Abstract
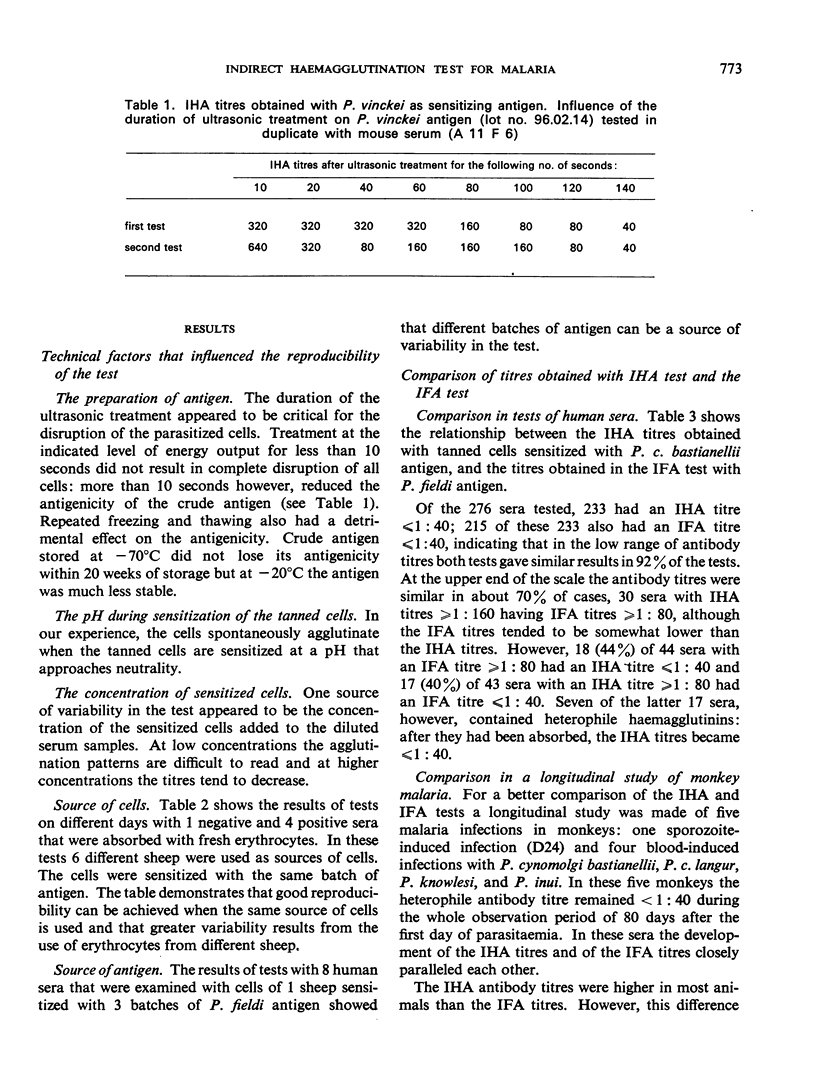
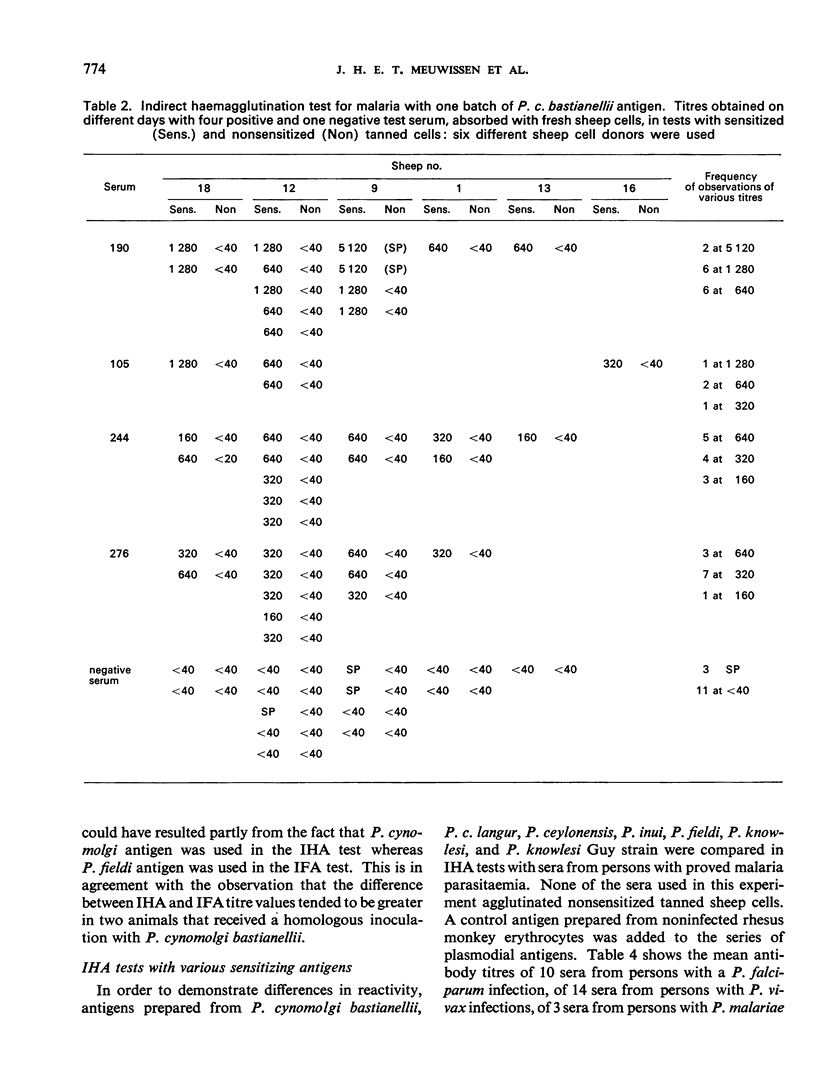
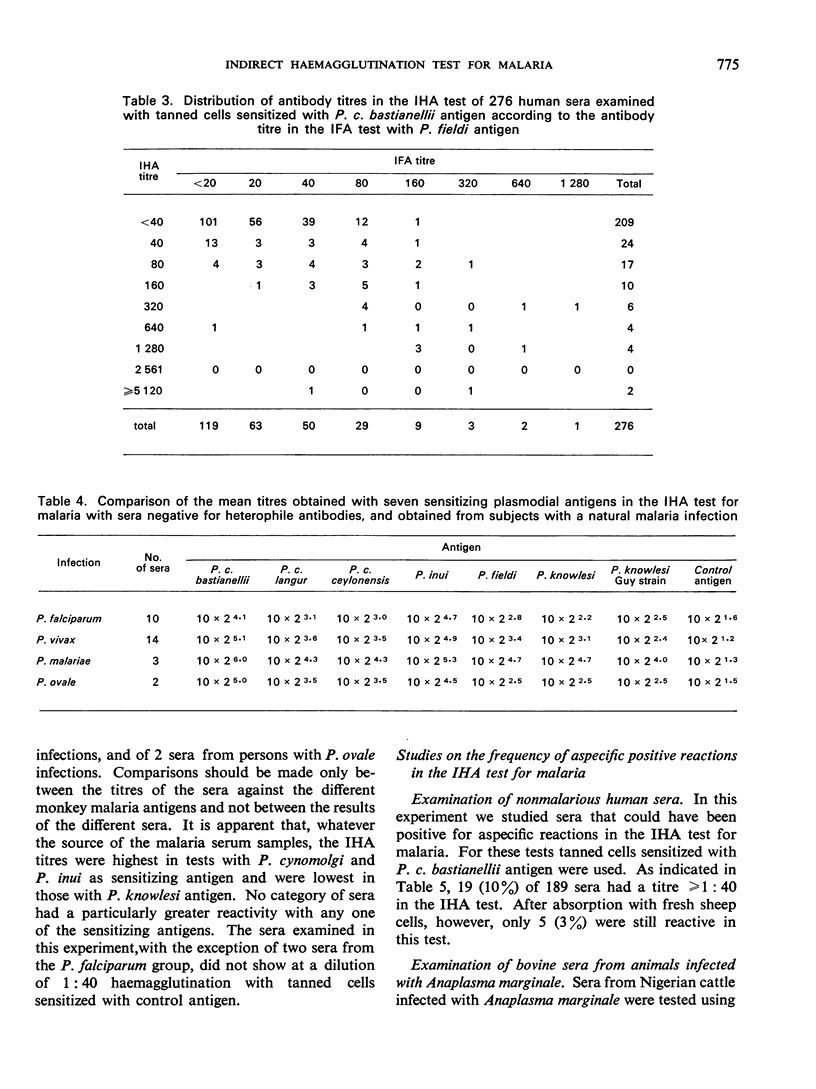
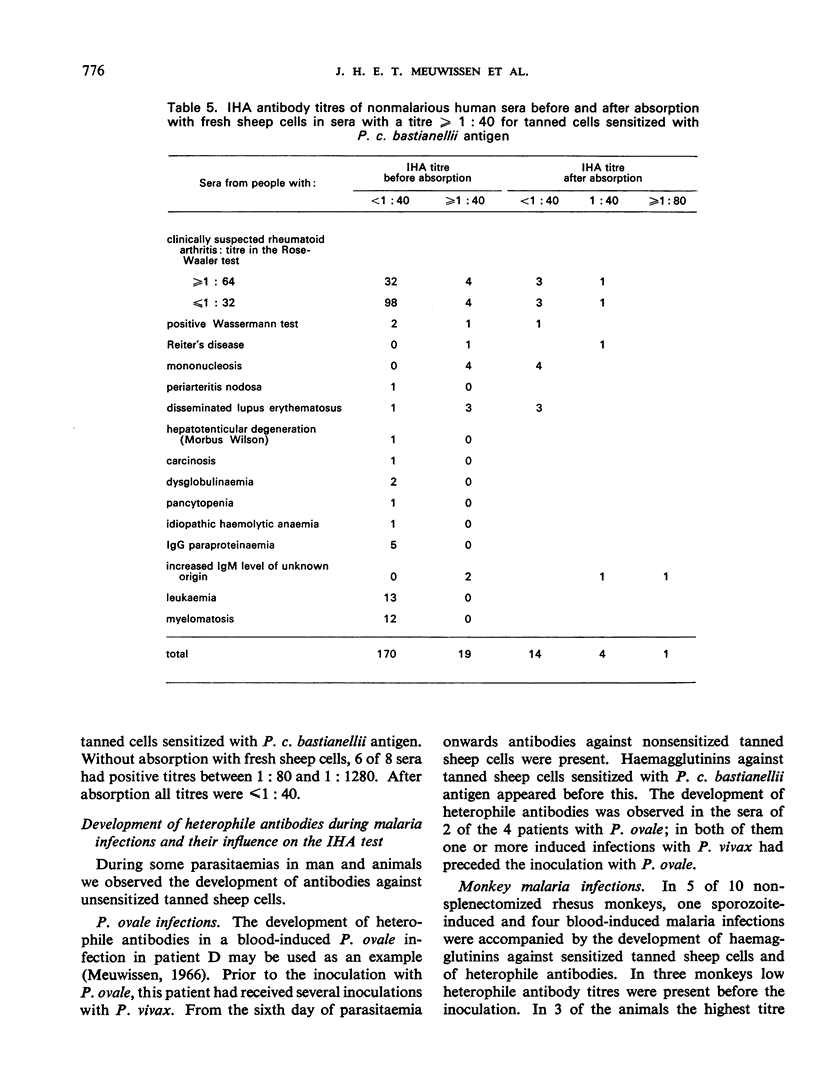
This paper gives the results of studies on various technical aspects of the indirect haemagglutination (IHA) test for malaria, on the similarity of the results obtained in the IHA test and in the indirect fluorescent antibody test, on the use of various plasmodial extracts as sensitizing antigens in the IHA test, and on the influence of heterophile antibodies on the titres obtained in the IHA test. Some longitudinal observations on induced malaria infections of man and monkey showed that the infection can induce the production of heterophile antibodies: their appearance, however, remains unpredictable. In some infections agglutinins against host erythrocyte components are also produced. Absorption of sera with tanned sheep cells sensitized with noninfected host red blood cell antigens is advocated as a control on the IHA titre for specific agglutinins.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adeniyi-Jones C. Agglutination of tanned sheep erythrocytes by serum from Nigerian adults and children. Lancet. 1967 Jan 28;1(7483):188–190. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91826-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray R. S. The Stein and Desowitz haemagglutination test for the detection of antibodies to Plasmodium berghei and Plasmodium vinckei. Ann Soc Belges Med Trop Parasitol Mycol. 1965;45(4):397–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray R. S., el-Nahal H. M. Indirect haemagglutination test for malarial antibody. Nature. 1966 Oct 1;212(5057):83–83. doi: 10.1038/212083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTAIN C. C., BAUMGARTEN A., GORMAN J., KIDSON C., CHAMPNESS L., RODRIGUE R., GAJDUSEK D. C. COLD HAEMAGGLUTININS: UNUSUAL INCIDENCE IN MELANESIAN POPULATIONS. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jul;11:471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M. Heterophile antibodies in Nigerian sera. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Feb;6(2):197–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba V., Allison A. C. M-antiglobulins (rheumatoid-factor-like globulins) and other gamma-globulins in relation to tropical parasitic infections. Lancet. 1966 Apr 16;1(7442):848–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano K., McGregor I. A., Milgrom F. Hemagglutinins in sera of Africans of Gambia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):849–853. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuwissen J. H. Fluorescent antibodies in human malaria, especially in Plasmodium ovale. Trop Geogr Med. 1966 Sep;18(3):250–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers W. A., Jr, Fried J. A., Kagan I. G. A modified, indirect microhemagglutination test for malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 Nov;17(6):804–809. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAVITSKY A. B. Micromethods for the study of proteins and antibodies. I. Procedure and general applications of hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition reactions with tannic acid and protein-treated red blood cells. J Immunol. 1954 May;72(5):360–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN B., DESOWITZ R. S. THE MEASUREMENT OF ANTIBODY IN HUMAN MALARIA BY A FORMOLIZED TANNED SHEEP CELL HAEMAGGLUTINATION TEST. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:45–49. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaper A. G., Kaplan M. H., Mody N. J., McIntyre P. A. Malarial antibodies and autoantibodies to heart and other tissues in the immigrant and indigenous peoples of Uganda. Lancet. 1968 Jun 22;1(7556):1342–1346. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M., Sulzer A. J., Rogers W. A., Jr, Fried J. A., Mathews H. M. Comparison of the indirect-fluorescent antibody and indirect-hemagglutination tests for malarial antibody. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Jan;20(1):6–9. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1971.20.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


