Abstract
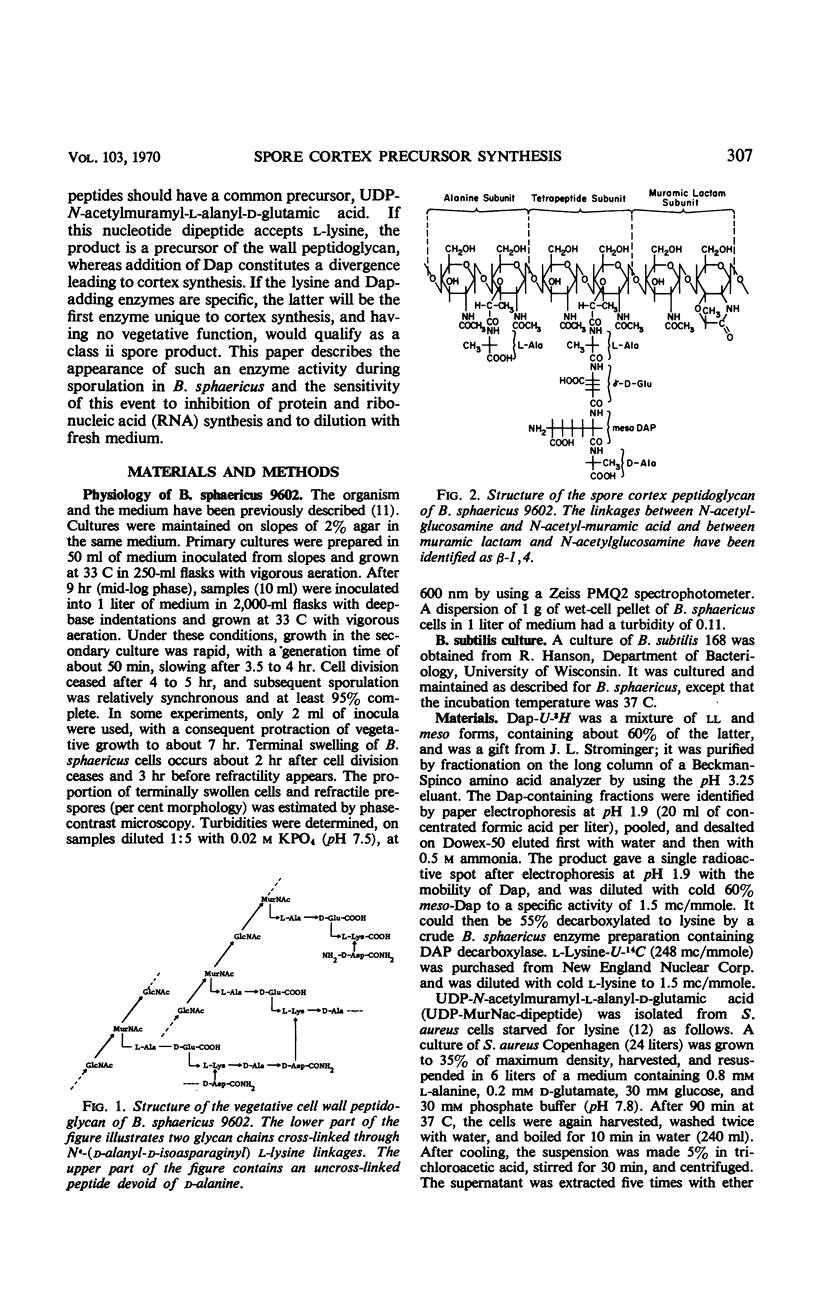
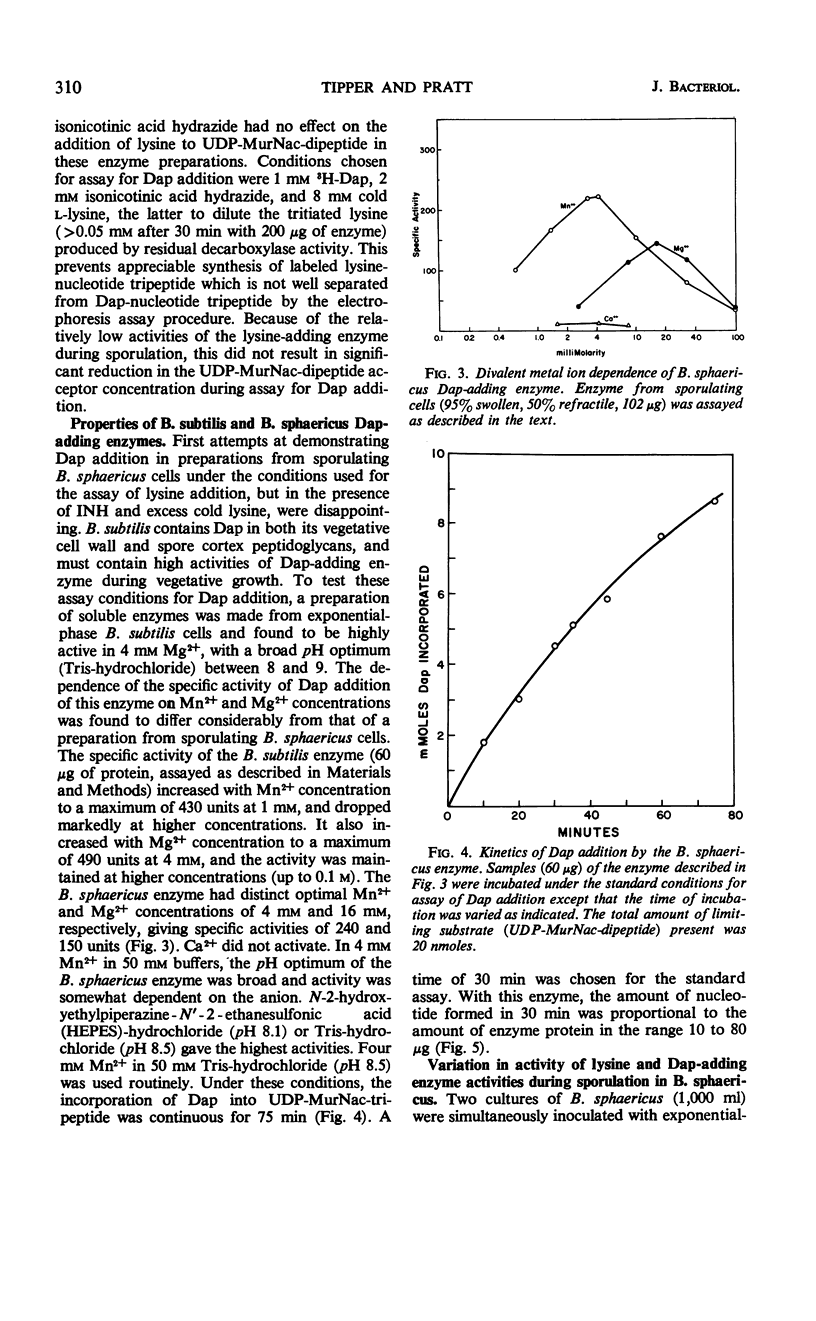
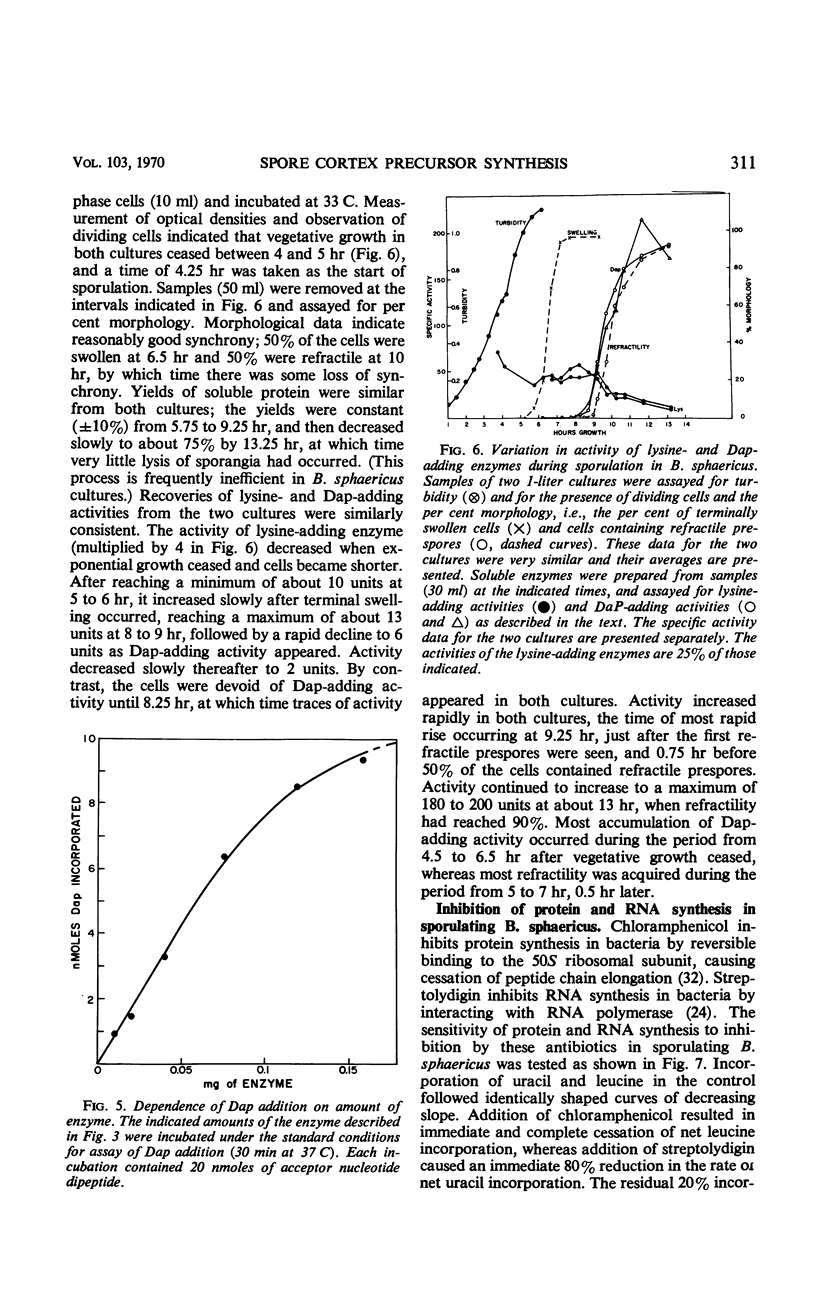
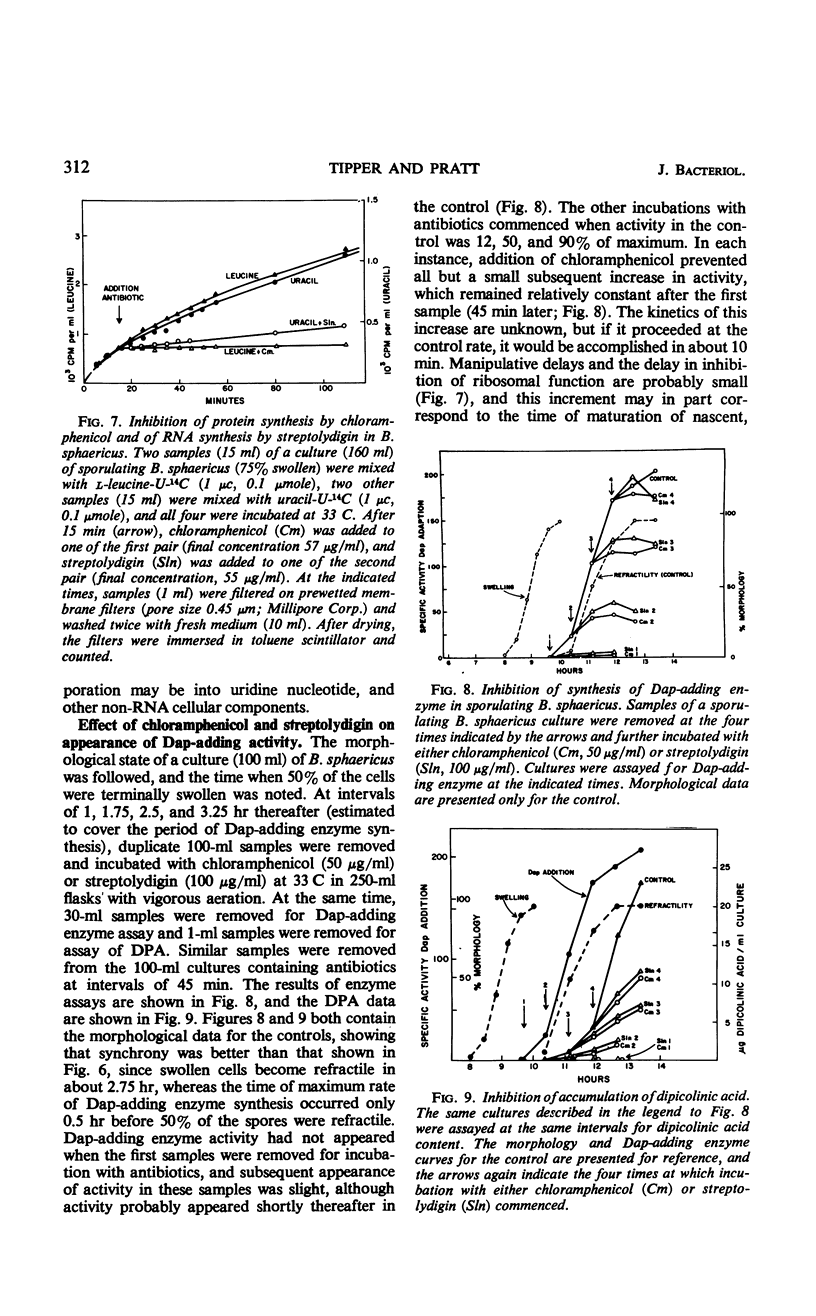
The cell wall peptidoglycan of vegetative cells of Bacillus sphaericus 9602 contains l-lysine and d-isoasparagine and is devoid of diaminopimelic acid (Dap), whereas the peptidoglycan of its spore cortex is devoid of l-lysine and d-isoasparagine and contains meso-Dap. These two structures have a common biosynthetic precursor, uridine-diphospho-N-acetylmuramyl-l- alanyl-d-glutamic acid, which accepts either l-lysine or meso-Dap, the latter reaction being the first unique to the synthesis of the spore cortex peptidoglycan. l-lysine-adding activity decays at the end of vegetative growth to a level which is maintained until Dap-adding activity appears, when it declines rapidly again. Dap-adding activity is not detectable in refractile spores, in vegetative cells, or in sporulating cells until about 4 hr after the end of vegetative growth, when it increases rapidly for about 1.5 hr in a process dependent on continued protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis. This process apparently involves transcription and translation during this period of a “sporulation-specific” gene whose product is essential for and unique to sporulation. It is closely followed by the acquirement of refractility. Another sporulation-specific gene, that for dipicolinate synthase, is apparently transcribed and translated in an overlapping period commencing about 0.5 hr later, although dipicolinate does not accumulate rapidly until 1.5 hr later, when about 75% of the cells are already refractile. Inhibition of protein synthesis with chloramphenicol or of RNA synthesis with streptolydigin inhibited accumulation of these enzymes in sporulating cells; this inhibition could be reversed by washing out the antibiotics after 1.5 hr. Sporulation recommenced with an unaltered sequence of events but with poorer synchrony. There was no evidence for a messenger RNA for either enzyme of lifetime greater than a small fraction of the period of enzyme accumulation, although dilution with 10 volumes of fresh medium failed to prevent synthesis of Dap-adding enzyme in cells which had become terminally swollen, a process preceding enzyme synthesis by about 1.5 hr. The synthesis of this enzyme in B. sphaericus is apparently dependent on programmed transcription of the appropriate gene.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Stahly D. P. Diaminopimelate decarboxylase of sporulating bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2099–2109. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2099-2109.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson H. O., Vary J. C., Steinberg W. Developmental changes during the formation and breaking of the dormant state in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:169–188. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungerer K. D., Tipper D. J. Cell wall polymers of Bacillus sphaericus 9602. I. Structure of the vegetative cell wall peptidoglycan. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3577–3587. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A., Spudich J. A., Nelson D. L., Deutscher M. P. Origin of proteins in sporulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:51–78. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.000411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C. Determination of dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores by ultraviolet spectrometry of the calcium chelate. Anal Biochem. 1967 May;19(2):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C., Snell N. S., Burr H. K. Water Permeability of Bacterial Spores and the Concept of a Contractile Cortex. Science. 1960 Aug 26;132(3426):544–545. doi: 10.1126/science.132.3426.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Sonenshein A. L. Change in the template specificity of RNA polymerase during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):35–37. doi: 10.1038/224035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F., HUNTER J. R. The sporulation of Bacillus sphaericus stimulated by association with other bacteria: an effect of carbon dioxide. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Aug;13(1):54–58. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-1-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F., STRANGE R. E. Alpha-Epsilon-Diaminopimelic acid metabolism and sporulation in Bacillus sphaericus. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):700–708. doi: 10.1042/bj0650700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoff H. L., Hitchins A. D., Celikkol E. Properties of fructose 1,6-diphosphate aldolases from spores and vegetative cells of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1208–1218. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1208-1218.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddhikol C., Erbstoeszer J. W., Weisblum B. Mode of action of streptolydigin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):151–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.151-155.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L., Izaki K., Matsuhashi M., Tipper D. J. Peptidoglycan transpeptidase and D-alanine carboxypeptidase: penicillin-sensitive enzymatic reactions. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):9–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Burgessrr Cyclic re-use of the RNA polymerase sigma factor. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):537–540. doi: 10.1038/222537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARTH A. D., OHYE D. F., MURRELL W. G. Location and composition of spore mucopeptide in Bacillus species. J Cell Biol. 1963 Mar;16:593–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE P. J., KELLY B. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF DIAMINOPIMELATE DECARBOXYLASE FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:75–84. doi: 10.1042/bj0960075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Davies J. Antibiotic inhibitors of the bacterial ribosome. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):493–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. J., Kelly B., Suffling A., Work E. Variation of activity of bacterial diaminopimelate decarboxylase under different conditions of growth. Biochem J. 1964 Jun;91(3):600–610. doi: 10.1042/bj0910600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



