Abstract
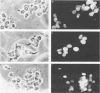
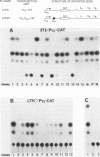
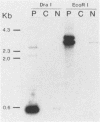
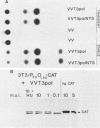
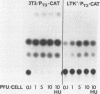
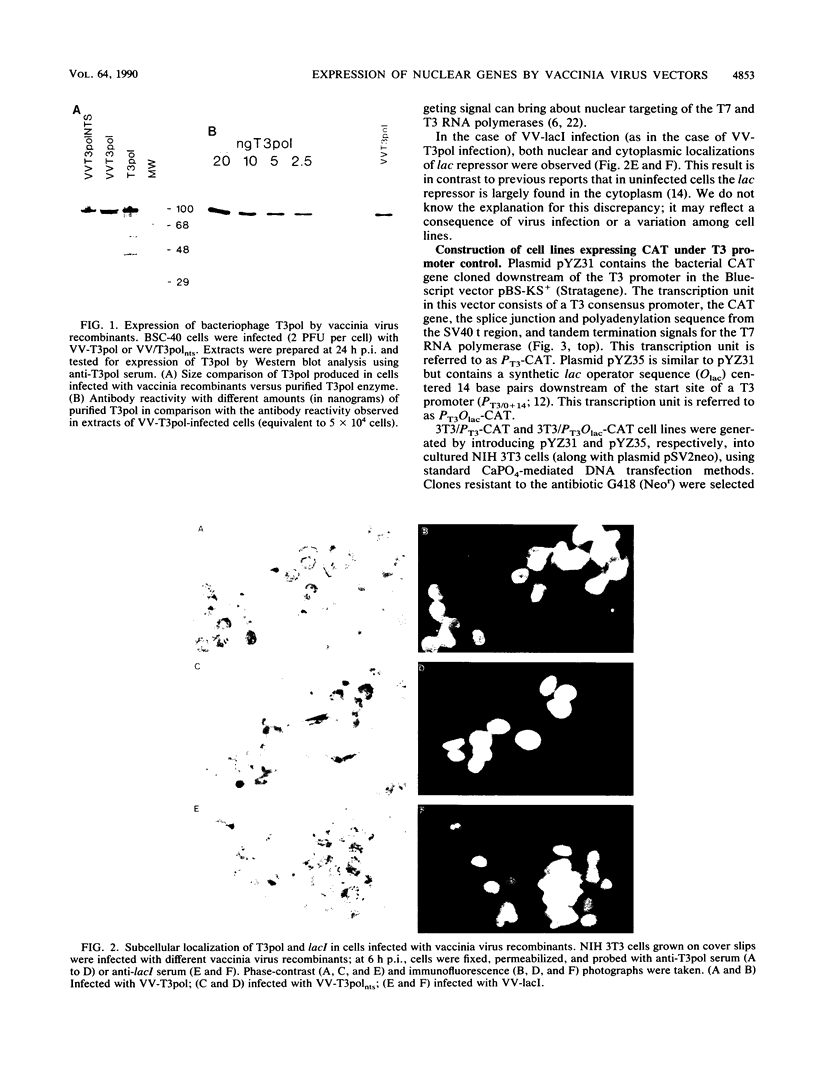
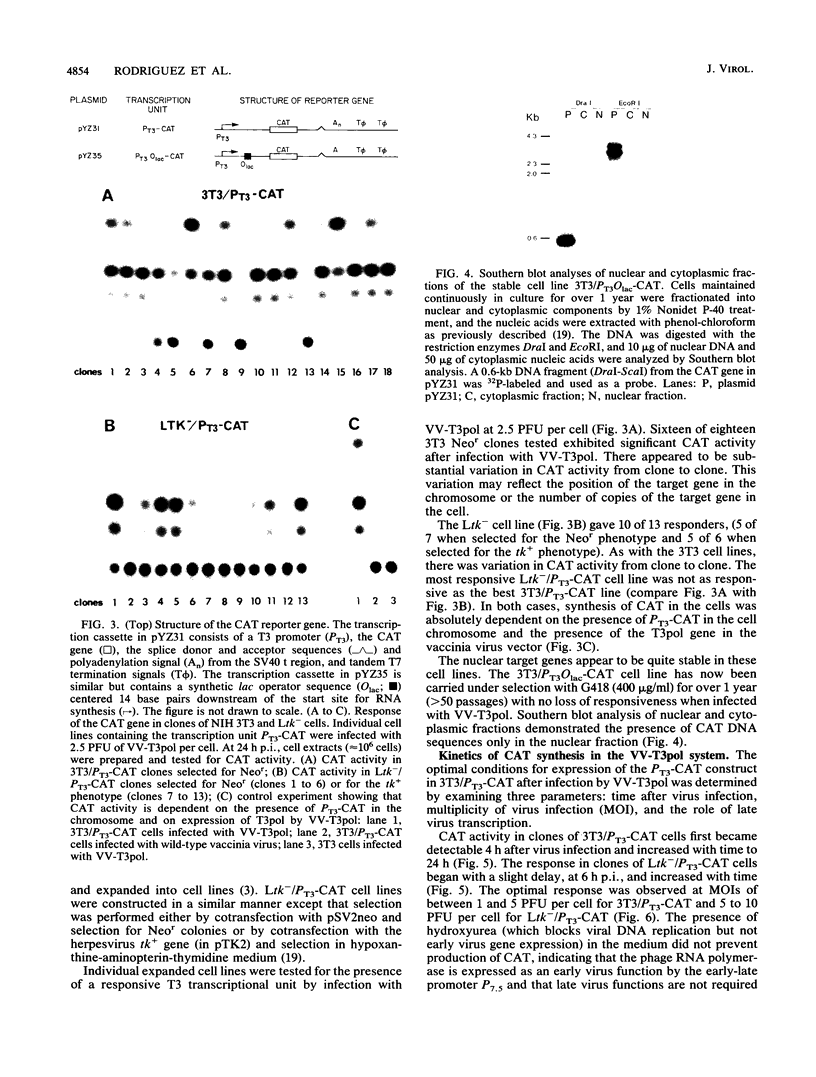
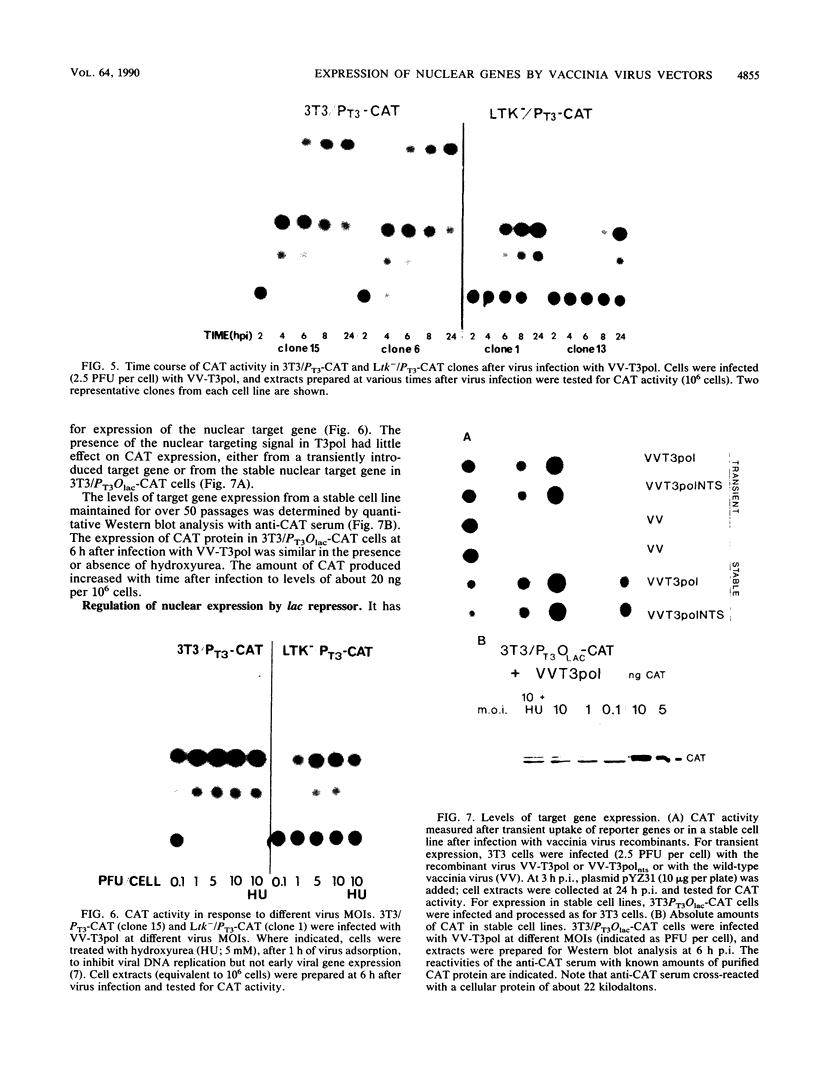
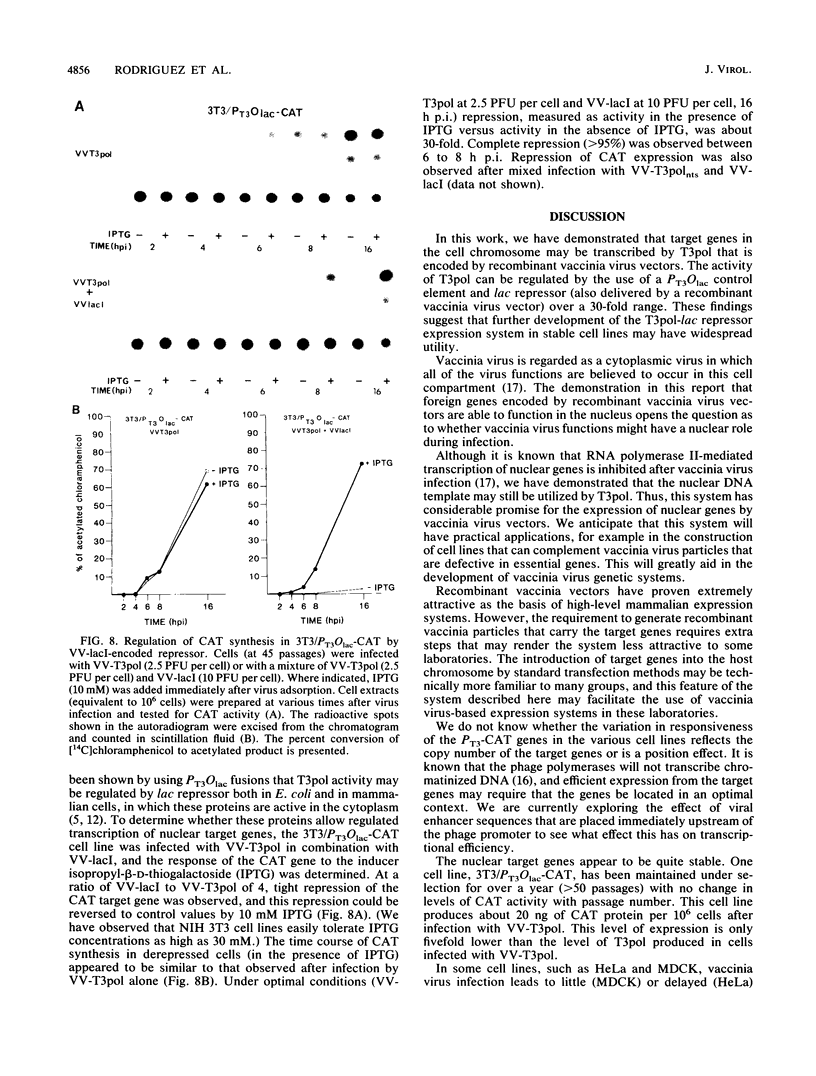
Recombinant vaccinia viruses that express the bacteriophage T3 RNA polymerase (VV-T3pol) or the Escherichia coli lac repressor (VV-lacI) under control of the early-late vaccinia promoter P7.5 were constructed. To determine whether phage polymerase and lac repressor can function in the nucleus of mammalian cells, the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene was cloned downstream of a T3 promoter (PT3-CAT) or downstream of a T3 promoter-lac operator fusion element (PT3Olac-CAT), and these reporter gene cassettes were introduced stably into NIH 3T3 or Ltk- cells. Infection of 3T3/PT3-CAT or Ltk-/PT3-CAT cells by VV-T3pol led to rapid expression of CAT (greater than 20 ng of CAT protein per 10(6) cells). The presence of hydroxyurea (which blocks virus DNA replication) did not prevent CAT production. When 3T3/PT3Olac-CAT cells were infected with both VV-T3pol and VV-lacI (multiplicities of infection of 2.5 and 10, respectively), greater than 30-fold repression of CAT gene activity by lac repressor was observed. This could be reversed to unrepressed levels by the presence of 10 mM o-nitrophenyl-beta-D-galactoside (IPTG) in the medium. Regulated expression of the target gene was observed with cell lines that had been maintained for over 1 year (greater than 50 passages in culture), and Southern blot analysis revealed the presence of the CAT gene only in the nuclear fraction in these cells, demonstrating the stability of the target gene. These results indicate that vaccinia virus-encoded proteins can function in the mammalian nucleus and provide the basis for a genetic system in which essential vaccinia virus genes, placed in the chromosome of a cell, can be used to complement defective virus particles. This approach may prove useful for other virus systems.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton B. M., Eng W. K., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Sternglanz R., Fisher P. A. Signal-mediated import of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae nucleus and specific transcription of target genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):353–360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallo S., Esteban M. Isolation and characterization of attenuated mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):408–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Pepperkok R., Wang F. B., Giordano T. J., McAllister W. T., Ansorge W., Bujard H. Regulated expression of foreign genes in mammalian cells under the control of coliphage T3 RNA polymerase and lac repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5400–5404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Krippl B., Bernstein K. E., Westphal H., Studier F. W. Targeting bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to the mammalian cell nucleus. Gene. 1988 Sep 7;68(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90028-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban M., Holowczak J. A. Replication of vaccinia DNA in mouse L cells. IV. Protein synthesis and viral DNA replication. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):376–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Earl P. L., Moss B. Use of a hybrid vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase system for expression of target genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2538–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Fernandez M. P., Moss B. Transfer of the inducible lac repressor/operator system from Escherichia coli to a vaccinia virus expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2549–2553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Moss B. Structure and stability of mRNA synthesized by vaccinia virus-encoded bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase in mammalian cells. Importance of the 5' untranslated leader. J Mol Biol. 1989 Mar 20;206(2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90483-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano T. J., Deuschle U., Bujard H., McAllister W. T. Regulation of coliphage T3 and T7 RNA polymerases by the lac repressor-operator system. Gene. 1989 Dec 14;84(2):209–219. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90494-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. The inducible lac operator-repressor system is functional in mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Nucleosomes inhibit the initiation of transcription but allow chain elongation with the displacement of histones. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90561-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paez E., Dallo S., Esteban M. Generation of a dominant 8-MDa deletion at the left terminus of vaccinia virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellicer A., Esteban M. Gene-transfer, stability, and biochemical properties of animal cells transformed with vaccinia DNA. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):363–380. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Esteban M. Inhibitory effect of interferon on the genetic and oncogenic transformation by viral and cellular genes. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):229–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.229-232.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Rodriguez D., Rodriguez J. R., McGowan E. B., Esteban M. Expression of the firefly luciferase gene in vaccinia virus: a highly sensitive gene marker to follow virus dissemination in tissues of infected animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1667–1671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]