Abstract
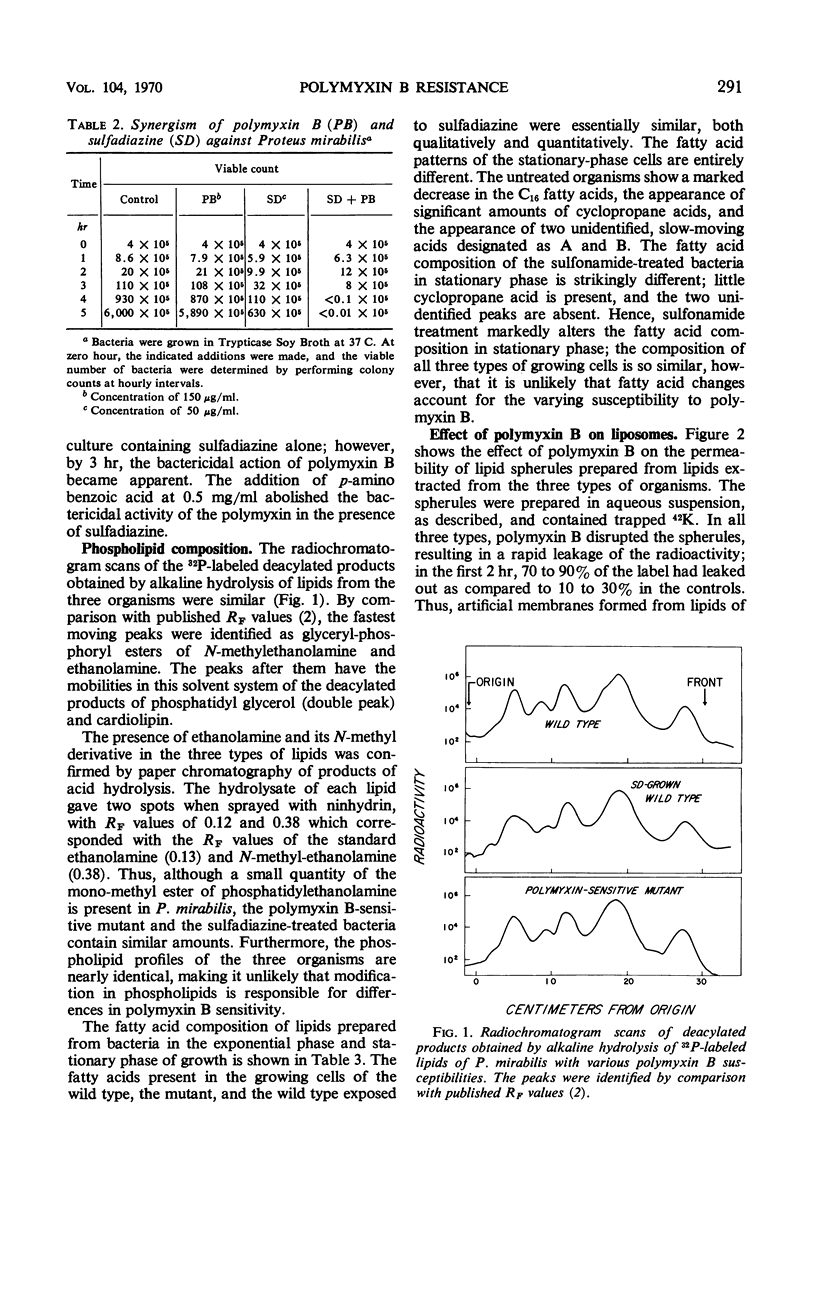
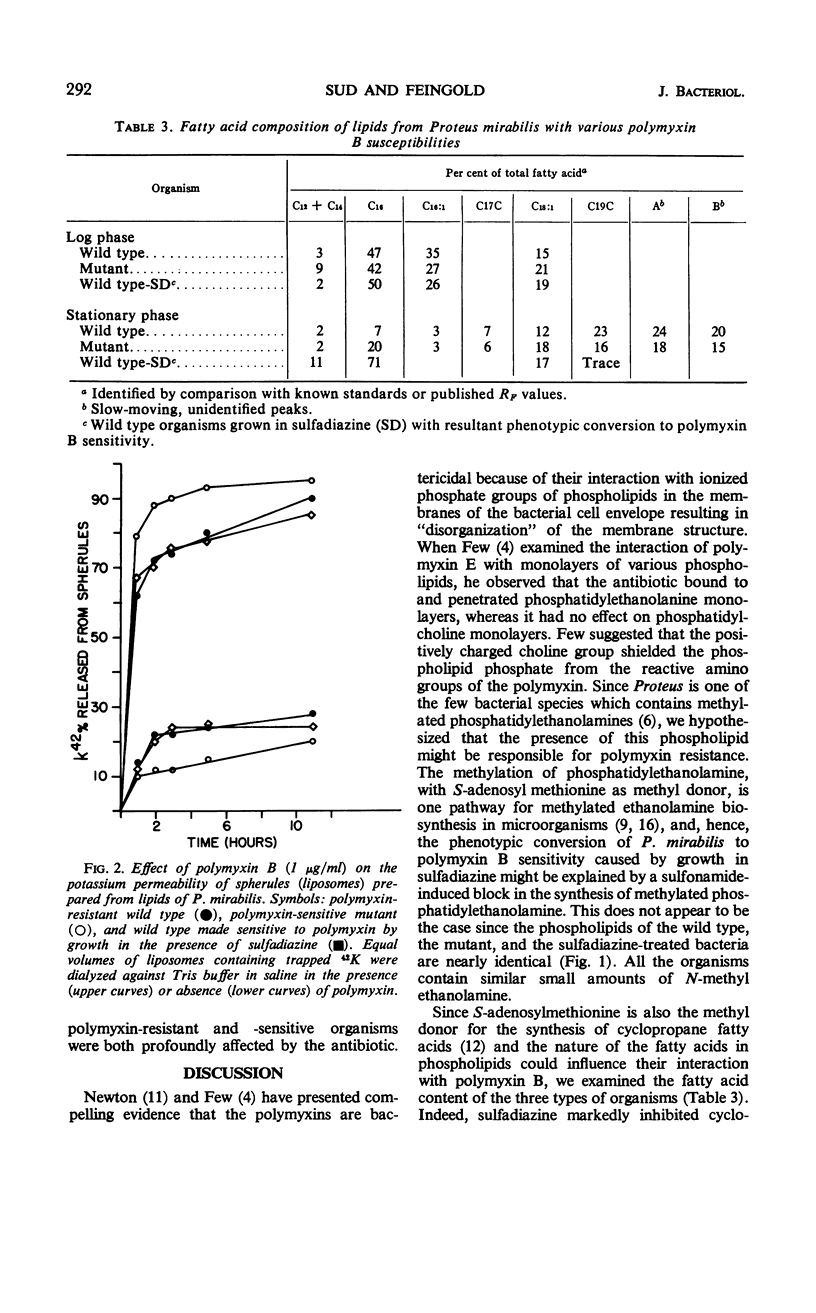
The lipids from three types of organisms—a Proteus mirabilis wild type highly resistant to polymyxin B, a polymyxin B-sensitive mutant derived from the wild type, and the wild type grown in the presence of sulfadiazine resulting in phenotypic conversion to polymyxin B sensitivity—were examined to determine the nature of polymyxin B resistance. The phospholipid compositions were nearly identical; each organism contained similar small amounts of N-methyl phosphatidylethanolamine in addition to comparable quantities of phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, and cardiolipin. the fatty acid compositions were similar in the exponential phase of growth; in the stationary phase, sulfadiazine markedly inhibited the synthesis of cyclopropane fatty acids. Liposomes prepared from the dried lipids of the three types of organisms were extensively and similarly disrupted by the polymyxin. These findings suggest that polymyxin B resistance in P. mirabilis is determined by the cell envelope which prevents access of the antibiotic to the susceptible lipid target sites.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deykin D., Desser R. K. The incorporation of acetate and palmitate into lipids by human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1590–1602. doi: 10.1172/JCI105851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEW A. V. The interaction of polymyxin E with bacterial and other lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDFINE H., ELLIS M. E. N-METHYL GROUPS IN BACTERIAL LIPIDS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:8–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.8-15.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield S., Feingold D. S. The synergistic action of the sulfonamides and the polymyxins against Serratia marcescens. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):555–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERMAN L. G. Antibiotic sensitivity using pretreated plates. II. A demonstration of inhibitory activity with a low level combination of a sulfonamide and polymyxin B against Proteus species. Antibiot Annu. 1958;6:836–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANESHIRO T., LAW J. H. PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE SYNTHESIS IN AGROBACTERIUM TUMEFACIENS. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF A PHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE N-METHYLTRANSFERASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1705–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIVE L. A NONSPECIFIC INCREASE IN PERMEABILITY IN ESCHERICHIA COLI PRODUCED BY EDTA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Apr;53:745–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. The properties and mode of action of the polymyxins. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):14–27. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.14-27.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL F. E. SYNERGISM BETWEEN SULPHONAMIDE DRUGS AND ANTIBIOTICS OF THE POLYMYXIN GROUP AGAINST PROTEUS SP. IN VITRO. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jul;16:362–366. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.4.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D. Drug resistance of bacteria. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jan 9;280(2):91–94. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196901092800208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A., Nyc J. F. Methylation of ethanolamine phosphatides by microsomes from normal and mutant strains of Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):238–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARLOV A. R., KENNEDY E. P. THE BETA-GALACTOSIDE PERMEASE SYSTEM AND THE METABOLISM OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBENECK U. Susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis and its stable L-forms to erythromycin and other macrolides. Nature. 1962 Oct 13;196:195–196. doi: 10.1038/196195b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M. Susceptibility to polymyxin B in penicillin G-induced Proteus mirabilis L forms and spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):347–350. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.347-350.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


