Abstract
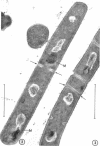
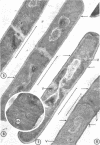
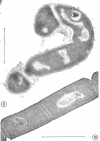
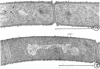
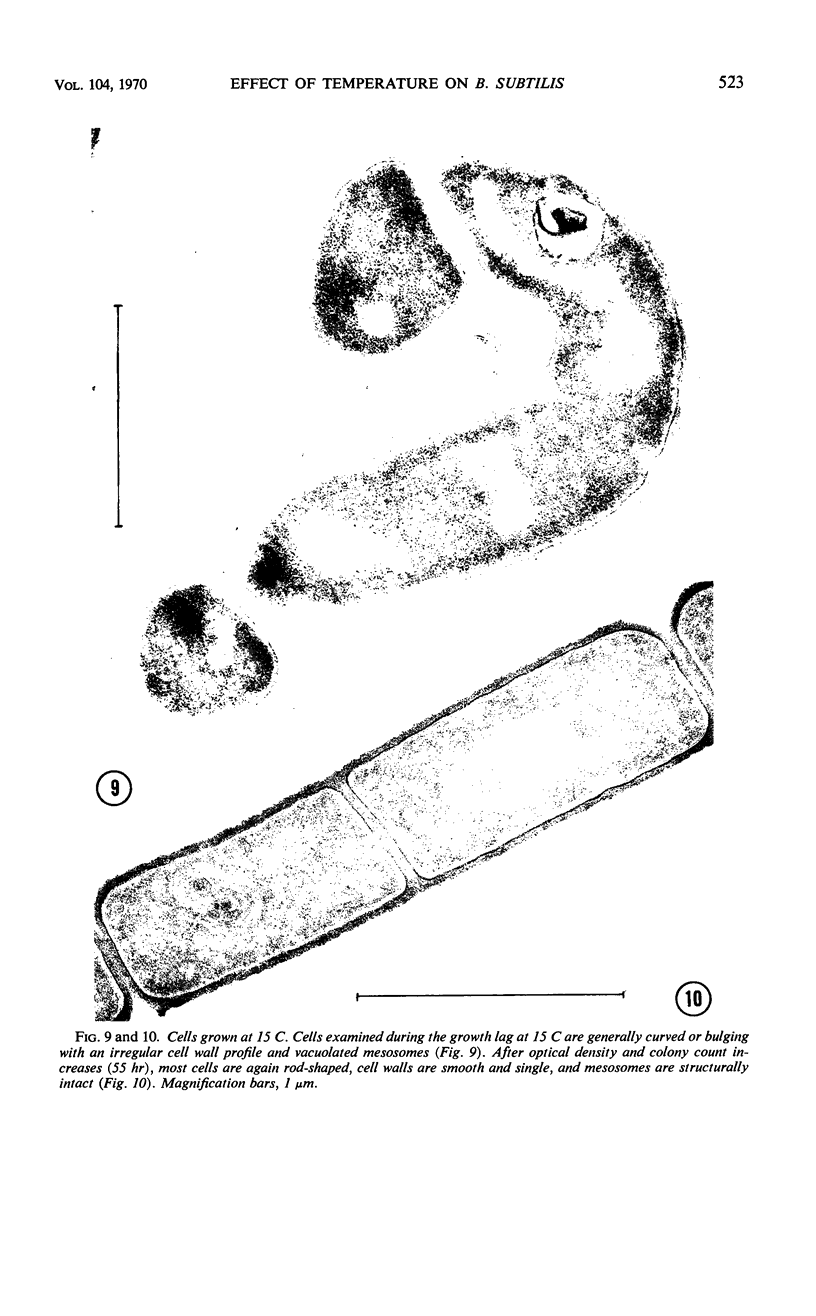
Logarithmically growing cultures of Bacillus subtilis transferred from 37 to 15 C present atypical growth curves, and ultrathin sections of such cells reveal structural modifications involving mesosome deterioration and double cell wall formation. After a time, optical density and viable count increase, and cells regain the appearance typical of control cells, indicating a recovery from thermal stress. Subcultures of such recovered cells continue to grow well at 15 C. Cultures transferred from 37 to 12 C show atypical growth and fine structure, although no recovery from this stress is seen. Cultures previously grown at 15 C continue to grow at 12 C, and, furthermore, do not show the ultrastructural alterations seen in similar cells with a 37 C thermal history. The results of these studies suggest that low temperatures induce structural modifications in B. subtilis, that the response of a population to thermal stress may change during the period of the stress, and that thermal history may influence the response of a population to thermal stress.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAPMAN G. B., HILLIER J. Electron microscopy of ultra-thin sections of bacteria I. Cellular division in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1953 Sep;66(3):362–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.3.362-373.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellar D. J., Lundgren D. G., Slepecky R. A. Fine structure of Bacillus megaterium during synchronous growth. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1189–1205. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1189-1205.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell J., Rose A. Temperature effects on microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:101–120. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitz-James P. C. DISCUSSION. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Sep;29(3):293–298. doi: 10.1128/br.29.3.293-298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAHAM J. L. Growth of psychrophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):75–80. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.1.75-80.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landman O. E., Ryter A., Fréhel C. Gelatin-induced reversion of protoplasts of Bacillus subtilis to the bacillary form: electron-microscopic and physical study. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2154–2170. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2154-2170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr A. G., Ingraham J. L. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE COMPOSITION OF FATTY ACIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1260-1267.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NG H., INGRAHAM J. L., MARR A. G. Damage and derepression in Escherichia coli resulting from growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:331–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.331-339.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE A. H., EVISON L. M. STUDIES ON THE BIOCHEMICAL BASIS OF THE MINIMUM TEMPERATURES FOR GROWTH OF CERTAIN PSYCHROPHILIC AND MESOPHILIC MICRO-ORGANISMS. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:131–141. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., McConnell M., Burdett I. D. Cell wall or membrane mutants of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis with grossly deformed morphology. Nature. 1968 Jul 20;219(5151):285–288. doi: 10.1038/219285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Association of the nucleus and the membrane of bacteria: a morphological study. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):39–54. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.39-54.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. K. Formation of filaments and synthesis of macromolecules at temperatures below the minimum for growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):221–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.221-230.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw M. K., Ingraham J. L. Fatty Acid Composition of Escherichia coli as a Possible Controlling Factor of the Minimal Growth Temperature. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):141–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.141-146.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. L., Larkin J. M. Comparative effect of temperature on the oxidative metabolism of whole and disrupted cells of a psychrophilic and a mesophilic species of Bacillus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):95–98. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.95-98.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigand R. A., Shively J. M., Greenawalt J. W. Formation and ultrastructure of extra membranes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):240–249. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.240-249.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]