Abstract
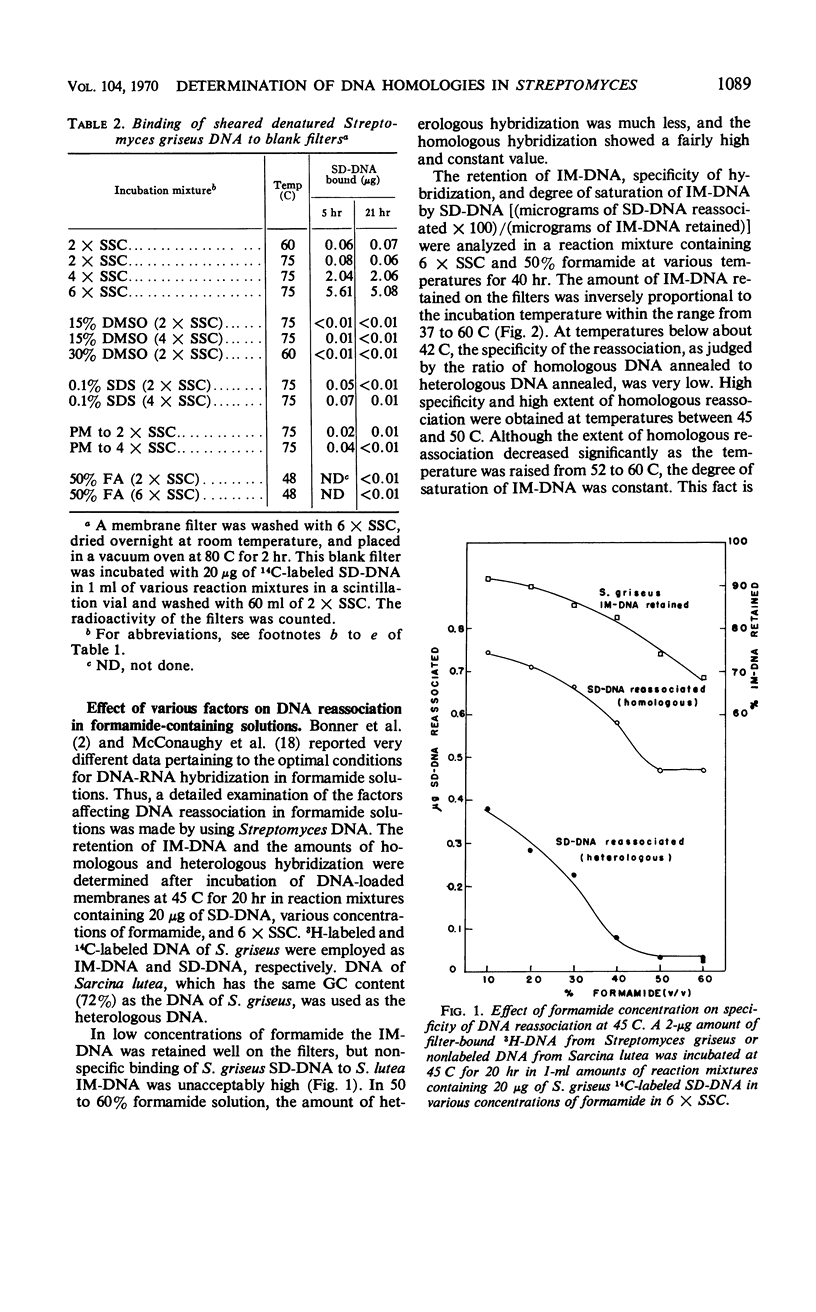
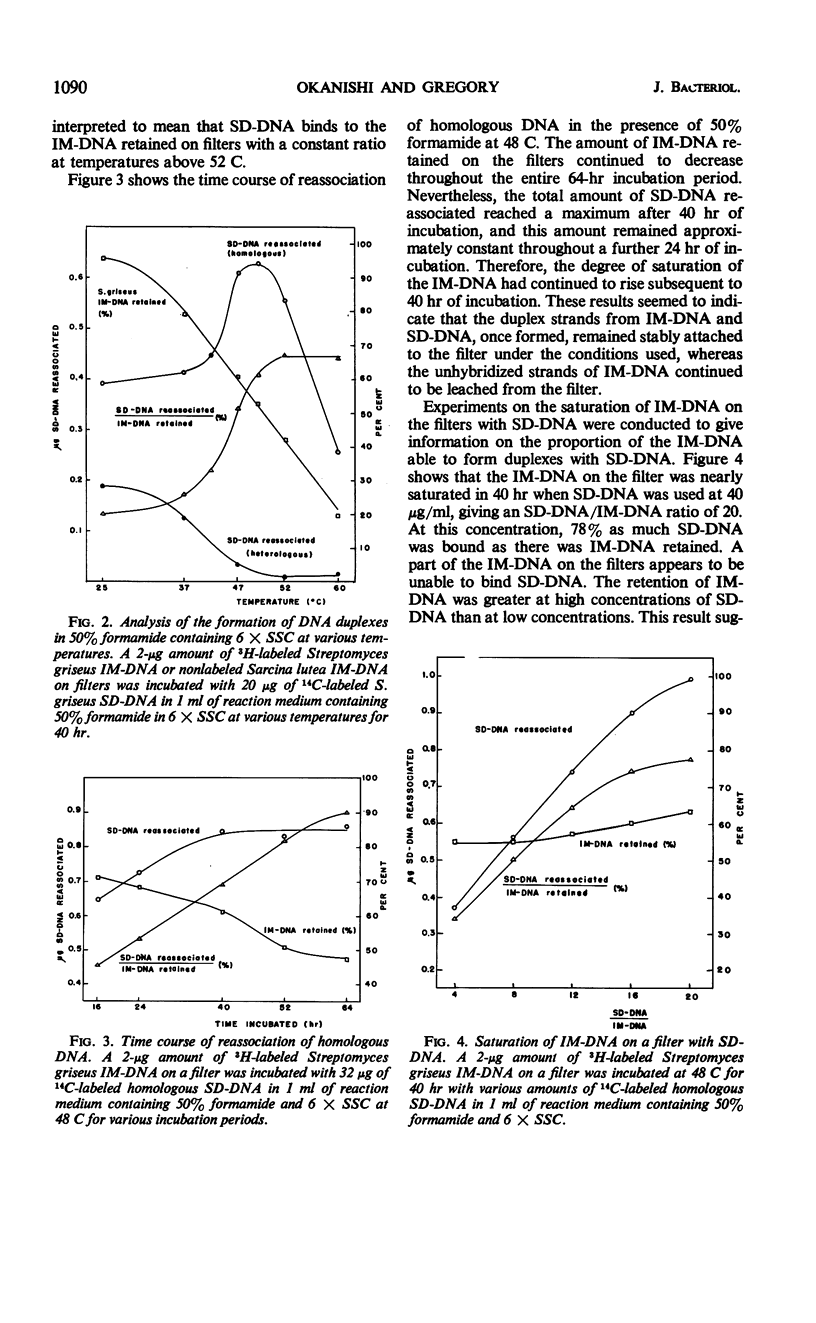
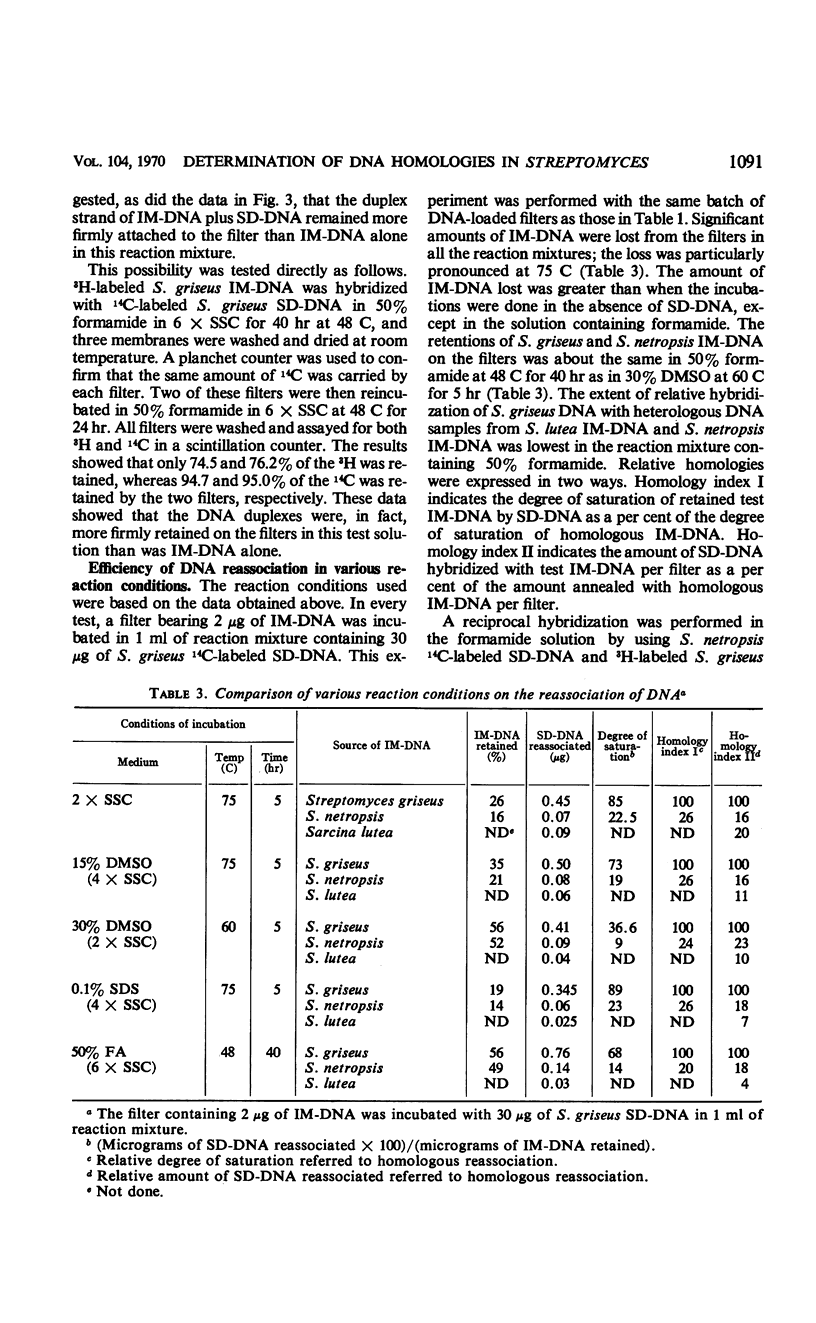
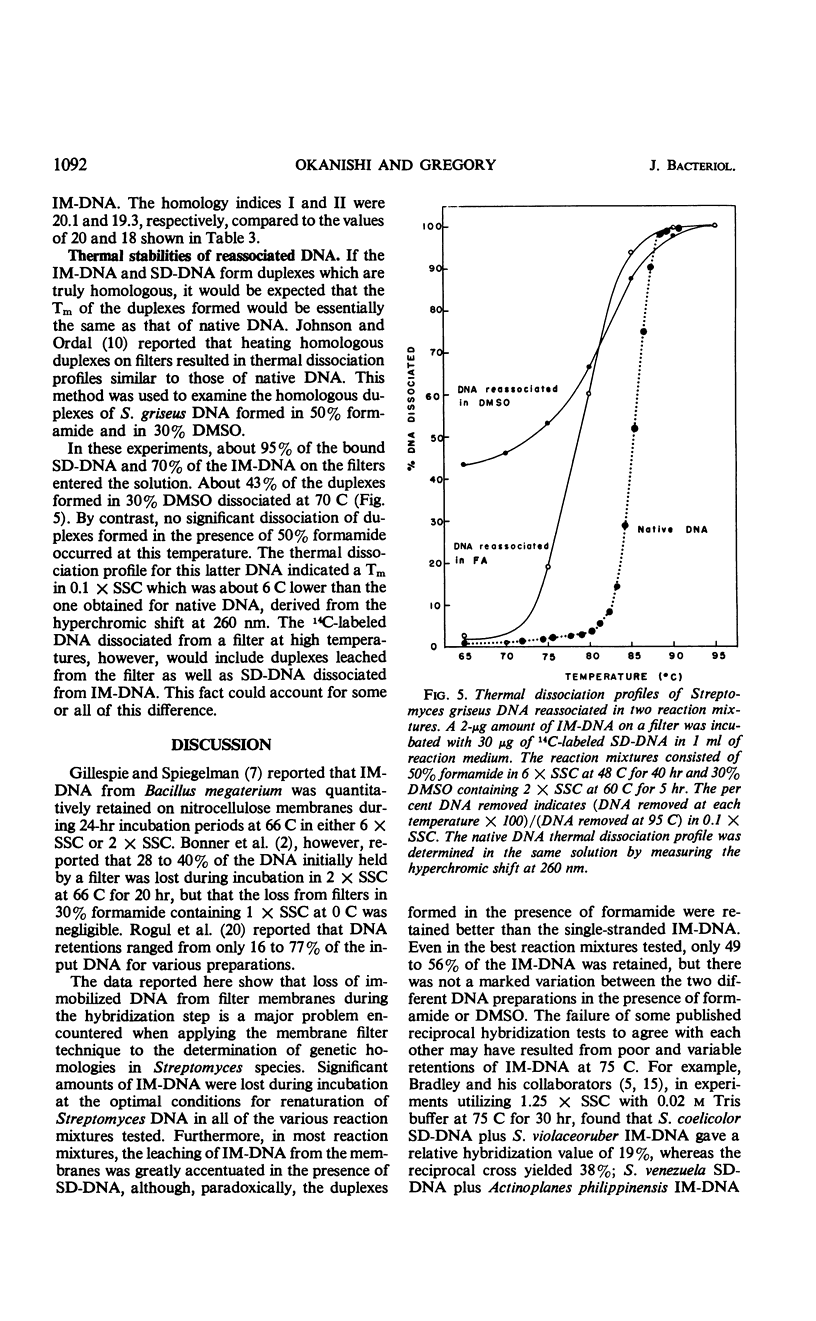
Variations of the membrane filter technique for deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) hybridizations were studied with respect to Streptomyces species. At the temperatures required for specific hybridization of DNA with the high melting temperature (Tm) characteristic of Streptomyces, large amounts (up to 97%) of filter-bound DNA became eluted, in all reaction mixtures studied, within 21 hr. In most solutions this leaching was increased by the presence of sheared denatured DNA. Incubation of DNA-loaded filters in a solution of 50% formamide containing 6× standard saline citrate, at 48 C for 40 hr, was judged to be the best set of conditions tested based on relatively good retention of immobilized DNA, very low hybridization with unrelated DNA of a similarly high Tm (from Sarcina lutea), and the formation of complexes similar in thermal stability to the native DNA. The expression of results as sheared DNA bound in relation to long-chain DNA retained is recommended when a high concentration of sheared DNA relative to immobilized DNA is used.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGI E., HERSHEY A. D. Sedimentation rate as a measure of molecular weight of DNA. Biophys J. 1963 Jul;3:309–321. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86823-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J., Kung G., Bekhor I. A method for the hybridization of nucleic acid molecules at low temperature. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3650–3653. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farina G., Bradley S. G. Reassociation of deoxyribonucleic acids from Actinoplanes and other actinomycetes. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):30–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.30-35.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIDUSCHEK E. P. On the factors controlling the reversibility of DNA denaturation. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:467–487. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Ordal E. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid homology in bacterial taxonomy: effect of incubation temperature on reaction specificity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):893–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.893-900.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE L., GORDON J. A., JENCKS W. P. The relationship of structure to the effectiveness of denaturing agents for deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1963 Jan-Feb;2:168–175. doi: 10.1021/bi00901a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legault-Démare J., Desseaux B., Heyman T., Séror S., Ress G. P. Studies on hybrid molecules of nucleic acids. I. DNA-DNA hybrids on nitrocellulose filters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):550–557. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90349-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Thermal renaturation of deoxyribonucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1961 Oct;3:585–594. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY B. J., BOLTON E. T. An approach to the measurement of genetic relatedness among organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jul;50:156–164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy B. J. Arrangement of base sequences in deoxyribonucleic Acid. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):215–229. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.215-229.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConaughy B. L., Laird C. D., McCarthy B. J. Nucleic acid reassociation in formamide. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3289–3295. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson A. M., Bradley S. G., Enquist L. W., Cruces G. Genetic homologies among Streptomyces violaceoruber strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):702–706. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.702-706.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Dulbecco R. Regulation of transcription of the SV40 DNA in productively infected and in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):525–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogul M., Brendle J. J., Haapala D. K., Alexander A. D. Nucleic acid similarities among Pseudomonas pseudomallei, Pseudomonas multivorans, and Actinobacillus mallei. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):827–835. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.827-835.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewfik E. M., Bradley S. G. Characterization of deoxyribonucleic acids from streptomycetes and nocardiae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1994–2000. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1994-2000.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmaar S. O., Cohen J. A. A quantitative assay for DNA-DNA hybrids using membrane filters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 23;24(4):554–558. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



