Abstract
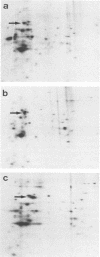
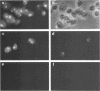
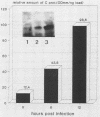
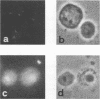
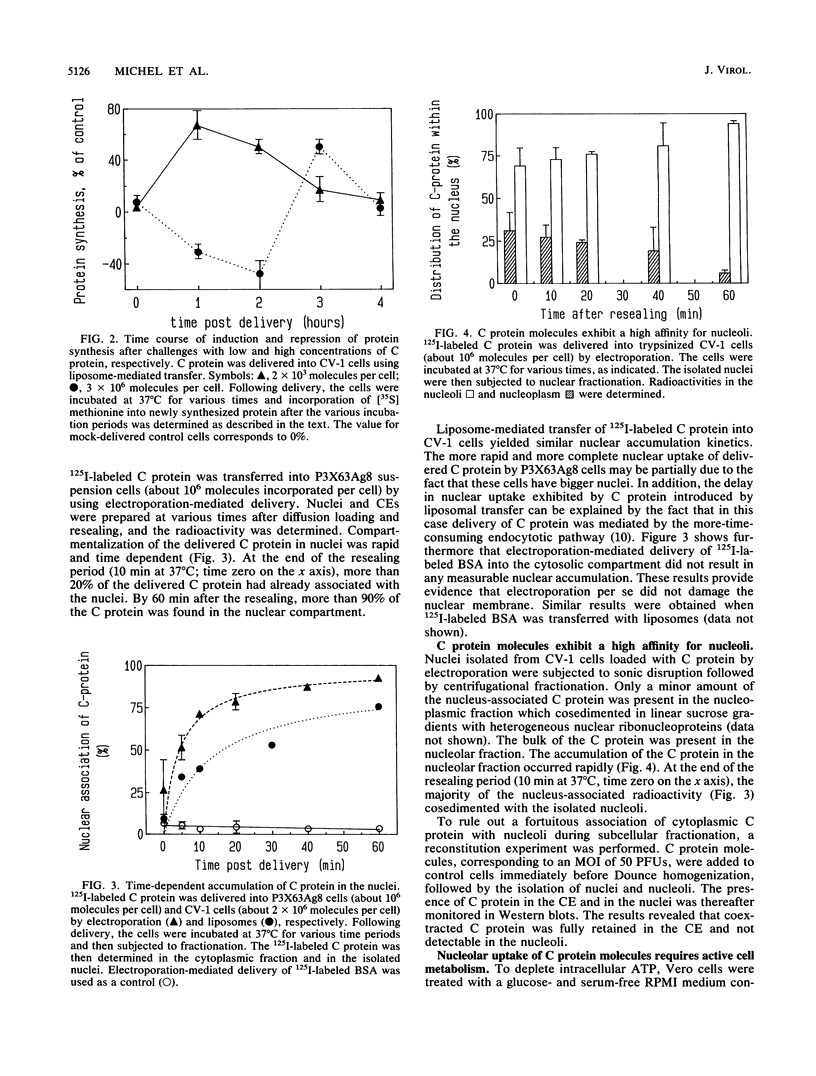
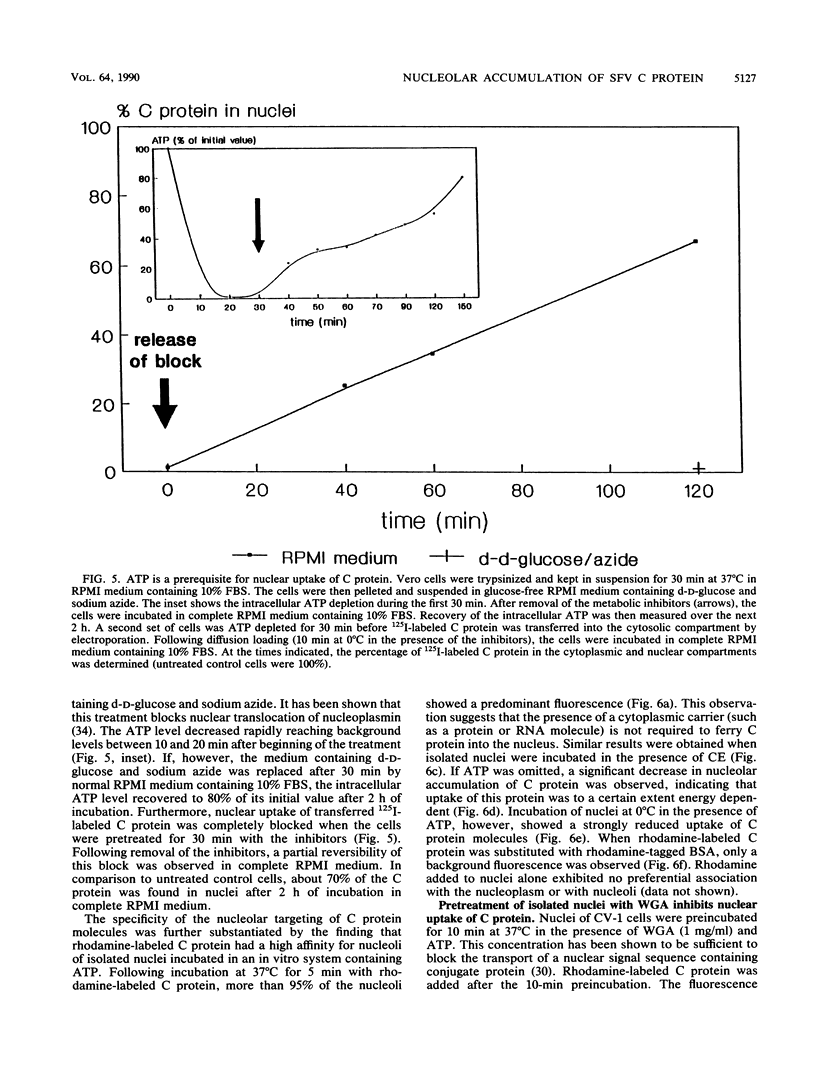
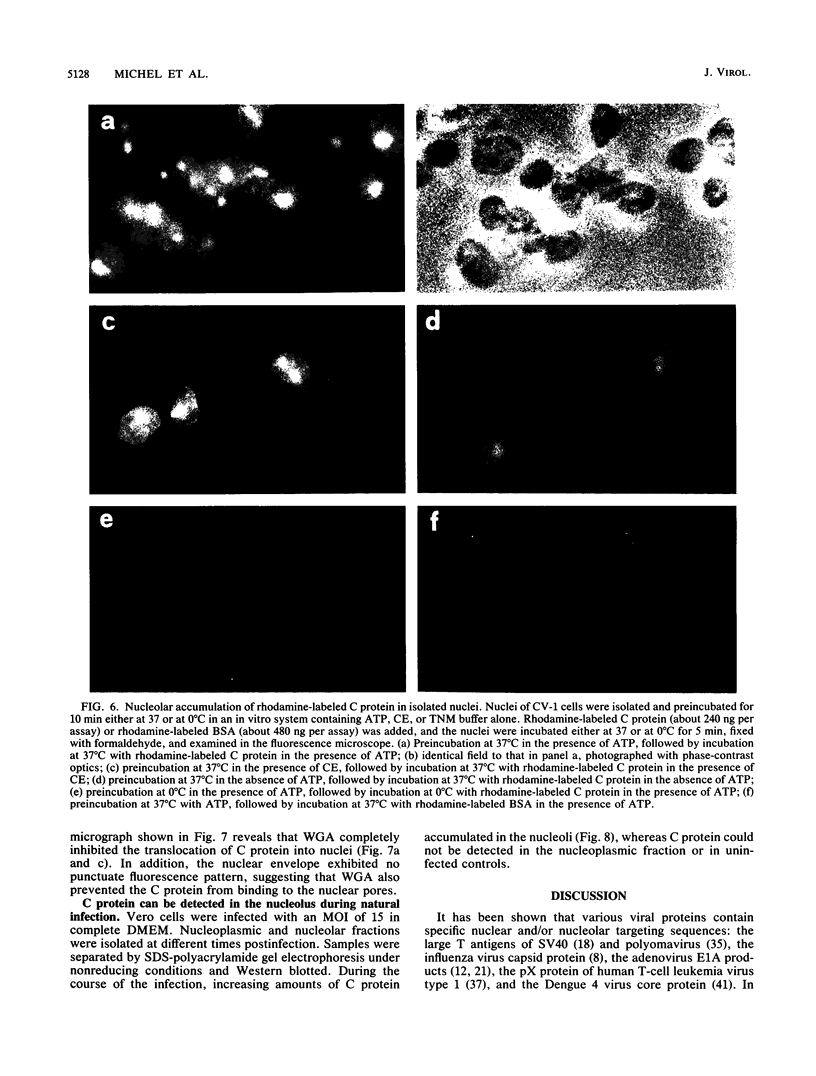
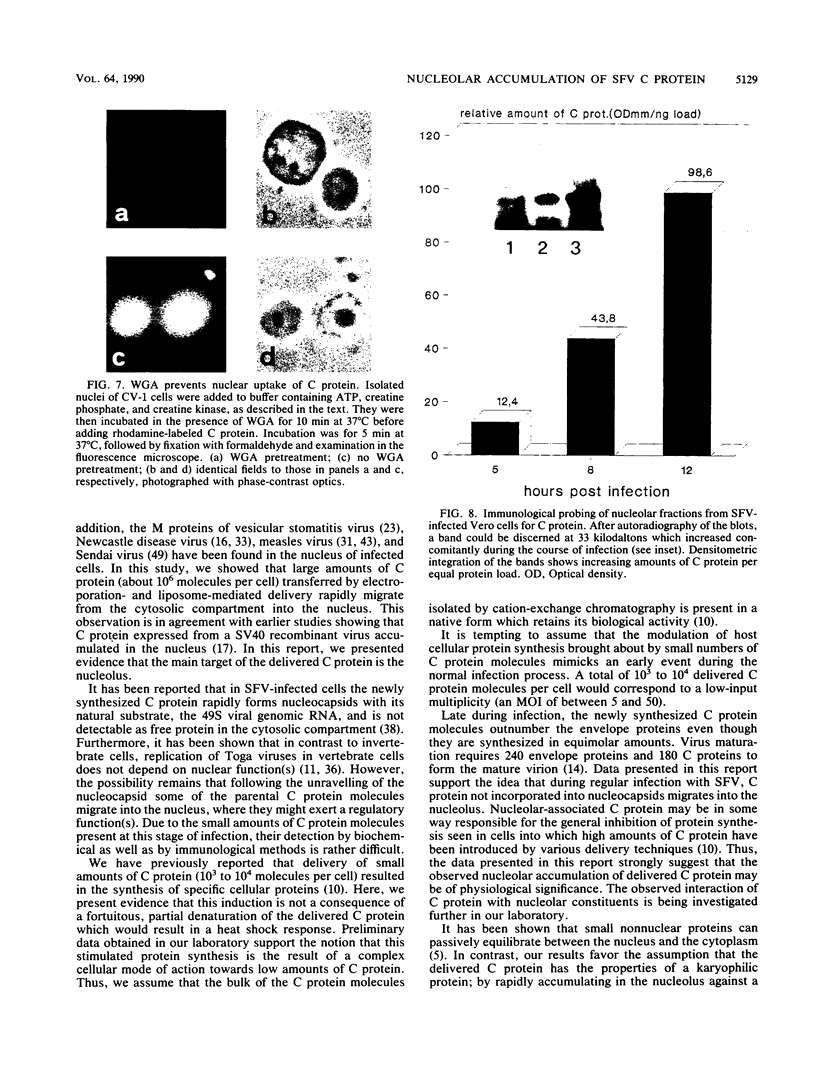
Semliki Forest virus capsid (C) protein molecules (Mr, 33,000) can be introduced efficiently into the cytoplasm of various target cells by electroporation, liposome, and erythrocyte ghost-mediated delivery (M. Elgizoli, Y. Dai, C. Kempf, H. Koblet, and M.R. Michel, J. Virol. 63:2921-2928, 1989). Here, we show that the transferred C protein molecules partition rapidly from the cytosolic compartment into the nucleus. Transport of the C protein molecules into the nucleus was reversibly arrested by metabolic inhibitors, indicating that the transfer process is energy dependent. Fractionation of isolated nuclei revealed that the delivered C protein preferentially associates with the nucleoli. This finding was confirmed by morphological studies, showing that in an in vitro system containing ATP isolated nuclei rapidly accumulated rhodamine-labeled C protein in their nucleoli. Furthermore, in this assay system, the lectin wheat germ agglutinin prevented transfer of C protein through nuclear pores. These results are in agreement with our observation that nucleoli contain measurable amounts of newly synthesized C protein as early as 5 h after infection of cells with SFV. Thereafter, nucleolar-associated C protein increased progressively during the course of infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aliperti G., Schlesinger M. J. Evidence for an autoprotease activity of sindbis virus capsid protein. Virology. 1978 Oct 15;90(2):366–369. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90321-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ananthan J., Goldberg A. L., Voellmy R. Abnormal proteins serve as eukaryotic stress signals and trigger the activation of heat shock genes. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.3083508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Welch W. J. Characterization and purification of the small 28,000-dalton mammalian heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15359–15369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boege U., Wengler G., Wittmann-Liebold B. The core protein of alphaviruses. 1. Purification of peptides and complete amino-acid sequence of Semliki Forest virus core protein. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 15;133(2):405–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M. Protein migration into nuclei. II. Frog oocyte nuclei accumulate a class of microinjected oocyte nuclear proteins and exclude a class of microinjected oocyte cytoplasmic proteins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):431–437. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzeski H., Clegg J. C., Atkins G. J., Kennedy S. I. Regulation of the synthesis of Sindbis virus-specified RNA: role of the virion core protein. J Gen Virol. 1978 Mar;38(3):461–470. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-3-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelsky D., Ralph R., Jonak G. Sequence requirements for synthetic peptide-mediated translocation to the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2487–2492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Steiner-Pryor A., Wright P. J. A proposed regulator for poliovirus: the equestron. Intervirology. 1973;1(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000148826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J., Dimmock N. J., Colman A. Identification of the sequence responsible for the nuclear accumulation of the influenza virus nucleoprotein in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Roberts B., Richardson W. D. The nucleoplasmin nuclear location sequence is larger and more complex than that of SV-40 large T antigen. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):841–849. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgizoli M., Dai Y., Kempf C., Koblet H., Michel M. R. Semliki Forest virus capsid protein acts as a pleiotropic regulator of host cellular protein synthesis. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2921–2928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2921-2928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwin C., Brown D. T. Requirement of cell nucleus for Sindbis virus replication in cultured Aedes albopictus cells. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):792–799. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.792-799.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Protein synthesis directed by an arbovirus. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):26–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.26-32.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D. The T=4 envelope of Sindbis virus is organized by interactions with a complementary T=3 capsid. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):923–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90701-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Sequence analysis of three Sindbis virus mutants temperature-sensitive in the capsid protein autoprotease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4648–4652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Nishikawa K., Toyoda T., Yoshida T., Hanaichi T., Nagai Y. Transcriptive complex of Newcastle disease virus. II. Structural and functional assembly associated with the cytoskeletal framework. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalanko A. Expression of Semliki Forest virus capsid protein from SV40 recombinant virus. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 1;186(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karonen S. L., Mörsky P., Siren M., Seuderling U. An enzymatic solid-phase method for trace iodination of proteins and peptides with 125-iodine. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf C., Kohler U., Michel M. R., Koblet H. Semliki Forest virus-induced polykaryocyte formation is an ATP-dependent event. Arch Virol. 1987;95(1-2):111–122. doi: 10.1007/BF01311338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krippl B., Ferguson B., Jones N., Rosenberg M., Westphal H. Mapping of functional domains in adenovirus E1A proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7480–7484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., McConnell K. A. Subcellular localization of the env-related glycoproteins in Friend erythroleukemia cells. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):263–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.263-272.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., Puddington L., McCreedy B. J., Jr Vesicular stomatitis virus M protein in the nuclei of infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4387–4392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4387-4392.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. H., Ferguson B. Q., Rosenberg M. Pentapeptide nuclear localization signal in adenovirus E1a. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2451–2456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markland W., Smith A. E., Roberts B. L. Signal-dependent translocation of simian virus 40 large-T antigen into rat liver nuclei in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4255–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melancon P., Garoff H. Processing of the Semliki Forest virus structural polyprotein: role of the capsid protease. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1301–1309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1301-1309.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. R., Elgizoli M., Koblet H., Kempf C. Diffusion loading conditions determine recovery of protein synthesis in electroporated P3X63Ag8 cells. Experientia. 1988 Mar 15;44(3):199–203. doi: 10.1007/BF01941705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Onishi T. Rapid isolation of nucleoli from detergent-purified nuclei of tumor and tissue culture cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;15:221–234. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Finlay D. R., Forbes D. J. In vitro transport of a fluorescent nuclear protein and exclusion of non-nuclear proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2091–2102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Chen S. N., Togashi T., Shesberadaran H., Johnson K. P. Five measles virus antigens demonstrated by use of mouse hybridoma antibodies in productively infected tissue culture cells. Arch Virol. 1982;71(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF01315171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeples M. E. Differential detergent treatment allows immunofluorescent localization of the Newcastle disease virus matrix protein within the nucleus of infected cells. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):255–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Mills A. D., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Nuclear protein migration involves two steps: rapid binding at the nuclear envelope followed by slower translocation through nuclear pores. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Roberts B. L., Smith A. E. Nuclear location signals in polyoma virus large-T. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheefers-Borchel U., Scheefers H., Edwards J., Brown D. T. Sindbis virus maturation in cultured mosquito cells is sensitive to actinomycin D. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Shida H., Nam S. H., Nosaka T., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Sequence requirements for nucleolar localization of human T cell leukemia virus type I pX protein, which regulates viral RNA processing. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straubinger R. M., Düzgünes N., Papahadjopoulos D. pH-sensitive liposomes mediate cytoplasmic delivery of encapsulated macromolecules. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straubinger R. M., Hong K., Friend D. S., Papahadjopoulos D. Endocytosis of liposomes and intracellular fate of encapsulated molecules: encounter with a low pH compartment after internalization in coated vesicles. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1069–1079. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadano M., Makino Y., Fukunaga T., Okuno Y., Fukai K. Detection of dengue 4 virus core protein in the nucleus. I. A monoclonal antibody to dengue 4 virus reacts with the antigen in the nucleus and cytoplasm. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jun;70(Pt 6):1409–1415. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-6-1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. L., Rafter D. J., Orvell C., Norrby E. Isolation and immunological characterization of the nucleocapsid and membrane proteins of measles virus. J Gen Virol. 1980 Dec;51(Pt 2):307–315. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmanen I., Söderlund H., Käriäinen L. Semliki Forest virus capsid protein associates with the 60S ribosomal subunit in infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):203–210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.203-210.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Simons K. Studies on the amphipathic nature of the membrane proteins in Semliki Forest virus. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):569–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G. The mode of assembly of alphavirus cores implies a mechanism for the disassembly of the cores in the early stages of infection. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1987;94(1-2):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01313721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Wengler G., Boege U., Wahn K. Establishment and analysis of a system which allows assembly and disassembly of alphavirus core-like particles under physiological conditions in vitro. Virology. 1984 Jan 30;132(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Nagai Y'Yoshii S., Maeno K., Matsumoto T. Membrane (M) protein of HVJ (Sendai virus): its role in virus assembly. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):143–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziemiecki A., Müller R. G., Fu X. C., Hynes N. E., Kozma S. Oncogenic activation of the human trk proto-oncogene by recombination with the ribosomal large subunit protein L7a. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):191–196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steeg H., Kasperaitis M., Voorma H. O., Benne R. Infection of neuroblastoma cells by Semliki Forest virus. The interference of viral capsid protein with the binding of host messenger RNAs into initiation complexes is the cause of the shut-off of host protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 1;138(3):473–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]