-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., McClements W. L., Enquist L. W., Vande Woude G. F. Nucleotide sequences of integrated Moloney sarcoma provirus long terminal repeats and their host and viral junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3937–3941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A. Analysis of mutant Moloney murine leukemia viruses containing linker insertion mutations in the 3' region of pol. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3958–3964. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3958-3964.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Varmus H. E. A mutant murine leukemia virus with a single missense codon in pol is defective in a function affecting integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6461–6465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyk G., Leis J., Longiaru M., Skalka A. M. Selective cleavage in the avian retroviral long terminal repeat sequence by the endonuclease associated with the alpha beta form of avian reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6745–6749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyk G., Longiaru M., Cobrinik D., Kowal R., deHaseth P., Skalka A. M., Leis J. Circles with two tandem long terminal repeats are specifically cleaved by pol gene-associated endonuclease from avian sarcoma and leukosis viruses: nucleotide sequences required for site-specific cleavage. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):589–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.589-599.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Mason W. S., Linial M. Synthesis and processing of polymerase proteins of wild-type and mutant avian retroviruses. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):62–78. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.62-78.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Integration of mini-retroviral DNA: a cell-free reaction for biochemical analysis of retroviral integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3065–3069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golomb M., Grandgenett D. P. Endonuclease activity of purified RNA-directed DNA polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1606–1613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golomb M., Grandgenett D. P., Mason W. Virus-coded DNA endonuclease from avian retrovirus. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):548–555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.548-555.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Golomb M., Vora A. C. Activation of an Mg2+-dependent DNA endonuclease of avian myeloblastosis virus alpha beta DNA polymerase by in vitro proteolytic cleavage. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):264–271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.264-271.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Mumm S. R. Unraveling retrovirus integration. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90707-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C., Schiff R. D. A 32,000-dalton nucleic acid-binding protein from avian retravirus cores possesses DNA endonuclease activity. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C., Swanstrom R., Olsen J. C. Nuclease mechanism of the avian retrovirus pp32 endonuclease. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):970–974. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.970-974.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Mutschler A., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. A Rous sarcoma virus provirus is flanked by short direct repeats of a cellular DNA sequence present in only one copy prior to integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4299–4303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Shank P. R., Spector D. H., Kung H. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Vogt P. K., Breitman M. L. Proviruses of avian sarcoma virus are terminally redundant, co-extensive with unintegrated linear DNA and integrated at many sites. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1397–1410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. S., McClure M. A., Feng D. F., Gray J., Doolittle R. F. Computer analysis of retroviral pol genes: assignment of enzymatic functions to specific sequences and homologies with nonviral enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7648–7652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopchick J. J., Jamjoom G. A., Watson K. F., Arlinghaus R. B. Biosynthesis of reverse transcriptase from Rauscher murine leukemia virus by synthesis and cleavage of a gag-pol read-through viral precursor polyprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopchick J. J., Karshin W. L., Arlinghaus R. B. Tryptic peptide analysis of gag and gag-pol gene products of Rauscher murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):610–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.610-623.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. A., Springhorn S. S. Renaturation of enzymes after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7467–7473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. A., Prasad V., Tsichlis P. N. Splice acceptor site for the env message of Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):2038–2041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.2038-2041.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Duyk G., Johnson S., Longiaru M., Skalka A. Mechanism of action of the endonuclease associated with the alpha beta and beta beta forms of avian RNA tumor virus reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):727–739. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.727-739.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobel L. I., Goff S. P. Construction of mutants of Moloney murine leukemia virus by suppressor-linker insertional mutagenesis: positions of viable insertion mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4149–4153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk K. C., Gilmore T. D., Panganiban A. T. The spleen necrosis virus int gene product expressed in Escherichia coli has DNA binding activity and mediates att and U5-specific DNA multimer formation in vitro. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyman S. D., Rohrschneider L. R. Analysis of functional domains of the v-fms-encoded protein of Susan McDonough strain feline sarcoma virus by linker insertion mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3287–3296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miskimins W. K., Roberts M. P., McClelland A., Ruddle F. H. Use of a protein-blotting procedure and a specific DNA probe to identify nuclear proteins that recognize the promoter region of the transferrin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6741–6744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Grandgenett D. P., Parsons J. T. Avian retrovirus pp32 DNA-binding protein. I. Recognition of specific sequences on retrovirus DNA terminal repeats. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):330–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.330-343.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T. Retroviral DNA integration. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The retrovirus pol gene encodes a product required for DNA integration: identification of a retrovirus int locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Watson R. M., Vinograd J. Mapping of closed circular DNAs by cleavage with restriction endonucleases and calibration by agarose gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):851–855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Nathans D. Local mutagenesis within deletion loops of DNA heteroduplexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7214–7217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. P., Grandgenett D. P. Genetic evidence that the avian retrovirus DNA endonuclease domain of pol is necessary for viral integration. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2307–2312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2307-2312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Schwartzberg P. L., Goff S. P. Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Tanese N., Goff S. P. Gene product of Moloney murine leukemia virus required for proviral integration is a DNA-binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff R. D., Grandgenett D. P. Virus-coded origin of a 32,000-dalton protein from avian retrovirus cores: structural relatedness of p32 and the beta polypeptide of the avian retrovirus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):279–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.279-291.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Construction and analysis of deletion mutations in the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: a new viral function required for productive infection. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Sequence of retrovirus provirus resembles that of bacterial transposable elements. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):550–554. doi: 10.1038/285550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker C., Goff S., Gilboa E., Paskind M., Mitra S. W., Baltimore D. Structure of a cloned circular Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA molecule containing an inverted segment: implications for retrovirus integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3932–3936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker C., Hoffman J., Goff S. P., Baltimore D. Intramolecular integration within Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):164–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.164-172.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., DeLorbe W. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of cloned unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: viral DNA contains direct and inverted repeats similar to those in transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):124–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Goff S. P. Domain structure of the Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase: mutational analysis and separate expression of the DNA polymerase and RNase H activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Roth M. J., Goff S. P. Analysis of retroviral pol gene products with antisera raised against fusion proteins produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):328–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.328-340.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Roth M., Goff S. P. Expression of enzymatically active reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4944–4948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R., Soltis D. A., Katzman M., Cobrinik D., Leis J., Skalka A. M. Properties of avian sarcoma-leukosis virus pp32-related pol-endonucleases produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2358–2365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2358-2365.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]