Abstract
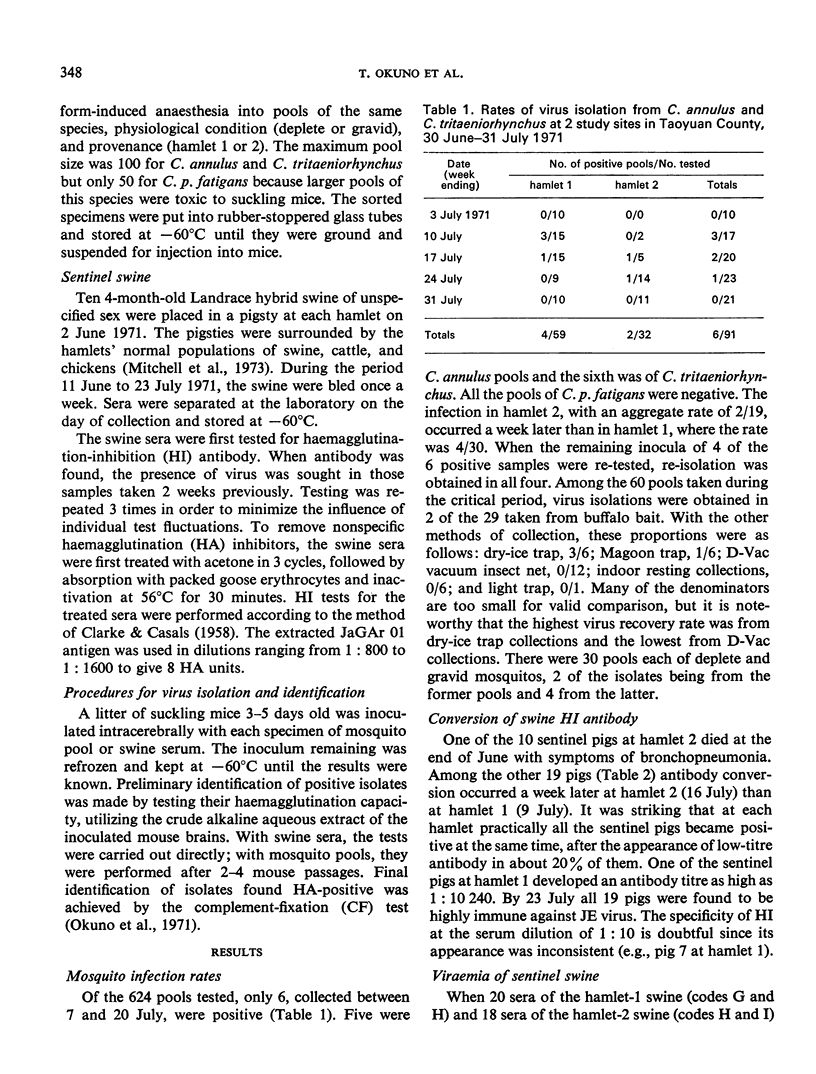
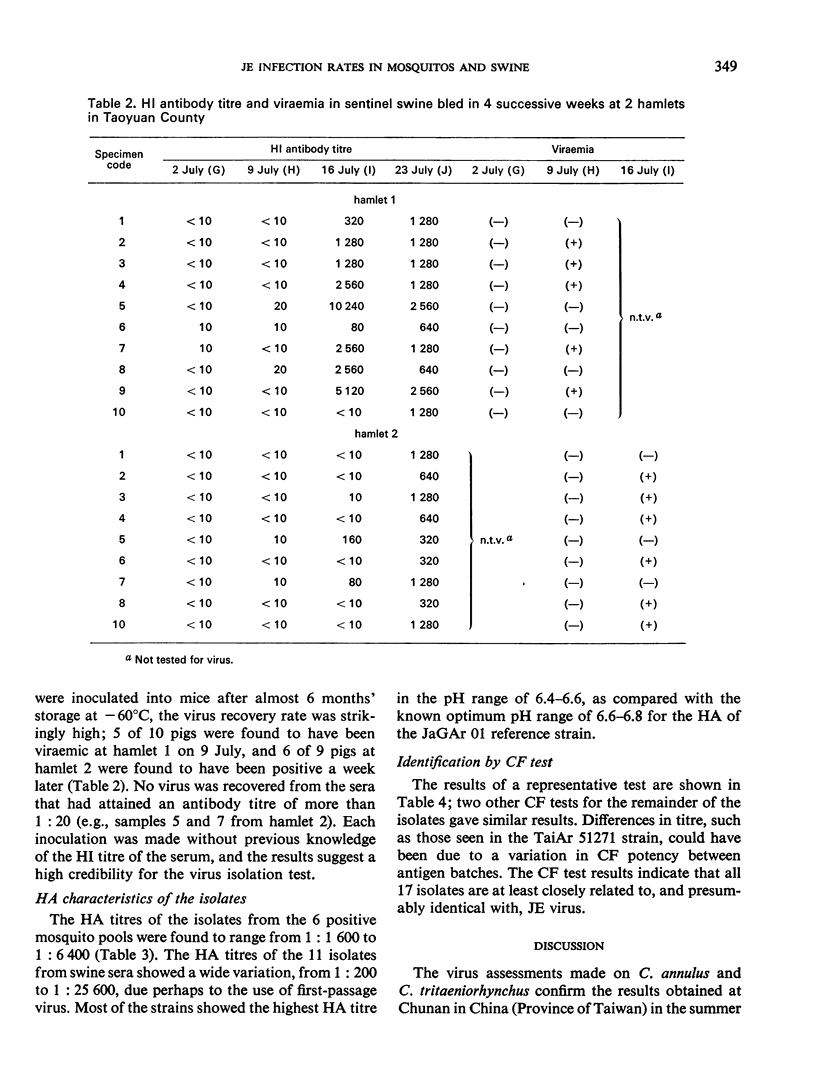
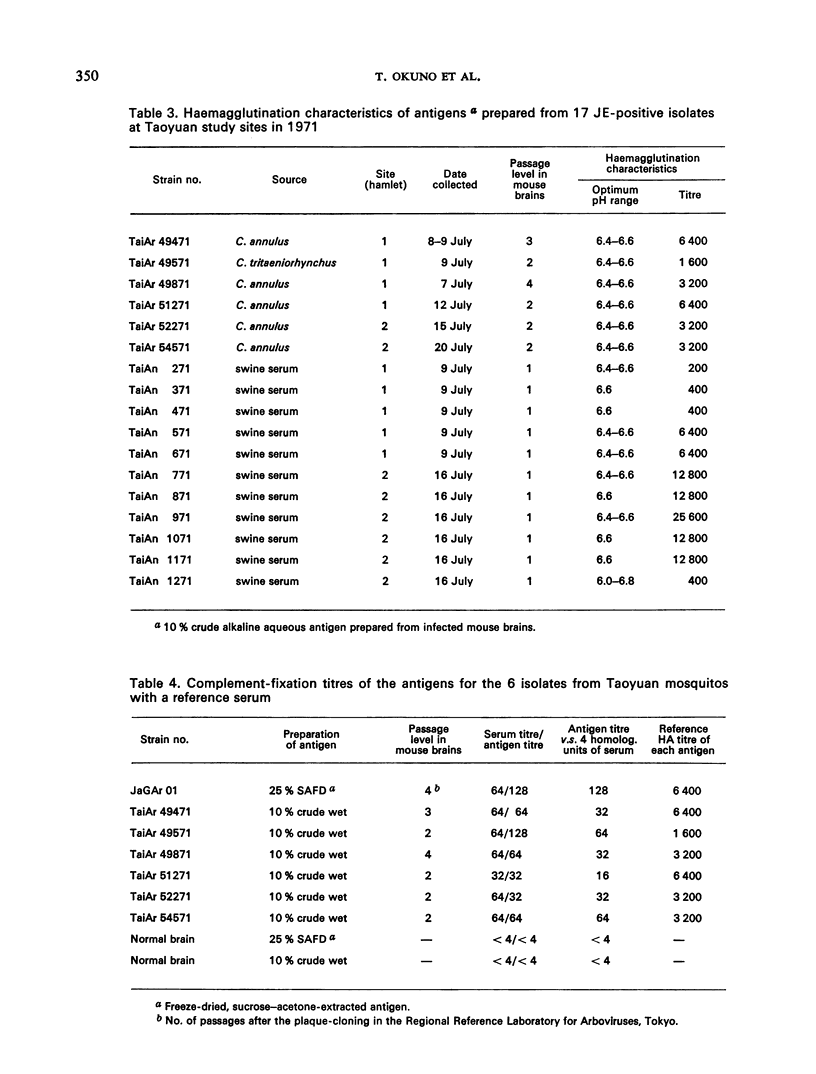
A year-round study of the infection rates of JE virus in Culex mosquitos was made during 1970-71 in 2 hamlets in Taoyuan County, China (Province of Taiwan). JE virus was recovered from 5 of 314 pools of C. annulus, and from 1 of 22 pools of C. tritaeniorhynchus; these recoveries occurred during a 14-day period in July 1971. None of the 288 pools of C. p. fatigans, which had been collected between October and April, was positive. In addition, sentinel swine were assessed for antibody and virus. All the pigs became highly immune by 23 July; in each hamlet all the pigs had become infected within 1 week, virus being detected in them for only 1-2 weeks. Virus-positive mosquitos appeared to have obtained their infections at about the time that viraemia was occurring in the sentinel swine. These observations illustrate once again the lower infection rate and shorter duration of virus-positive mosquitos in China (Province of Taiwan) as compared with Japan.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUESCHER E. L., SCHERER W. F. Ecologic studies of Japanese encephalitis virus in Japan. IX. Epidemiologic correlations and conclusions. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1959 Nov;8:719–722. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1959.8.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUESCHER E. L., SCHERER W. F., ROSENBERG M. Z., GRESSER I., HARDY J. L., BULLOCK H. R. Ecologic studies of Japanese encephalitis virus in Japan. II. Mosquito infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1959 Nov;8:651–664. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1959.8.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cates M. D., Detels R. Japanese encephalitis virus in Taiwan: preliminary evidence for Culex annulus Theob. as a vector. J Med Entomol. 1969 Aug;6(3):327–328. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/6.3.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cates M., McCroddan D., Huang W., Chiu S., Lien S. Japanese encephalitis virus surveillance in Taiwan. I. Isolations from mosquitoes 1967-1968. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1969 Dec 28;68(12):663–665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detels R., Cates M. D., Cross J. H., Irving G. S., Watten R. H. Ecology of Japanese encephalitis virus on Taiwan in 1968. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Jul;19(4):716–723. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRESSER I., HARDY J. L., HU S. M., SCHERER W. F. Factors influencing transmission of Japanese B encephalitis virus by a colonized strain of Culex tritaeniorhynchus Giles, from infected pigs and chicks to susceptible pigs and birds. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Jul;7(4):365–373. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRESSER I., HARDY J. L., SCHERER W. F. The growth curve of Japanese encephalitis virus in the vector mosquito of Japan, Culex tritaeniorhynchus. Jpn J Exp Med. 1958 Aug;28(4):243–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLBUT H. S. THE PIG-MOSQUITO CYCLE OF JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS IN TAIWAN. J Med Entomol. 1964 Oct;1:301–307. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/1.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno J., Endo K., Agatsuma H., Ishida N. Cyclic outbreaks of Japanese encephalitis among pigs and humans. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Sep;84(2):292–300. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. J., Chen P. S., Boreham P. F. Host-feeding patterns and behaviour of 4 Culex species in an endemic area of Japanese encephalitis. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;49(3):293–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. J., Chen P. S. Ecological studies on the mosquito vectors of Japanese encephalitis. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;49(3):287–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muangman D., Edelman R., Sullivan M. J., Gould D. J. Experimental transmission of Japanese encephalitis virus by Culex fuscocephala. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1972 Jul;21(4):482–486. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1972.21.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno T., Tseng P. T., Liu S. Y., Hsu S. Y., Huang C. T. Rates of infection with Japanese encephalitis virus of two culicine species of mosquito in Taiwan. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;44(5):599–604. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M. [Mosquito vector of Japanese encephalitis virus--its ecology and physiology]. Shinkei Kenkyu No Shimpo. 1967 Aug;11(2):215–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG S. P., GRAYSTON J. T., HU S. M. Encephalitis on Taiwan. III. Virus isolations from mosquitoes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1962 Jan;11:141–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


