Abstract
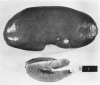
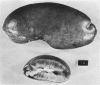
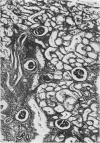
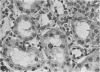
In Denmark a nephropathy in pigs characterized by tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis has been identified frequently during the last 5 decades in the course of meat inspection in slaughterhouses. The disease was first described by Larsen, who recognized the connexion between feeding mouldy rye to pigs and the development of the nephropathy. In this study kidneys were examined from 19 pigs coming from a farm with an outbreak of nephropathy. The barley fed to the pigs was contaminated with the mycotoxin ochratoxin A. Histological examination revealed different degrees of change ranging from slight regressive changes in the tubular epithelium and periglomerular and interstitial fibrosis to tubular atrophy, thickened basement membranes, glomerular sclerosis, and marked fibrosis. These differences were considered to be due to differences in the length of time of exposure to the mouldy barley and differences in the amount of mycotoxin consumed by the individual pig. However, it will be necessary to carry out experiments using crystalline ochratoxin A in order to prove such a relationship. Mycotoxins have also been suggested as etiological factors in Balkan nephropathy in man, which in the initial stages is characterized by tubular lesions similar to those seen in mycotoxic nephropathy in pigs.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Krogh P., Hald B., Pedersen E. J. Occurrence of ochratoxin A and citrinin in cereals associated with mycotoxic porcine nephropathy. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):689–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh P., Hasselager E., Friis P. Studies on fungal nephrotoxicity. 2. Isolation of two nephrotoxic compounds from Penicillium viridicatum Westling: citrinin and oxalic acid. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(4):401–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purchase I. F., Theron J. J. The acute toxicity of ochratoxin A to rats. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1968 Dec;6(4):479–483. doi: 10.1016/0015-6264(68)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotwell O. L., Hesseltine C. W., Goulden M. L. Ochratoxin A: occurrence as natural contaminant of a corn sample. Appl Microbiol. 1969 May;17(5):765–766. doi: 10.1128/am.17.5.765-766.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]