Abstract
A Vero cell line with a long-term rubella virus persistent infection was maintained for 45 weeks in the presence of anti-rubella virus antibody of sufficient titer to completely neutralize the virus in the culture fluid to determine the effect of the presence of antibody on the maintenance of the persistent infection. Prior to antibody treatment, virus was continuously detected as plaque-forming units in the persistently infected culture fluid. Virus clones that were plaque purified from the persistently infected culture fluid were temperature sensitive and exhibited a reduced efficiency of replication and ability to induce cytopathic effects in Vero cells at the persistently infected culture temperature compared with the standard virus used to initiate the persistently infected culture. Defective interfering RNAs were the major intracellular virus-specific RNA species present in the persistently infected cells. Treatment with antibody failed to cure the persistently infected culture of virus, and the cells retained the ability to release virus after antibody treatment was discontinued. Interestingly, the presence of antibody led to the selection of a population of virus which was markedly less cytopathic for Vero cells than the virus population which was selected during persistent infection in the absence of antibody.
Full text
PDF

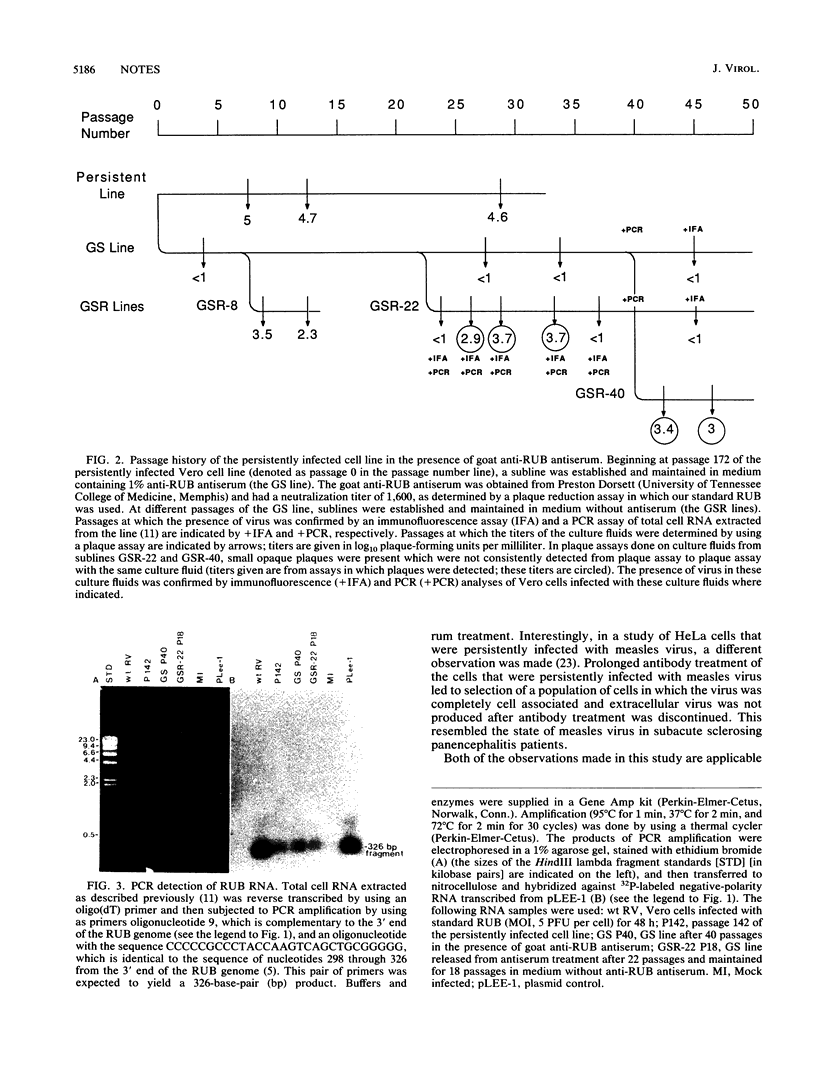

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardeletti G., Tektoff J., Gautheron D. Rubella virus maturation and production in two host cell systems. Intervirology. 1979;11(2):97–103. doi: 10.1159/000149019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buimovici-Klein E., Lang P. B., Ziring P. R., Cooper L. Z. Impaired cell-mediated immune response in patients with congenital rubella: correlation with gestational age at time of infection. Pediatrics. 1979 Nov;64(5):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantler J. K., Tingle A. J., Petty R. E. Persistent rubella virus infection associated with chronic arthritis in children. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 31;313(18):1117–1123. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510313131803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmyter J., Melnick J. L., Rawls W. E. Defectiveness of interferon production and of rubella virus interference in a line of African green monkey kidney cells (Vero). J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):955–961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.955-961.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez G., Wang C. Y., Frey T. K. Sequence of the genome RNA of rubella virus: evidence for genetic rearrangement during togavirus evolution. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90476-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudgeon J. A. Congenital rubella. Pathogenesis and immunology. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Jul;118(1):35–44. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100040037007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. R., Cunningham A. L., Hayes K., Leach R., Lunt R. Rubella arthritis in adults. Isolation of virus, cytology and other aspects of the synovial reaction. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1983 Oct-Dec;1(4):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey T. K., Hemphill M. L. Generation of defective-interfering particles by rubella virus in Vero cells. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):22–29. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90615-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey T. K., Marr L. D., Sanchez A., Simmons R. B. Identification of the 5' end of the rubella virus subgenomic RNA. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90422-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg-Fellner F., Witt M. E., Fedun B., Taub F., Dobersen M. J., McEvoy R. C., Cooper L. Z., Notkins A. L., Rubinstein P. Diabetes mellitus and autoimmunity in patients with the congenital rubella syndrome. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7 (Suppl 1):S170–S176. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.supplement_1.s170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENLE W. INTERFERENCE AND INTERFERON IN PERSISTENT VIRAL INFECTIONS OF CELL CULTURES. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill M. L., Forng R. Y., Abernathy E. S., Frey T. K. Time course of virus-specific macromolecular synthesis during rubella virus infection in Vero cells. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90395-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P., Welsh R. M., Oldstone M. B., Kohne D., Lazzarini R., Scolnick E. Long-term persistent vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus infection of cells in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1976 Nov;33(2):193–211. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-2-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katow S., Sugiura A. Low pH-induced conformational change of rubella virus envelope proteins. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2797–2807. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassab H. F., Veronelli J. A. Characteristics of serially propagated monkey kidney cell cultures with persistent rubella infection. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):436–441. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.436-441.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menser M. A., Forrest J. M., Bransby R. D. Rubella infection and diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1978 Jan 14;1(8055):57–60. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mifune K., Desmyter J., Rawls W. E. Effect of exogenous interferon on rubella virus production in carrier cultures of cells defective in interferon production. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):132–138. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.132-138.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norval M. Mechanism of persistence of rubella virus in LLC-MK2 cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):289–298. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oker-Blom C., Ulmanen I., Käriäinen L., Pettersson R. F. Rubella virus 40S genome RNA specifies a 24S subgenomic mRNA that codes for a precursor to structural proteins. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):403–408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.403-408.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L. Rubella virus carrier cultures derived from congenitally infected infants. J Exp Med. 1966 May 1;123(5):795–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustigian R. Persistent infection of cells in culture by measles virus. II. Effect of measles antibody on persistently infected HeLa sublines and recovery of a HeLa clonal line persistently infected with incomplete virus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1805–1811. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1805-1811.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingle A. J., Chantler J. K., Pot K. H., Paty D. W., Ford D. K. Postpartum rubella immunization: association with development of prolonged arthritis, neurological sequelae, and chronic rubella viremia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):606–612. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER D. L. THE VIRAL CARRIER STATE IN ANIMAL CELL CULTURES. Prog Med Virol. 1964;6:111–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Levis R., Schlesinger S. Evolution of virus and defective-interfering RNAs in BHK cells persistently infected with Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):676–684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.676-684.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. P., Brawner T. A., Riggs H. G., Jr, Roehrig J. T. Characteristics of a persistent rubella infection in a human cell line. J Gen Virol. 1981 Feb;52(Pt 2):321–328. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky J. S., Waxham M. N., Hess J. L., Townsend J. J., Baringer J. R. Immunochemical features of a case of progressive rubella panencephalitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 May;48(2):359–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters J. M., van der Veen J., van de Putte L. B., de Rooij D. J. Adult onset Still's disease and viral infections. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988 Sep;47(9):764–767. doi: 10.1136/ard.47.9.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziring P. R., Gallo G., Finegold M., Buimovici-Klein E., Ogra P. Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis: identification of rubella virus antigen in the thyroid of a child with congenital rubella. J Pediatr. 1977 Mar;90(3):419–420. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]