Abstract
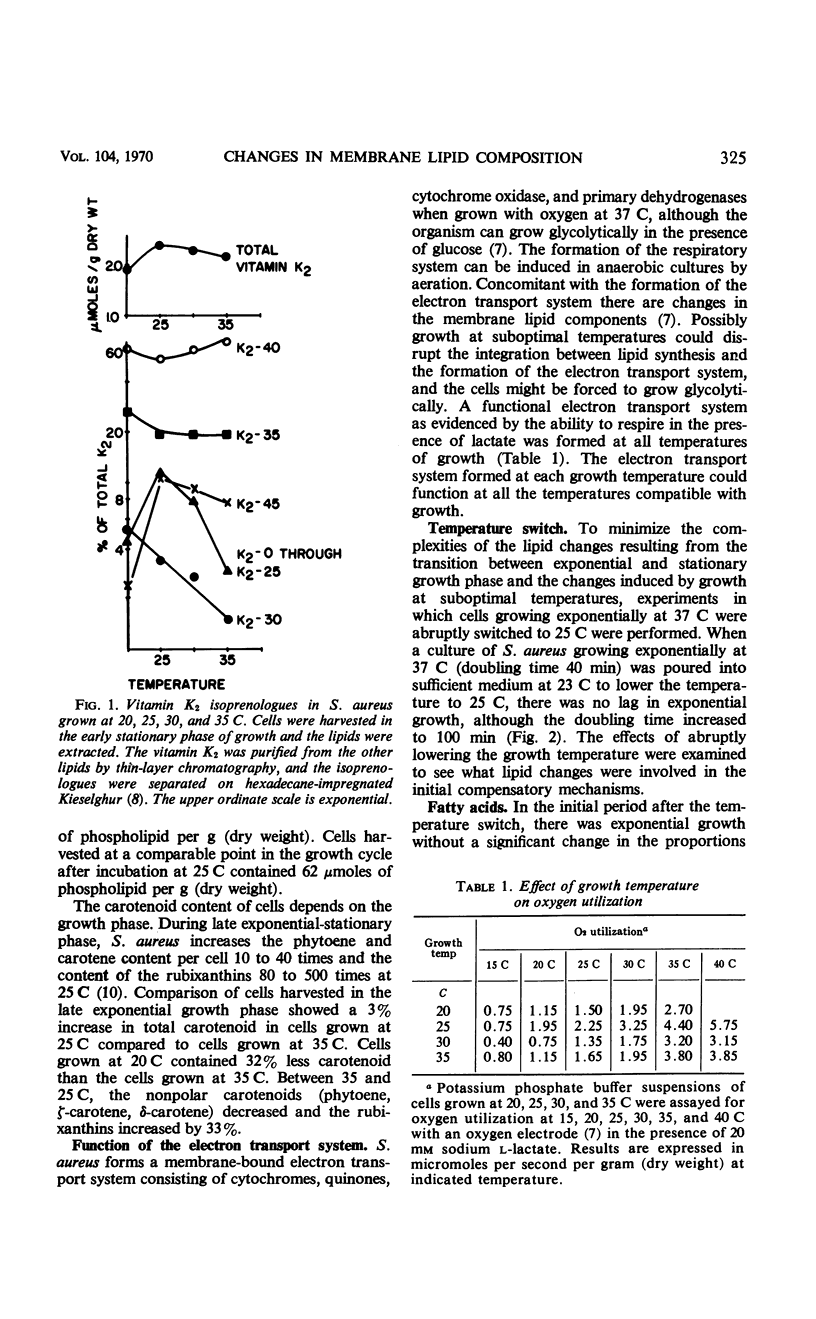
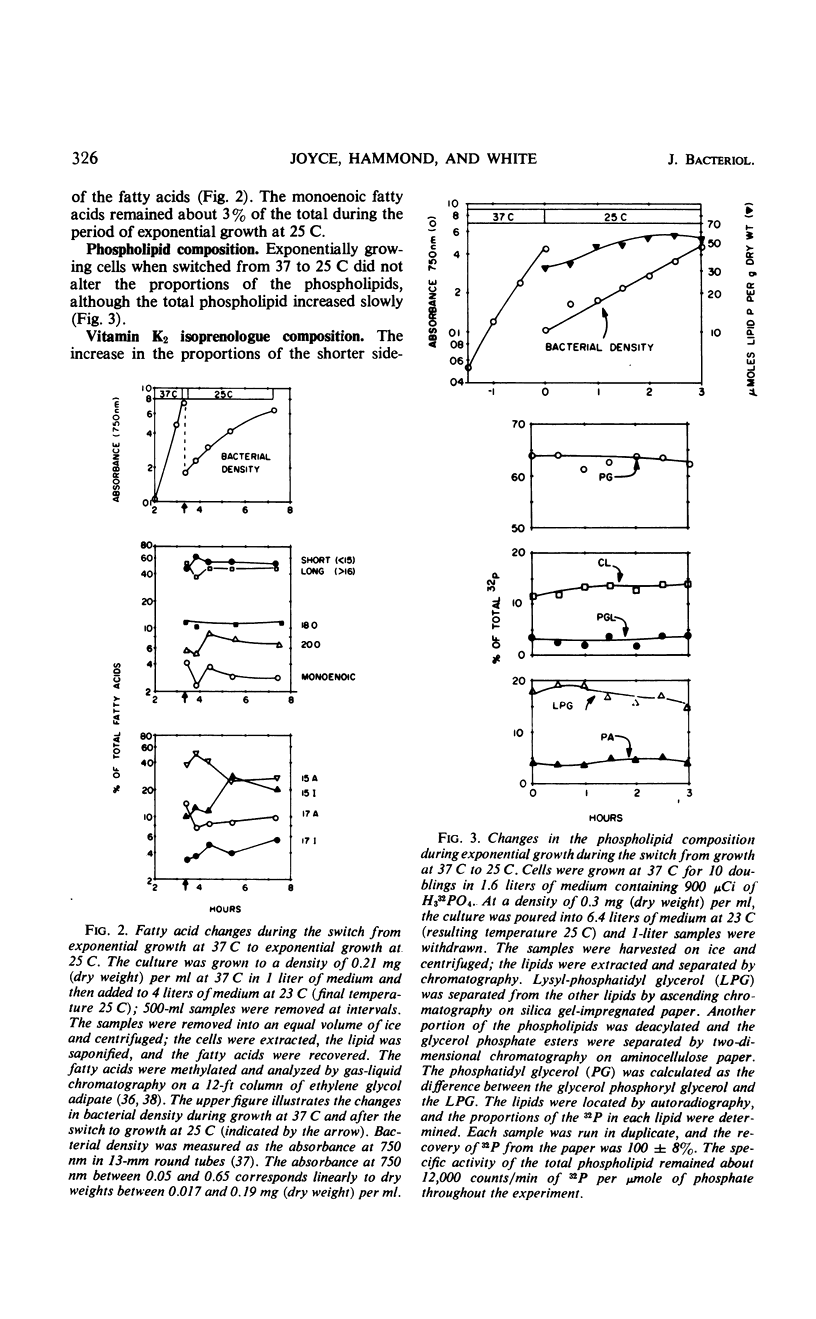
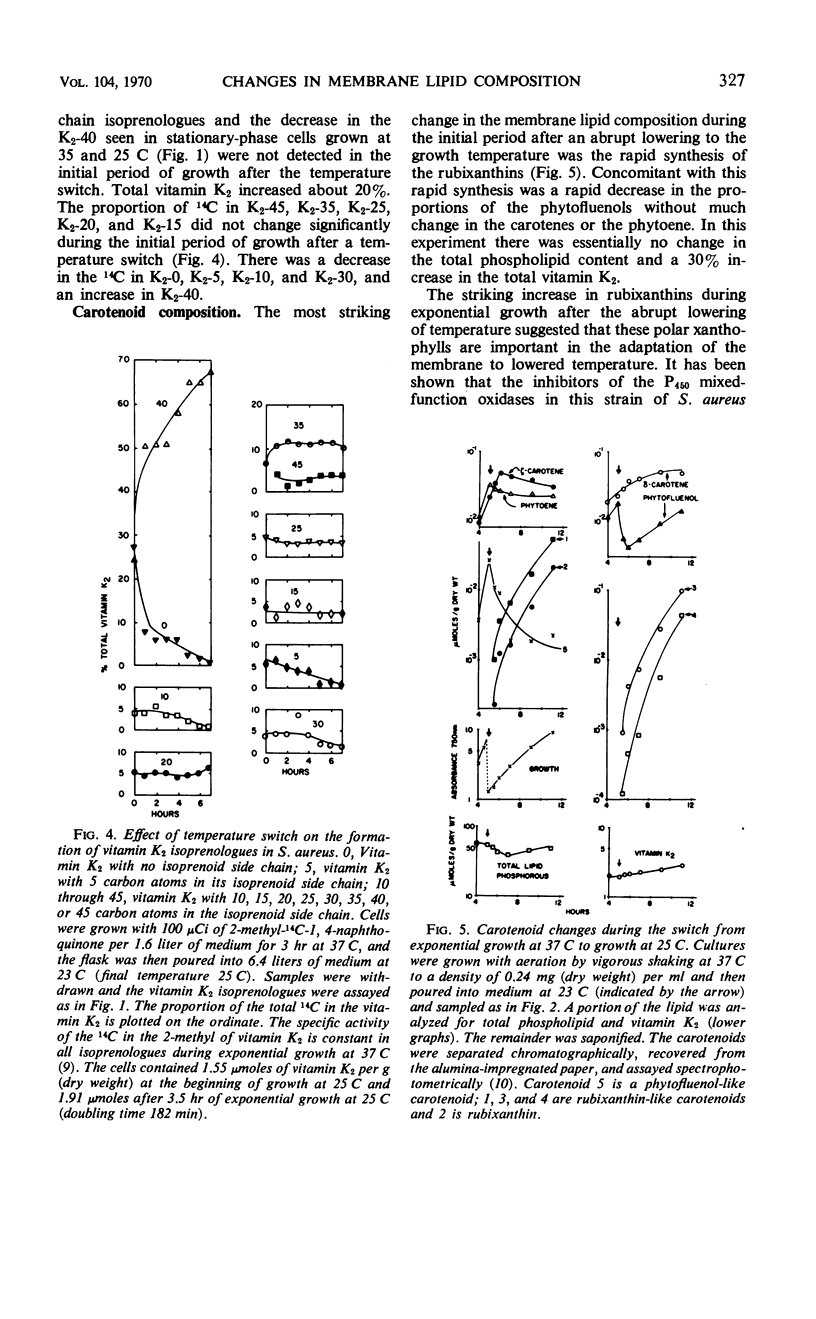
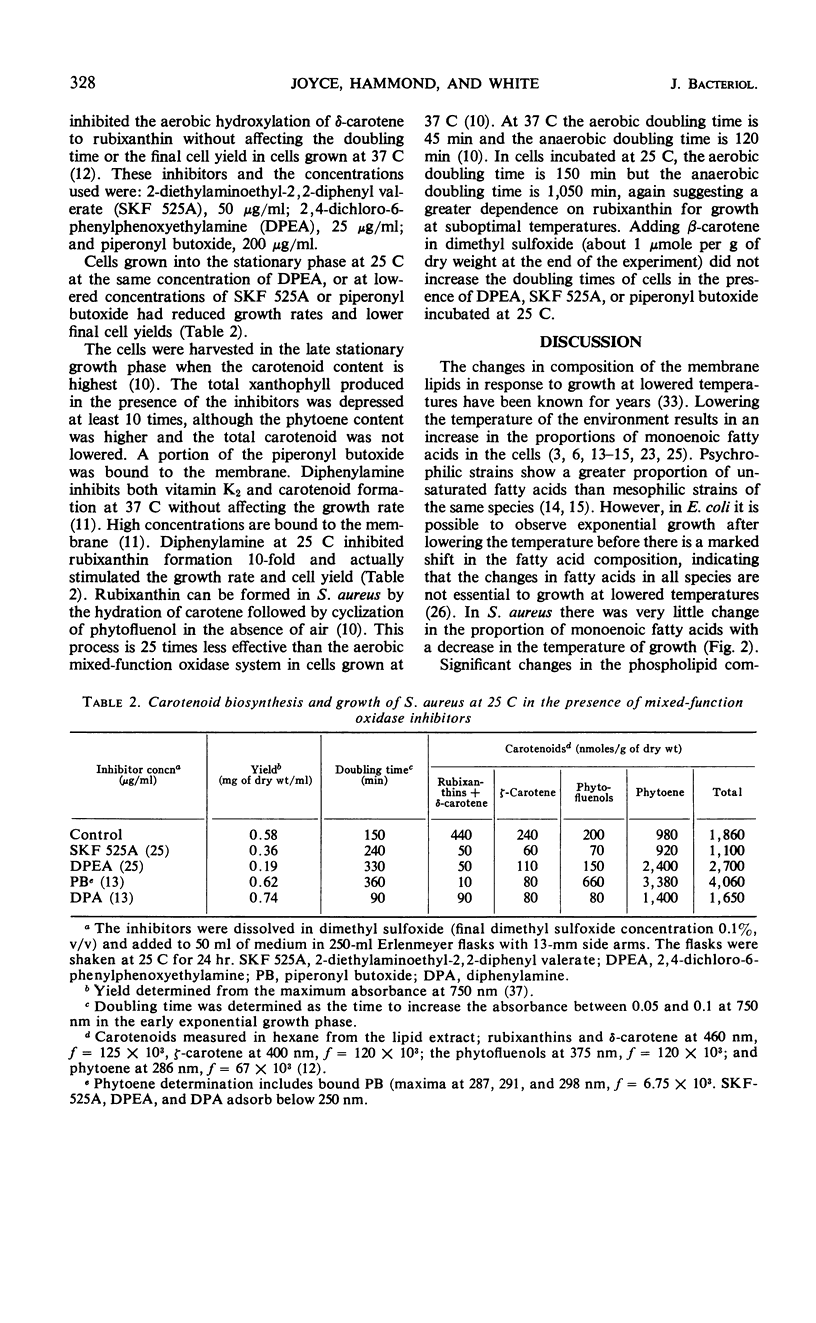
Lowering the temperature of growth of Staphylococcus aureus from 37 to 25 C decreased the growth rate and induced changes in the composition of the membrane lipids. Changes in lipid composition also occur in the transition between exponential and stationary growth phases at one temperature. To isolate the effects of lowering the temperature, exponentially growing S. aureus was abruptly switched from 37 to 25 C by transfer to cooler medium. Exponential growth continued at 25 C without a lag period but with a threefold increase in doubling time. In the period of exponential growth at suboptimal temperature, there was essentially no change in the fatty acid composition of the lipids, little change in the vitamin K2 composition with perhaps a slight increase in the total level, and essentially no change in the phospholipid composition, but a marked stimulation of the synthesis of the rubixanthins. Growth of cells at 25 C was much more sensitive to the inhibition of rubixanthin formation by mixed-function oxidase inhibitors than cells growing at 37 C, suggesting some function for the rubixanthins at suboptimal temperatures. The striking increases in the proportions of monoenoic fatty acids observed at lowered growth temperatures in many biological systems are not detected in S. aureus.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATRA P. P., RILLING H. C. ON THE MECHANISM OF PHOTOINDUCED CAROTENOID SYNTHESIS: ASPECTS OF THE PHOTOINDUCTIVE REACTION. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Sep;107:485–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90305-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP D. G., STILL J. L. FATTY ACID METABOLISM IN SERRATIA MARCESCENS. IV. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON FATTY ACID COMPOSITION. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:87–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batra P. P. Mechanism of photoinduced carotenoid synthesis. Induction of carotenoid synthesis by antimycin A in the absence of light in mycobacterium marinum. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5630–5635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Siervo A. J. Alterations in the phospholipid composition of Escherichia coli B during growth at different temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1342–1349. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1342-1349.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J., Rose A. Temperature effects on microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:101–120. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., White D. C. Membrane lipid changes during formation of a functional electron transport system in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1868–1874. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1868-1874.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Carotenoid formation by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):191–198. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.191-198.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Formation of vitamin K2 isoprenologues by Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):573–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.573-578.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Inhibition of carotenoid hydroxylation in Staphylococcus aureus by mixed-function oxidase inhibitors. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):607–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.607-610.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Inhibition of vitamin K2 and carotenoid synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus by diphenylamine. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):611–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.611-615.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. K., White D. C. Separation of vitamin K2 isoprenologues by reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1969 Dec 23;45(3):446–452. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)86242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. L. Biosynthesis and function of carotenoid pigments in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:163–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M., BAXTER R. M. Lipid composition of mesophilic and psychrophilic yeasts (Candida species) as influenced by environmental temperature. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Sep;40:1213–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATES M., HAGEN P. O. INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON FATTY ACID COMPOSITION OF PSYCHROPHILIC AND MESOPHILIC SERRATIA SPECIES. Can J Biochem. 1964 Apr;42:481–488. doi: 10.1139/o64-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. Bacterial lipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1964;2:17–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS M. M., SISTROM W. R. The function of the carotenoid pigments of Sarcina lutea. Arch Mikrobiol. 1960;35:139–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00425002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr A. G., Ingraham J. L. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE COMPOSITION OF FATTY ACIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1260-1267.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NG H., INGRAHAM J. L., MARR A. G. Damage and derepression in Escherichia coli resulting from growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:331–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.331-339.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuyama H. Phospholipid metabolism in Escherichia coli after a shift in temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;176(1):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILLING H. C. Photoinduction of carotenoid synthesis of a Mycobacterium sp. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 16;60:548–556. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90873-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. H. Physiology of micro-organisms at low temperatures. J Appl Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;31(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1968.tb00336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. THE CAROTENOID PIGMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:307–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEUER W. Die Bedeutung verschiedener Umwelteinflüsse auf die Zusammensetzung des Gesamtpigmentes von Micrococcus pyogenes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1957 Jun;168(7-8):558–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. K., Ingraham J. L. Fatty Acid Composition of Escherichia coli as a Possible Controlling Factor of the Minimal Growth Temperature. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):141–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.141-146.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C. Metabolism of the glycosyl diglycerides and phosphatidylglucose of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.126-132.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry O. C., Cooney J. J. Physicochemical factors influencing growth and pigment synthesis by Micrococcus roseus. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Aug;12(4):691–698. doi: 10.1139/m66-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Cox R. H. Indentification and localization of the fatty acids in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1079–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1079-1088.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Extraction, characterization, and cellular localization of the lipids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1854–1867. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1854-1867.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Fatty acid composition of the complex lipids of Staphylococcus aureus during the formation of the membrane-bound electron transport system. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2198–2209. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2198-2209.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C. Lipid composition of the electron transport membrane of Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1159–1170. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1159-1170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Tucker A. N. Phospholipid metabolism during changes in the proportions of membrane-bound respiratory pigments in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):199–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.199-209.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthier R. E. Two-dimensional chromatography on silica gel-loaded paper for the microanalysis of polar lipids. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):544–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


