Abstract
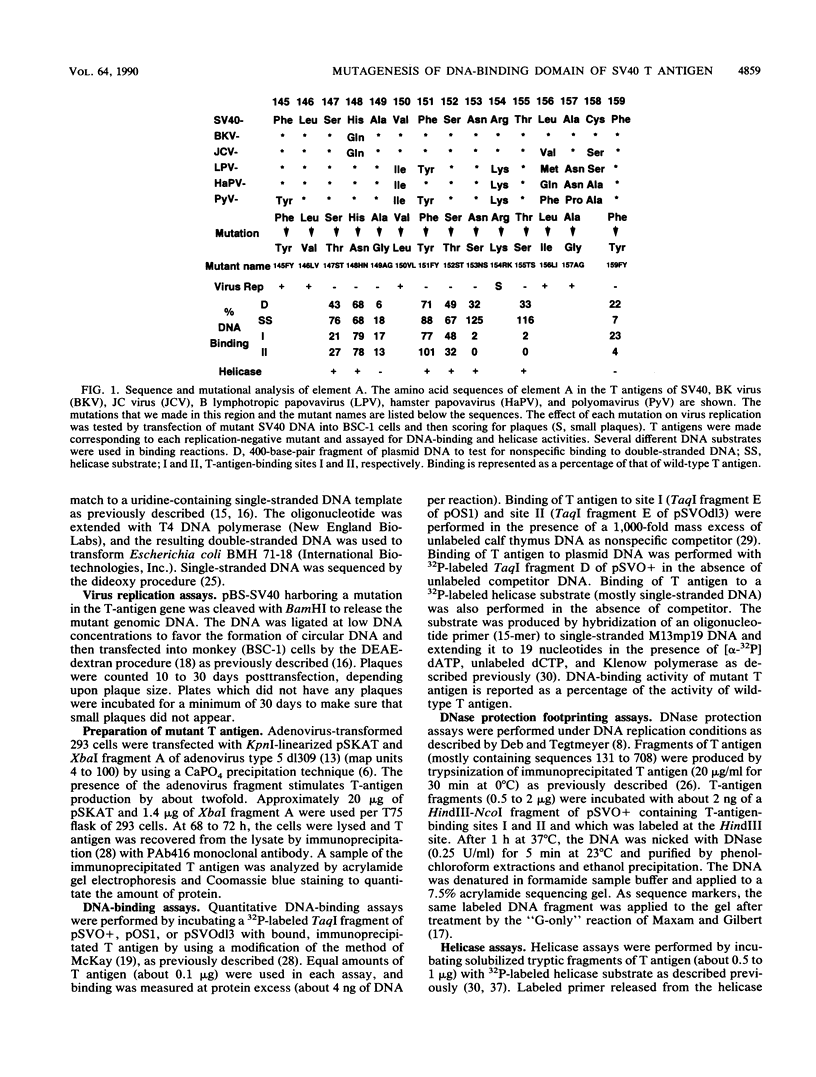
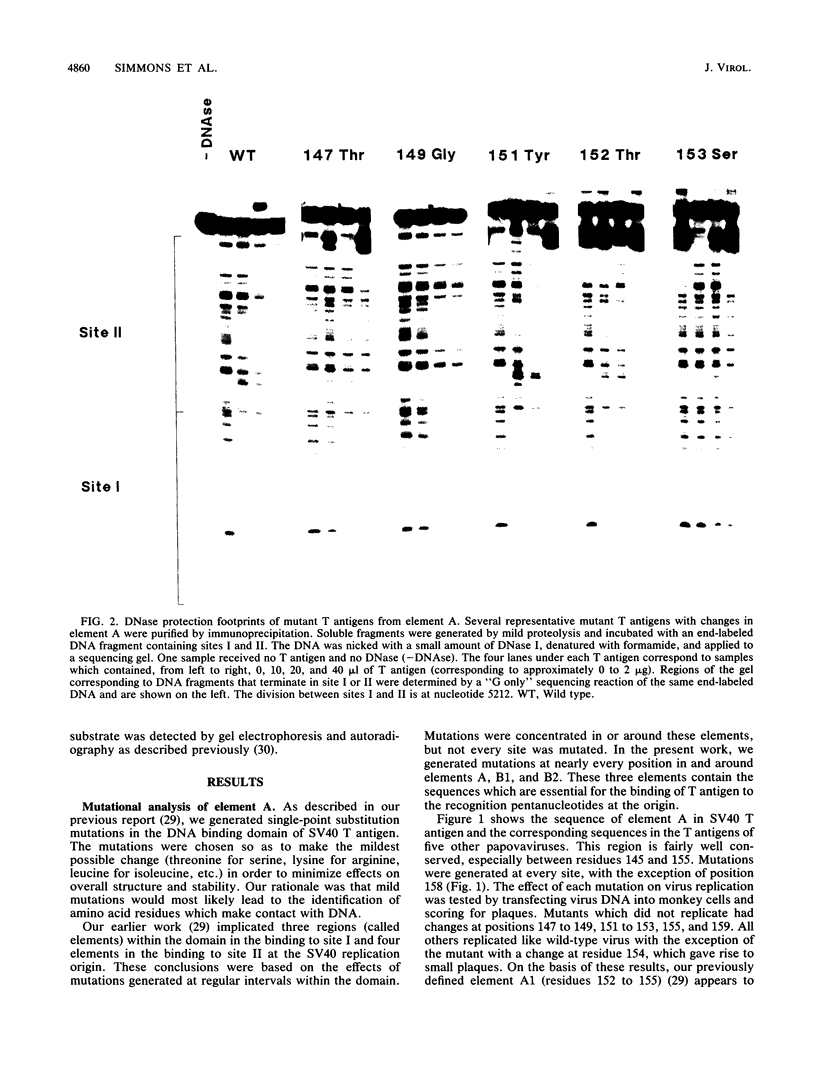
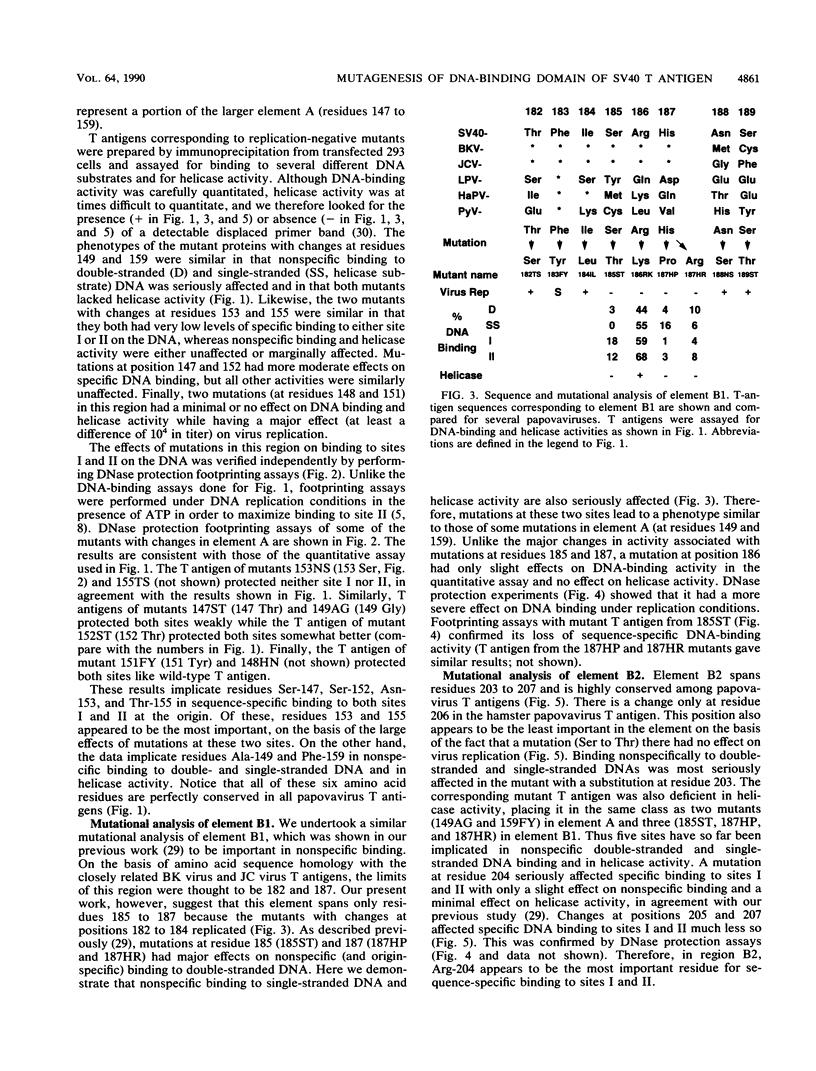
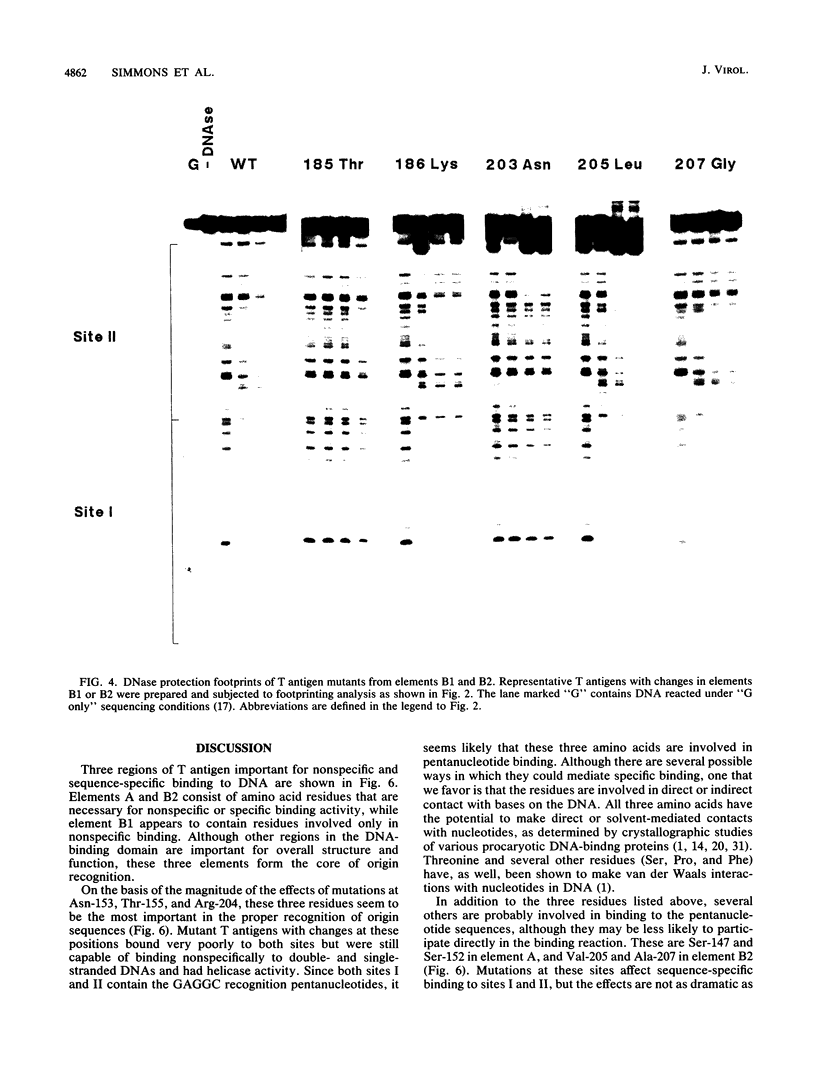
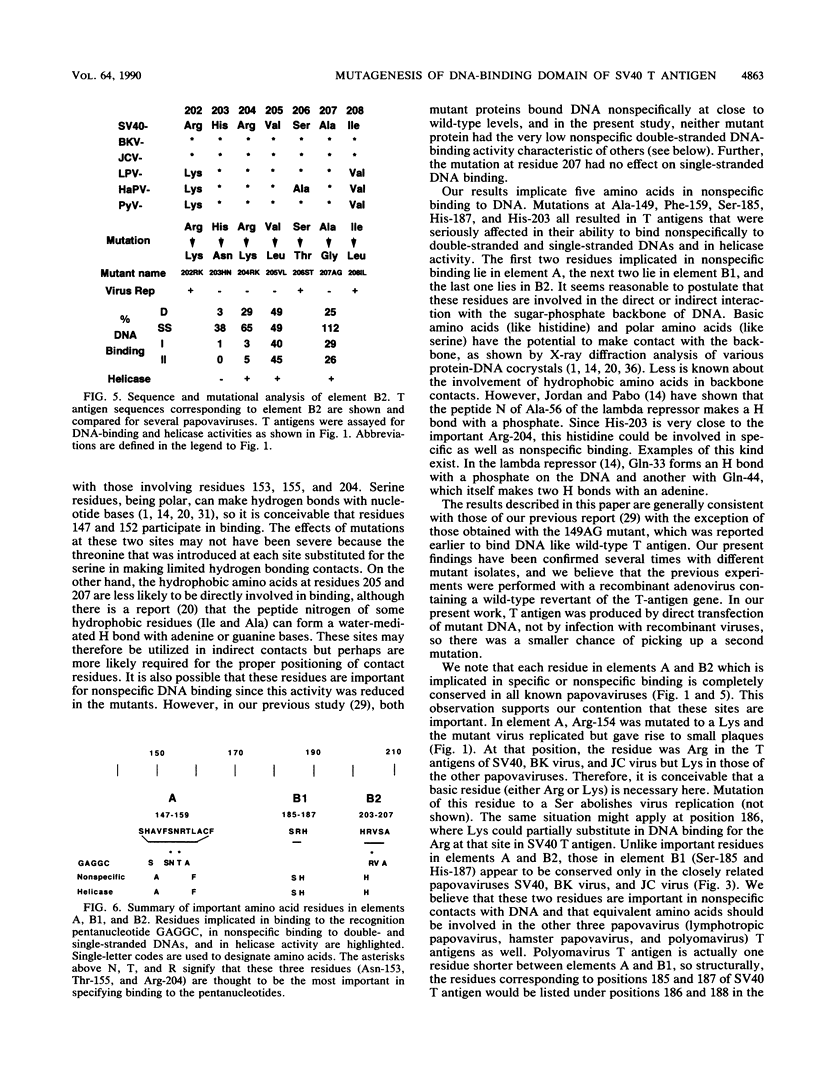
We have previously identified three regions (called elements) in the DNA-binding domain of simian virus 40 large tumor (T) antigen which are critical for binding of the protein to the recognition pentanucleotides GAGGC at the viral replication origin. These are elements A (residues 147 to 159), B1 (185 to 187), and B2 (203 to 207). In this study, we generated mutants of simian virus 40 in order to make single-point substitution mutations at nearly every site in these three elements. Each mutation was tested for its effect on virus replication, and T antigen was produced from all replication-negative mutants. The mutant proteins were assayed for binding to several different DNA substrates and for helicase activity. We found that within each element, mutations at some sites had major effects on DNA binding while mutations at other sites had moderate, mild, or minimal effects, suggesting that some residues are more important than others in mediating DNA binding. Furthermore, we provide evidence that certain residues in elements A and B2 (Ala-149, Phe-159, and His-203) participate in nonspecific double-stranded and helicase substrate (single-stranded) DNA binding while others (Ser-147, Ser-152, Asn-153, Thr-155, Arg-204, Val-205, and Ala-207) are involved in sequence-specific binding at the origin. The residues in element B1 (primarily Ser-185 and His-187) take part only in nonspecific DNA binding. The amino acids important for nonspecific DNA binding are also required for helicase activity, and we hypothesize that they make contact with the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA. On the other hand, those involved in sequence-specific binding are not needed for helicase activity. Finally, our analysis showed that three residues (Asn-153 and Thr-155 in element A and Arg-204 in element B2) may be the most important for sequence-specific binding. They are likely to make direct or indirect contacts with the pentanucleotide sequences at the origin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A. K., Rodgers D. W., Drottar M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a DNA operator by the repressor of phage 434: a view at high resolution. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):899–907. doi: 10.1126/science.3187531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur A. K., Höss A., Fanning E. Expression of simian virus 40 T antigen in Escherichia coli: localization of T-antigen origin DNA-binding domain to within 129 amino acids. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1999–2006. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1999-2006.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auborn K., Guo M., Prives C. Helicase, DNA-binding, and immunological properties of replication-defective simian virus 40 mutant T antigens. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):912–918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.912-918.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. ATP stimulates the binding of simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen to the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. Localized melting and structural changes in the SV40 origin of replication induced by T-antigen. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3149–3158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Tjian R., Tegtmeyer P. Topography of simian virus 40 A protein-DNA complexes: arrangement of pentanucleotide interaction sites at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.143-150.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S. P., Tegtmeyer P. ATP enhances the binding of simian virus 40 large T antigen to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3649–3654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3649-3654.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Koff A., Tsui S., Tegtmeyer P. The adenine-thymine domain of the simian virus 40 core origin directs DNA bending and coordinately regulates DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4578–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Cowie A., Kamen R. I., Griffin B. E. DNA binding activity of polyoma virus large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1941–1945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb P., Nasoff M. S., Fisher E. F., Walsh A. M., Caruthers M. H. Binding studies of SV40 T-antigen to SV40 binding site II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6621–6634. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Essential contact residues within SV40 large T antigen binding sites I and II identified by alkylation-interference. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. R., Pabo C. O. Structure of the lambda complex at 2.5 A resolution: details of the repressor-operator interactions. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.3187530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeber G., Parsons R., Tegtmeyer P. The zinc finger region of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.94-100.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. Binding of a simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 25;145(3):471–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otwinowski Z., Schevitz R. W., Zhang R. G., Lawson C. L., Joachimiak A., Marmorstein R. Q., Luisi B. F., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of trp repressor/operator complex at atomic resolution. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):321–329. doi: 10.1038/335321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R., Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. Three domains in the simian virus 40 core origin orchestrate the binding, melting, and DNA helicase activities of T antigen. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):509–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.509-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz B. J., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T antigens bind to common DNA sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):925–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.925-937.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., DeLucia A. L., Tegtmeyer P. Binding of SV40 a protein to the BK virus origin of DNA replication. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90412-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Silver S., DeLucia A. L., Fanning E., Tegtmeyer P. An altered DNA conformation in origin region I is a determinant for the binding of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):719–725. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90838-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Chou W., Rodgers K. Phosphorylation downregulates the DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):888–894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.888-894.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T. DNA-binding region of the simian virus 40 tumor antigen. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):776–785. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.776-785.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T. Geometry of the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen-DNA complex as probed by protease digestion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2086–2090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. T., Loeber G., Tegtmeyer P. Four major sequence elements of simian virus 40 large T antigen coordinate its specific and nonspecific DNA binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1973–1983. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1973-1983.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B., Gerard R. D., Guggenheimer R. A., Gluzman Y. T antigen and template requirements for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2933–2939. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss M., Argani P., Mohr I. J., Gluzman Y. Studies on the origin-specific DNA-binding domain of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3326–3330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3326-3330.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. Protein-DNA interactions at the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):655–661. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Dong Y. C., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of a phage 434 Cro/DNA complex. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):789–795. doi: 10.1038/335789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wun-Kim K., Simmons D. T. Mapping of helicase and helicase substrate-binding domains on simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2014–2020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2014-2020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]