Abstract
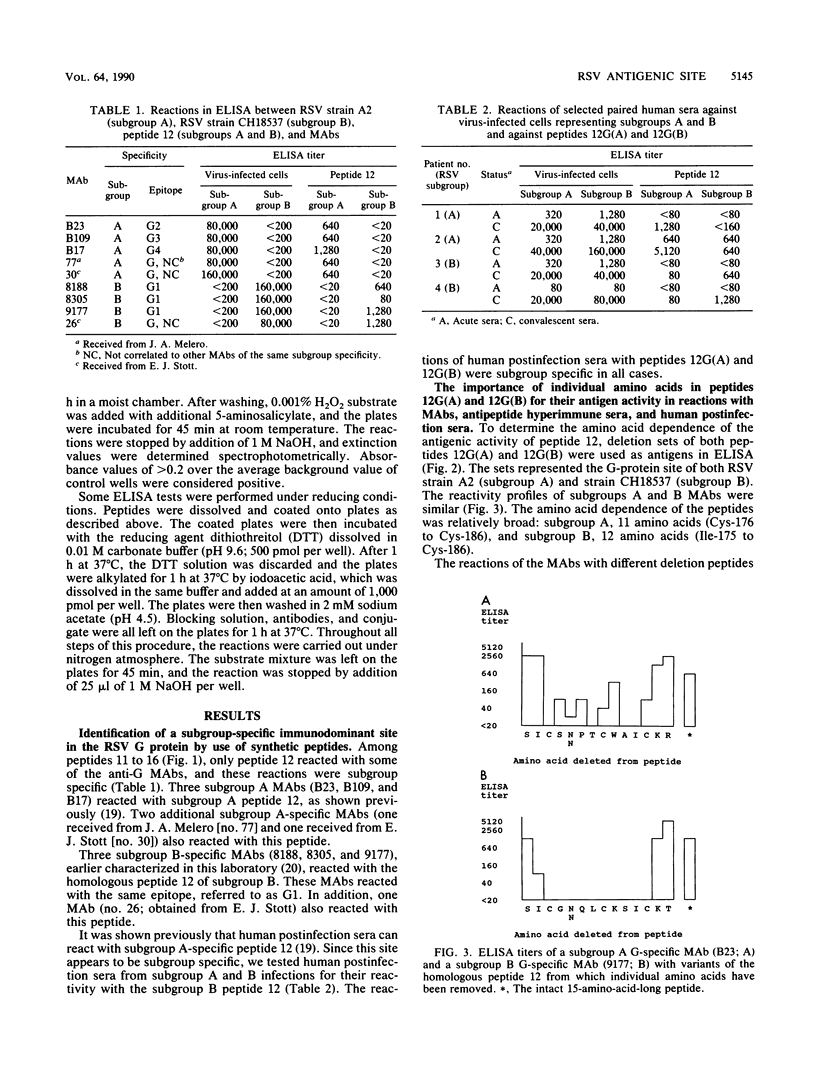
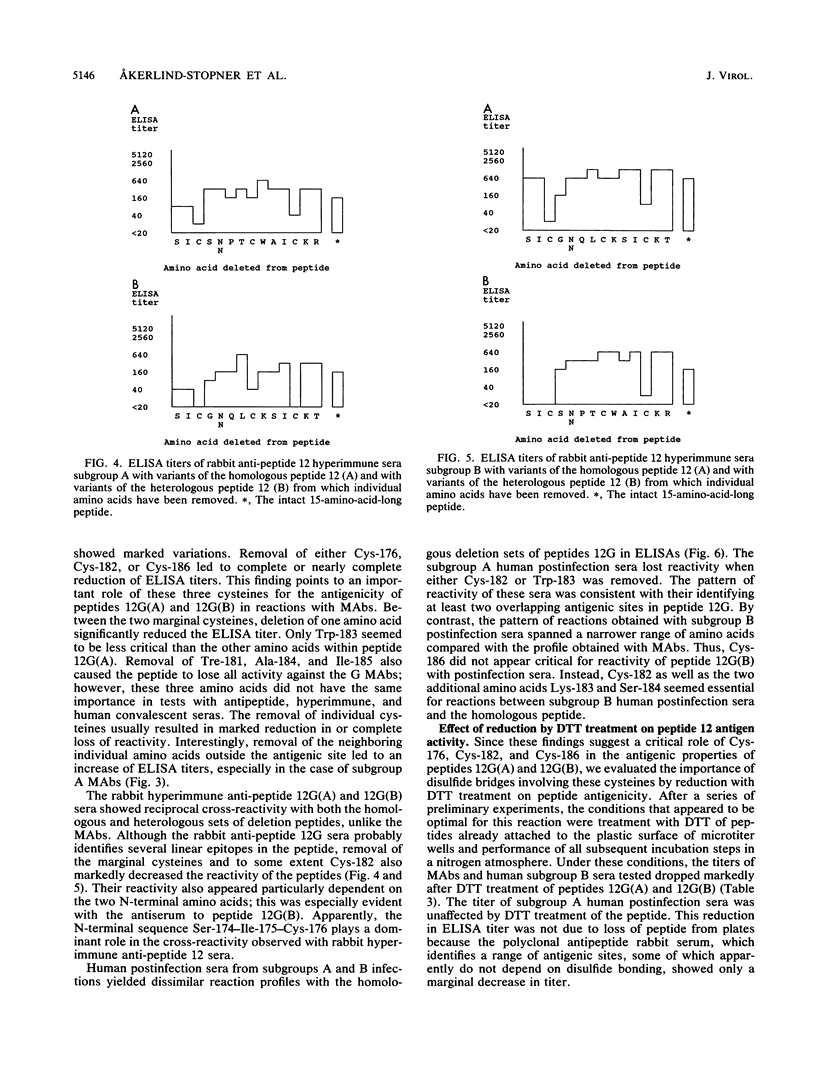
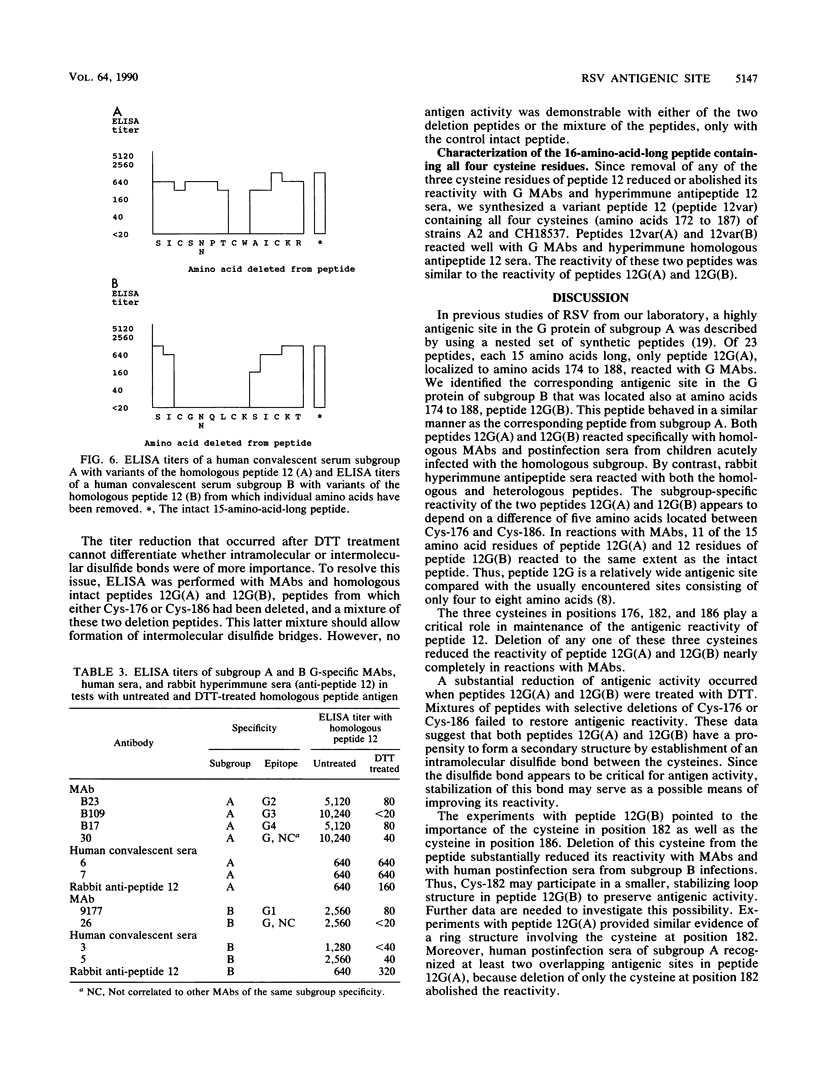
An antigenic site (represented by 15 amino acids, residues 174 to 188, designated peptide 12) of the large glycoprotein G of respiratory syncytial virus was demonstrated to be subgroup specific in peptide enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests with murine monoclonal antibodies and human postinfection sera. The role of individual amino acids in this subgroup-specific site was determined by use of single-amino-acid-deletion sets of peptides. When monoclonal antibodies were reacted with the deletion sets, a broad amino acid dependence of 11 or 12 residues, Cys-176 (Ile-175 in subgroup B) to Cys-186, was found. Human postinfection sera exhibited a narrower reaction profile (for subgroup A, Cys-182 to Trp-183; for subgroup B, Cys-176 to Lys-183). Reduction of peptides on microtiter plates by treatment with dithiothreitol completely destroyed their antigenic activity in tests with monoclonal antibodies and human postinfection sera of subgroup B. A variant of peptide 12 containing all four cysteines of the G protein (represented by 16 amino acids, residues 172 to 187, designated peptide 12var) also was subgroup specific. We concluded that the activity of the antigenic site in tests with monoclonal antibodies for subgroups A and B appears to depend on intrapeptide disulfide bonds. Reactions with postinfection sera of subgroup B also may depend on a disulfide bond. In contrast, postinfection sera of subgroup A appeared to have the capacity to identify a subgroup-specific site in a linear form of the selected 15-amino-acid-long peptide. Treatment of peptides with dithiothreitol had no effect on their antigenic activity in tests with human postinfection sera of subgroup A. These findings have relevance for molecular engineering of peptide antigens for use in respiratory syncytial virus subgroup-specific site-directed serology.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerlind B., Norrby E., Orvell C., Mufson M. A. Respiratory syncytial virus: heterogeneity of subgroup B strains. J Gen Virol. 1988 Sep;69(Pt 9):2145–2154. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-9-2145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. J., Hierholzer J. C., Tsou C., Hendry R. M., Fernie B. F., Stone Y., McIntosh K. Antigenic characterization of respiratory syncytial virus strains with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):626–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R., ROIZMAN B., MYERS R. Recovery from infants with respiratory illness of a virus related to chimpanzee coryza agent (CCA). I. Isolation, properties and characterization. Am J Hyg. 1957 Nov;66(3):281–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COATES H. V., KENDRICK L., CHANOCK R. M. Antigenic differences between two strains of respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Apr;112:958–964. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett J. E., Taylor-Robinson D. Serological studies with respiratory syncytial virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;15(5):601–608. doi: 10.1007/BF01245207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernie B. F., Gerin J. L. Immunochemical identification of viral and nonviral proteins of the respiratory syncytial virus virion. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):243–249. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.243-249.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez H. B., Hardman N., Keir H. M., Cash P. Antigenic variation between human respiratory syncytial virus isolates. J Gen Virol. 1986 May;67(Pt 5):863–870. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-5-863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber C., Levine S. Respiratory syncytial virus polypeptides. IV. The oligosaccharides of the glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):417–432. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Jr, Olmsted R. A., Prince G. A., Murphy B. R., Alling D. W., Walsh E. E., Collins P. L. Antigenic relatedness between glycoproteins of human respiratory syncytial virus subgroups A and B: evaluation of the contributions of F and G glycoproteins to immunity. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3163–3166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3163-3166.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. R., Spriggs M. K., Olmsted R. A., Collins P. L. The G glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial viruses of subgroups A and B: extensive sequence divergence between antigenically related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5625–5629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson M. A., Orvell C., Rafnar B., Norrby E. Two distinct subtypes of human respiratory syncytial virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Oct;66(Pt 10):2111–2124. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-10-2111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J. A., Mitchell M. A., Levely M. E., Rubino K. L., Kinner J. H., Harn N. K., Smith C. W. Mapping an antibody-binding site and a T-cell-stimulating site on the 1A protein of respiratory syncytial virus. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4465–4473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4465-4473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Mufson M. A., Alexander H., Houghten R. A., Lerner R. A. Site-directed serology with synthetic peptides representing the large glycoprotein G of respiratory syncytial virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6572–6576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Mufson M. A., Sheshberadaran H. Structural differences between subtype A and B strains of respiratory syncytial virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2721–2729. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orvell C., Norrby E., Mufson M. A. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against five structural components of human respiratory syncytial virus subgroup B. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3125–3135. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake M., Coligan J. E., Elango N., Norrby E., Venkatesan S. Respiratory syncytial virus envelope glycoprotein (G) has a novel structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7795–7812. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott E. J., Ball L. A., Young K. K., Furze J., Wertz G. W. Human respiratory syncytial virus glycoprotein G expressed from a recombinant vaccinia virus vector protects mice against live-virus challenge. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):607–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.607-613.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Stott E. J., Bew M., Fernie B. F., Cote P. J., Collins A. P., Hughes M., Jebbett J. Monoclonal antibodies protect against respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice. Immunology. 1984 May;52(1):137–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WULFF H., KIDD P., WENNER H. A. RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS: OBSERVATIONS ON ANTIGENIC HETEROGENEITY. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jan;115:240–243. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh E. E., Schlesinger J. J., Brandriss M. W. Protection from respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):756–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.756-758.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Collins P. L., Huang Y., Gruber C., Levine S., Ball L. A. Nucleotide sequence of the G protein gene of human respiratory syncytial virus reveals an unusual type of viral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4075–4079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


