Abstract
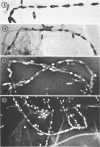
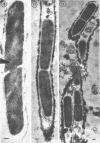
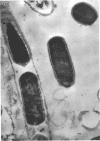
Many strains of Clostridium sporogenes were shown to contain two types of cells which exhibited strikingly different growth habits. Over 99% of the population of most strains were motile bacilli which occurred singly or in short chains. Infection by any of several C. sporogenes bacteriophages lysed most of these cells and revealed a minority population component consisting of cells which grew in extremely long chains. Each chain was surrounded by and contained in a long tubular polysaccharide sheath which was ultrastructurally quite separate and distinct from the cell walls of the enclosed cells. The sheathed cells were identical to “normal” cells of C. sporogenes in anaerobiosis, Gram reaction, sporulation, deoxyribonucleic base composition, general morphology, and ultrastructure. They differed from the “normal” cells in having a sheath, in being nonmotile, and in that they were infected by C. sporogenes bacteriophages but not usually lysed by them. The sheathed cells appeared spontaneously in cultures cloned from single colonies and were demonstrably present in cultures before bacteriophage infection. Thus, they were not contaminants but were normal, although inconspicuous, growth forms of C. sporogenes which were selected but not induced by bacteriophage infection.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BETZ J. V., ANDERSON K. E. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BACTERIOPHAGES ACTIVE ON CLOSTRIDIUM SPOROGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:408–415. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.408-415.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz J. V. Some properties of bacteriophages active on the obligate anaerobe Clostridium sporogenes. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONDERO N. C. Sphaerotilus, its nature and economic significance. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1961;3:77–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70507-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Johnson A., Stokes J. L. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of Sphaerotilus natans and Sphaerotilus discophorus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1657–1658. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1657-1658.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Murray R. G. Ultrastructure of the cell wall of Bacillus polymyxa. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1949–1965. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1949-1965.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santo L. M., Hohl H. R., Frank H. A. Ultrastructure of putrefactive anaerobe 3679h during sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):824–833. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.824-833.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONOMURA B., MALKIN R., RABINOWITZ J. C. DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BASE COMPOSITION OF CLOSTRIDIAL SPECIES. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1438–1439. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1438-1439.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi A., Nakamura K., Ueda M. Electron microscope studies of the intracytoplasmic membrane system in Clostridium tetani and Clostridium botulinum. Jpn J Microbiol. 1965 Sep;9(3):131–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1965.tb00282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]