Abstract
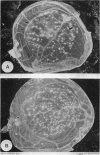
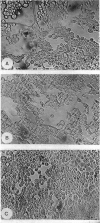
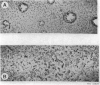
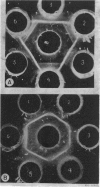
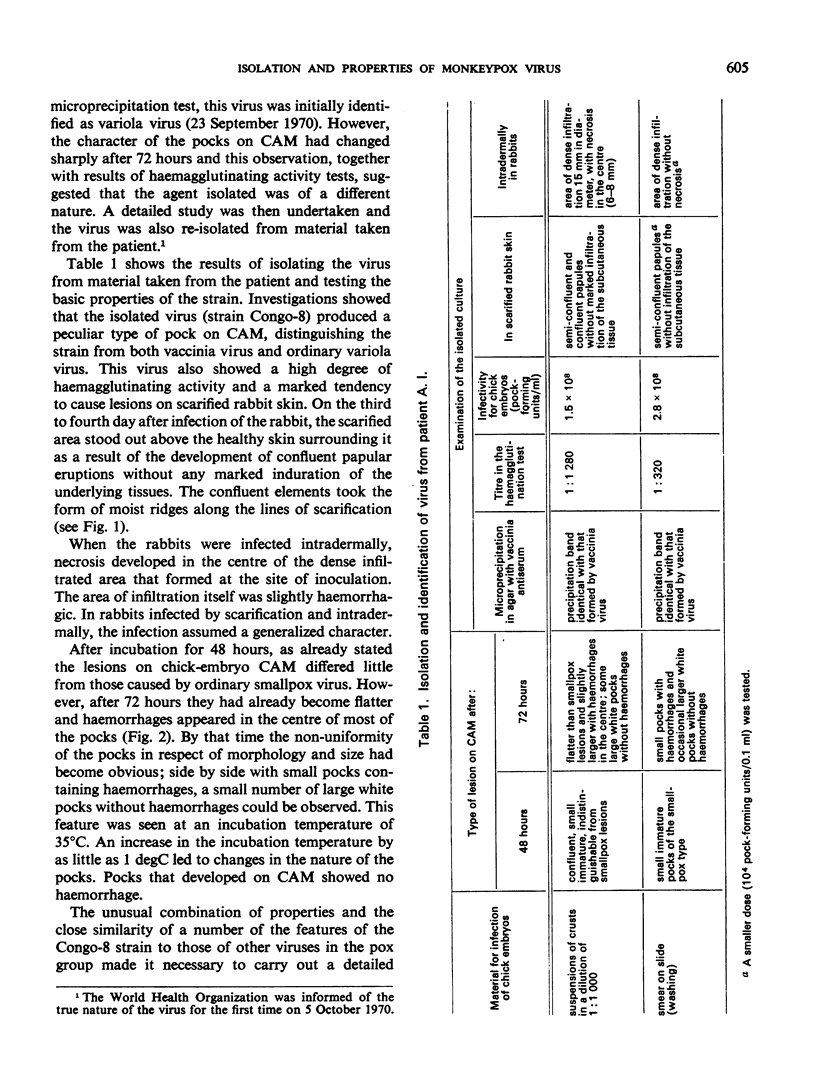
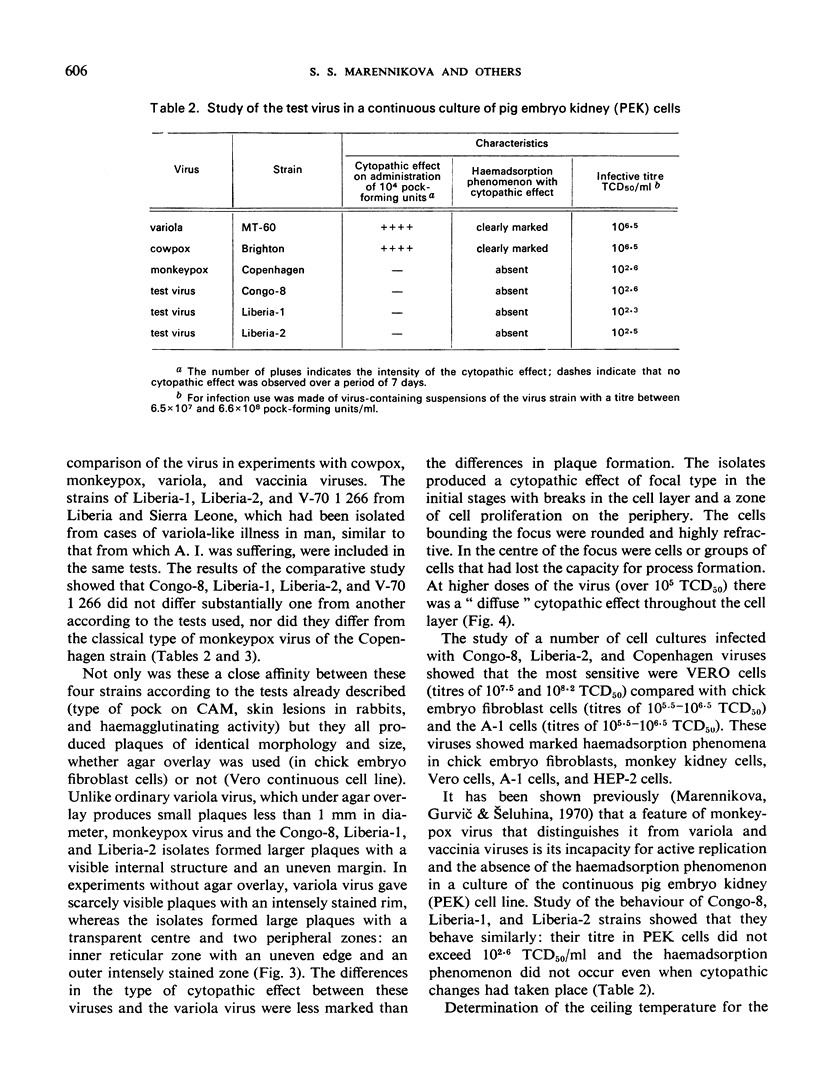
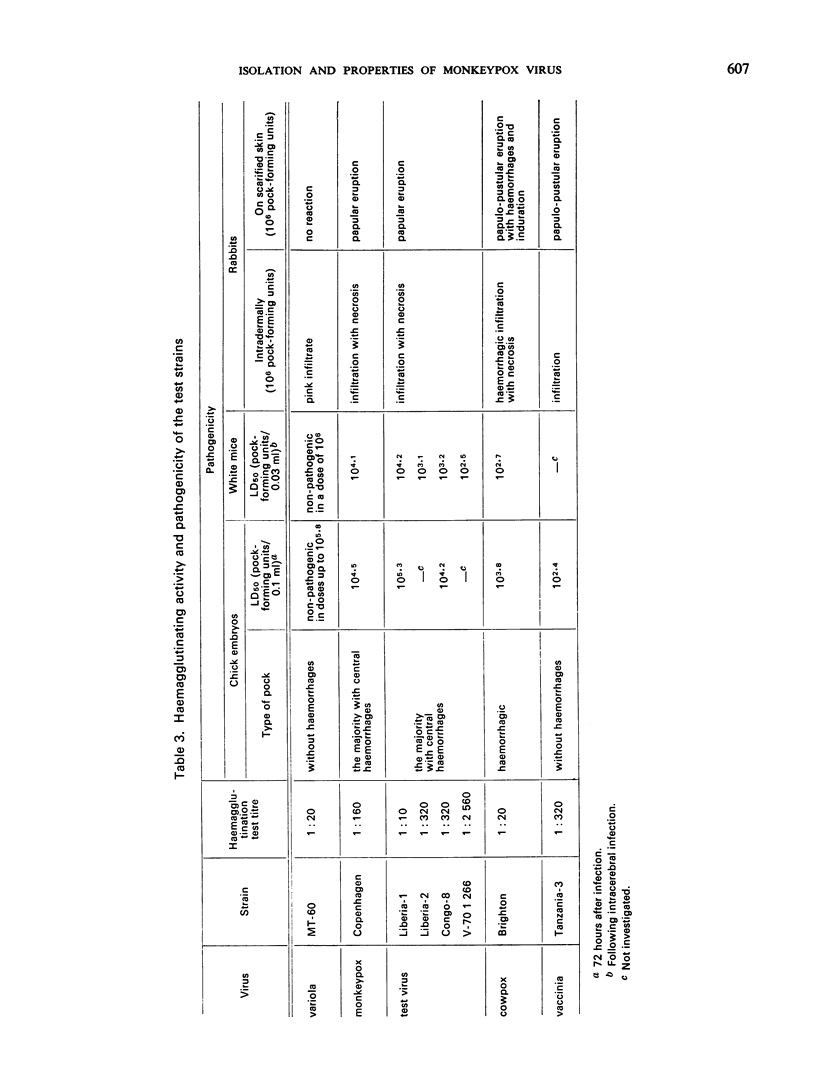
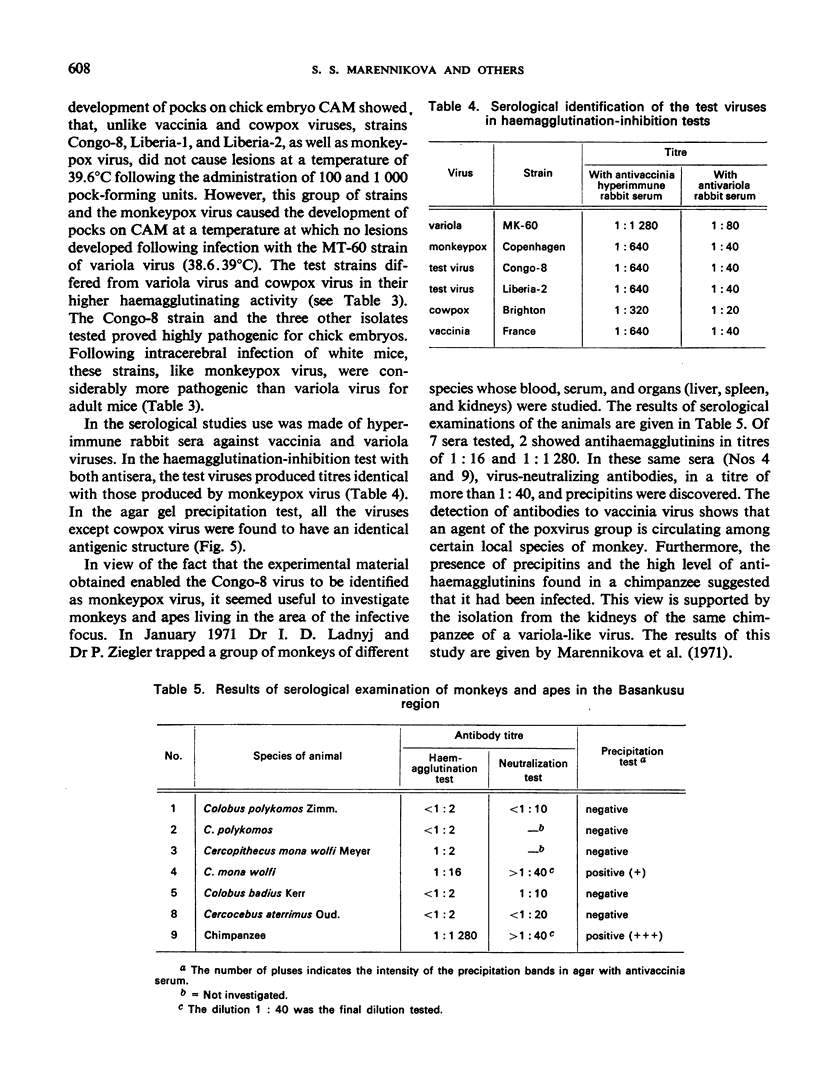
The causal agent of a case of disease in man occurring in the Democratic Republic of the Congo with a similar clinical picture to smallpox was isolated and studied. The agent was identified as monkeypox virus. A comparative study of the isolated strain (Congo-8) and of viruses isolated from similar cases of illness in Liberia (Liberia-1 and Liberia-2 strains) and Sierra Leone (V-70 1 266 strain) showed that they were identical. A number of local species of monkeys and apes were examined serologically in the Congo region to determine the probability of human infection with monkeypox virus. It was confirmed that the animals had had contact with an agent of the poxvirus group. In 2 of the 7 sera examined, antibodies of the variola—vaccinia group of poxviruses were discovered (virus-neutralizing antibodies, precipitins, and antihaemagglutinins). In a chimpanzee, antihaemagglutinins were found in a titre of 1: 1 280, and in the same animal a variola-like virus was isolated from the kidneys. In the course of the investigation, it was shown conclusively that monkeypox virus and the strains under investigation could be distinguished from o dinary variola and vaccinia viruses on the basis of their behaviour in pig embryo kidney continuous cell line culture.
Full text
PDF


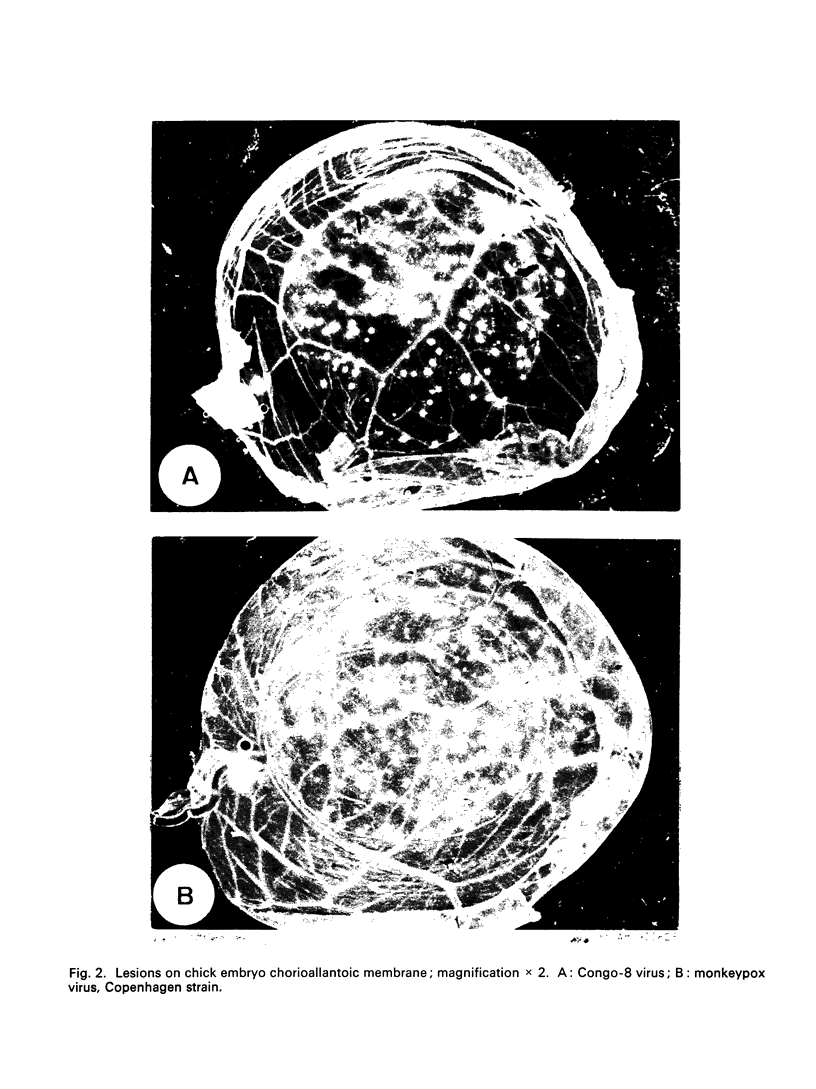

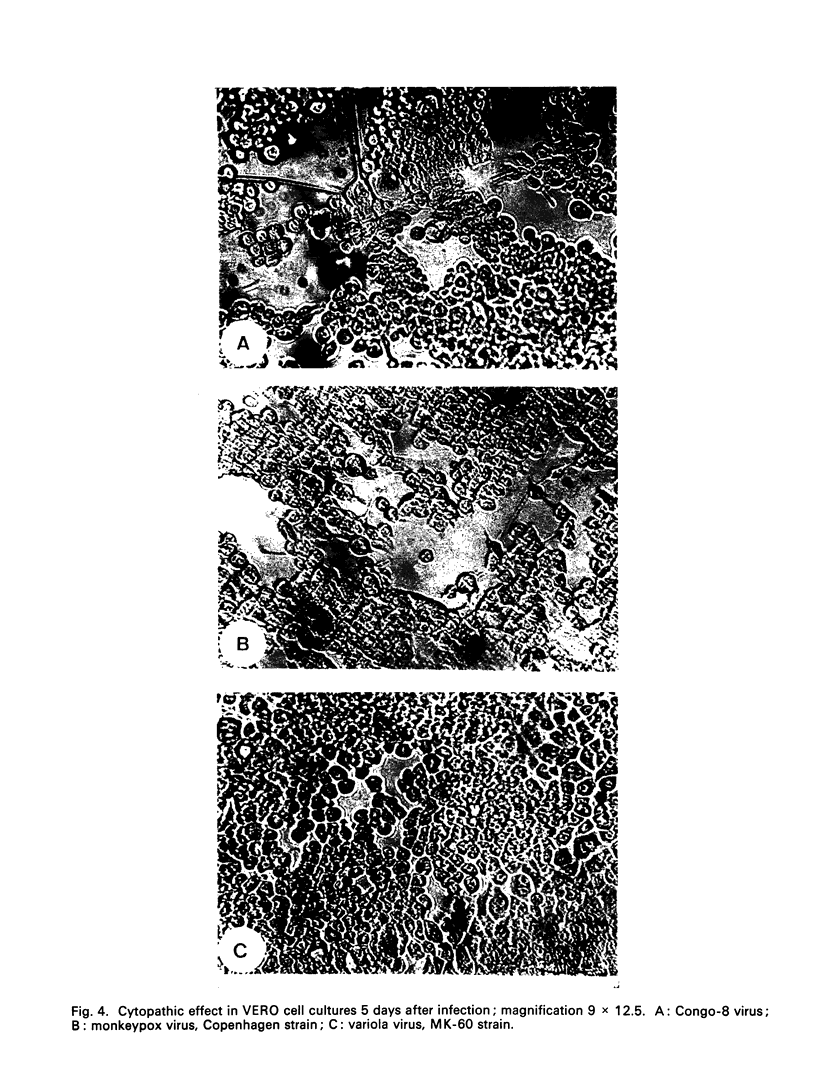


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOULTER E. A. The titration of vaccinial neutralizing antibody on chorio-allantoic membranes. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Dec;55(4):502–512. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladnyj I. D., Ziegler P., Kima E. A human infection caused by monkeypox virus in Basankusu Territory, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Bull World Health Organ. 1972;46(5):593–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marennikova S. S., Shafikova R. A. Comparative studies on the properties of variola virus strains. I. Characteristics of chorioallantoic membrane lesions and pathogenicity for chick embryos after different methods of inoculation. Acta Virol. 1969 Nov;13(6):538–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. An in-vitro test of the toxin-producing capacity of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Lancet. 1949 Feb 26;1(6548):346–348. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(49)90642-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTERFIELD J. S., ALLISON A. C. Studies with poxviruses by an improved plaque technique. Virology. 1960 Feb;10:233–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIER J. E., SAUER R. M., MALSBERGER R. G., SILLAMAN J. M. Studies on a pox disease of monkeys. II. Isolation of the etiologic agent. Am J Vet Res. 1960 May;21:381–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben R. Some entomological and epidemiological observations on the 1964 outbreak of Chikungunya fever in South India. Indian J Med Res. 1967 Jan;55(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]