Abstract
Halobacterium halobium amylase had optimal activity at pH 6.4 to 6.6 in sodium β-glycerophosphate buffer containing 0.05% NaCl at 55 C; Ca2+ was not required. End products from amylose were maltose, maltotriose, and glucose. The amylase, which was devoid of transglucosylase activity, had a multichain attack mechanism.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- French D., Mancusi J. L., Abdullah M., Brammer G. L. Separation of starch oligosaccharides by high temperature paper chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1965 Aug;19(2):445–447. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)99480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS N. E. The effect of salt concentrations on the biochemical reactions of some halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1957 Mar;3(2):249–255. doi: 10.1139/m57-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES P. K., HALVORSON H. O. PROPERTIES OF A PURIFIED HALOPHILIC MALIC DEHYDROGENASE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:316–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.316-326.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner D. J. Halophilic bacteria. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1968;10:73–99. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K., Stevenson J. Effect of salts and organic solvents on the activity of Halobacterium cutirubrum catalase. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):611–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.611-616.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBYT J., FRENCH D. Action pattern and specificity of an amylase from Bacillus subtilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Mar;100:451–467. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
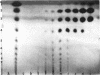
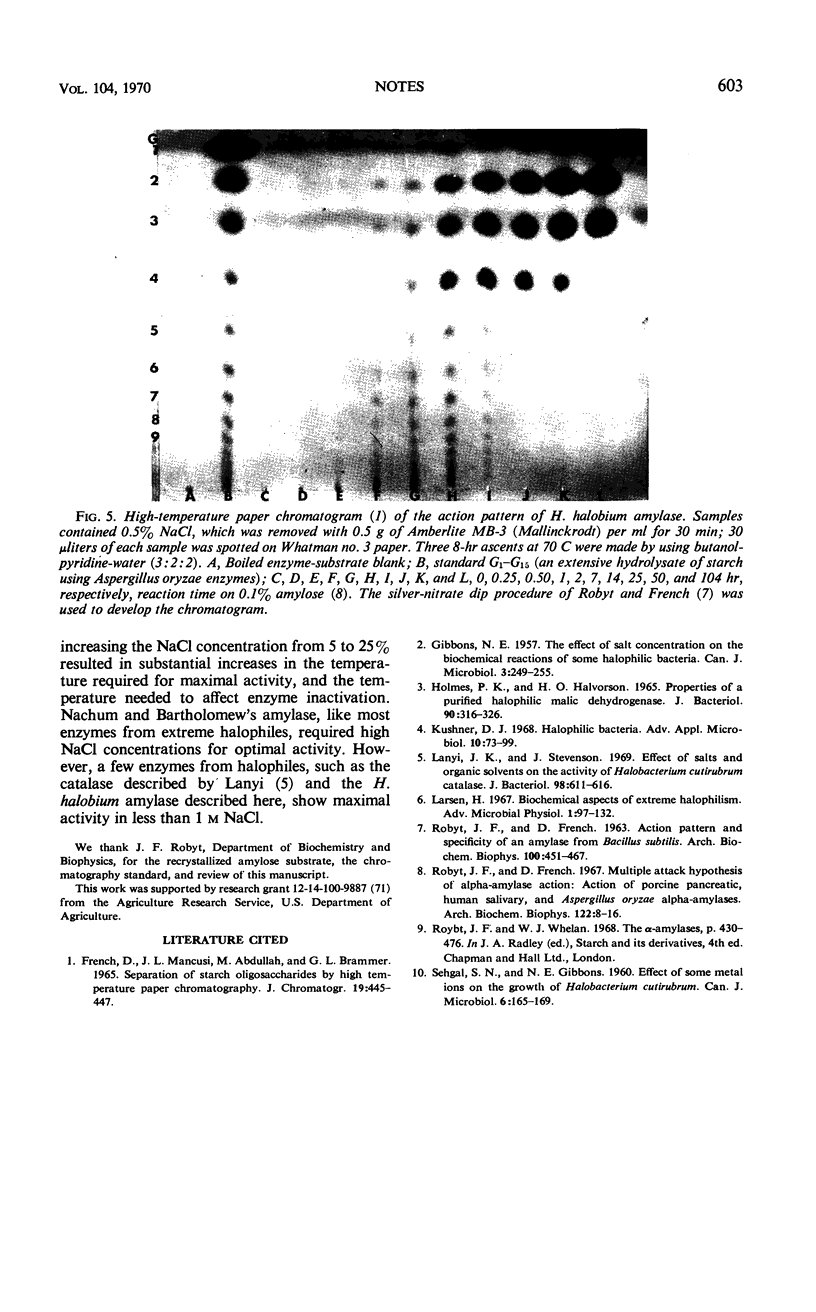
- Robyt J. F., French D. Multiple attach hypothesis of alpha-amylase action: action of porcine pancreatic, human salivary, and Aspergillus oryzae alpha-amylases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Oct;122(1):8–16. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEHGAL S. N., GIBBONS N. E. Effect of some metal ions on the growth of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Apr;6:165–169. doi: 10.1139/m60-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]