Abstract
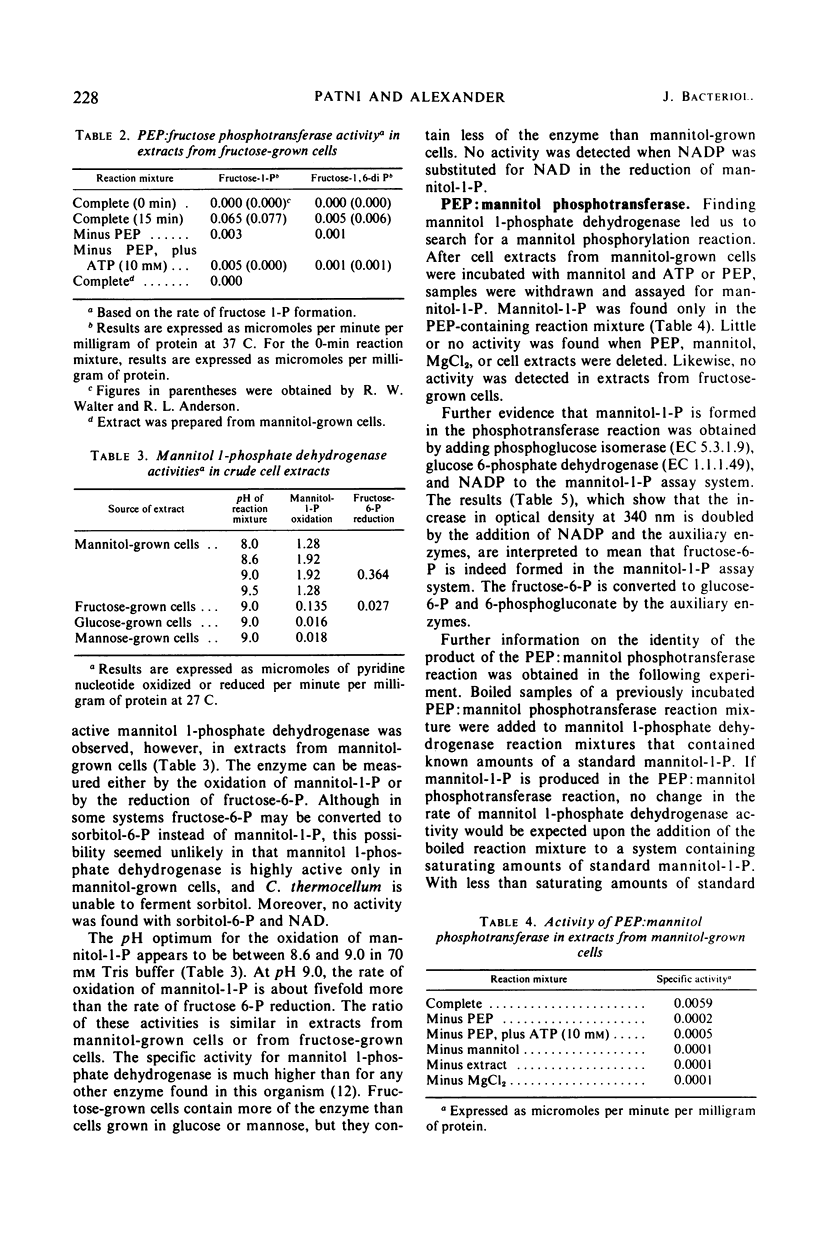
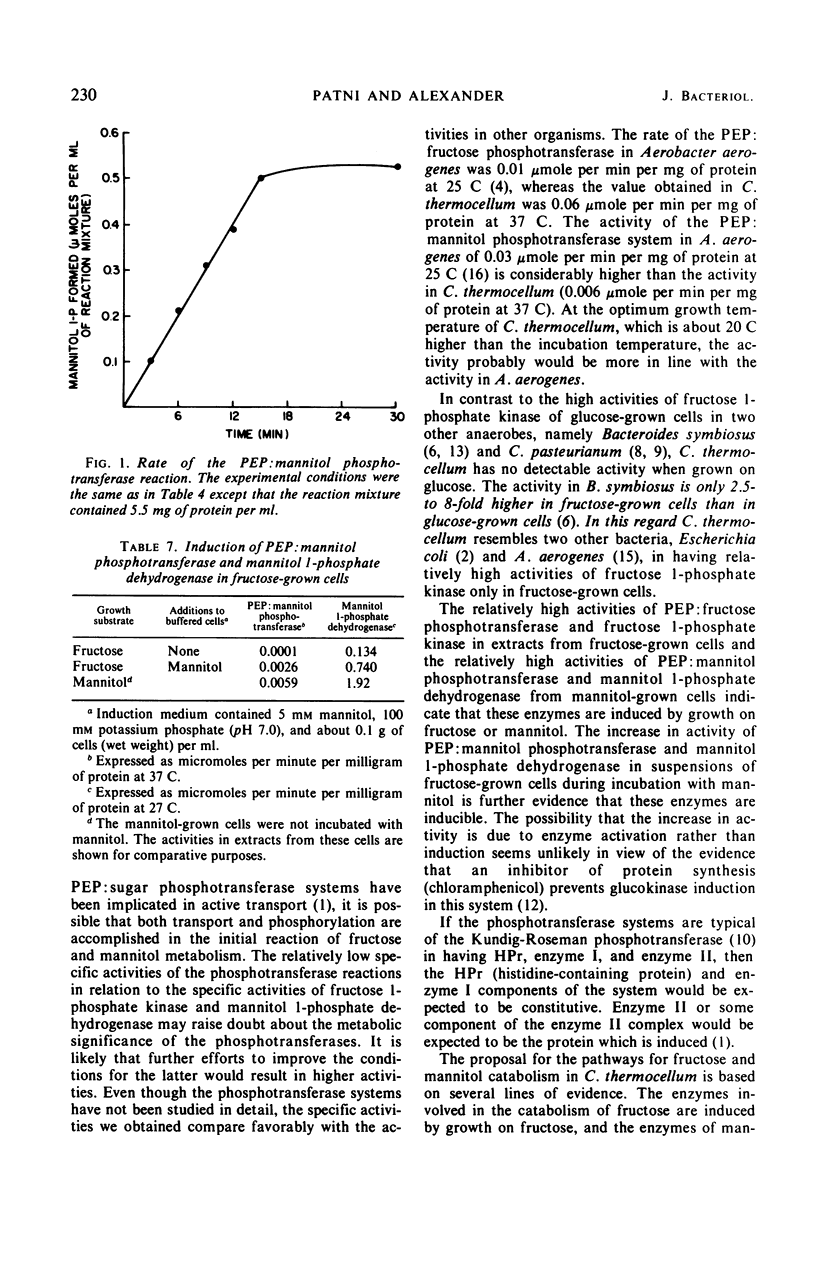
Fructose and mannitol are fermented by Clostridium thermocellum in a medium containing salts and 0.5% yeast extract. The initial reaction in the catabolism of fructose was found to be the formation of fructose l-phosphate by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP):fructose phosphotransferase which resembles the Kundig-Roseman phosphotransferase system. The phosphorylation of fructose l-phosphate to form fructose-1, 6-diphosphate is catalyzed by fructose l-phosphate kinase. Fructose-1, 6-diphosphate can be further metabolized by the Embden-Meyerhof pathway. The formation of both PEP:fructose phosphotransferase and fructose l-phosphate kinase is induced by growth in fructose medium. Mannitol catabolism was found to proceed by the phosphorylation of mannitol by PEP:mannitol phosphotransferase to form mannitol l-phosphate. Mannitol l-phosphate is converted to fructose 6-phosphate by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-specific mannitol l-phosphate dehydrogenase. The fructose 6-phosphate formed in the reaction can enter the glycolytic scheme. The formation of both PEP:mannitol phosphotransferase and mannitol l-phosphate dehydrogenase is induced by growth in mannitol medium. Evidence is presented for the induction by mannitol of PEP:mannitol phosphotransferase and mannitol l-phosphate dehydrogenase in suspensions of fructose-grown cells.
Full text
PDF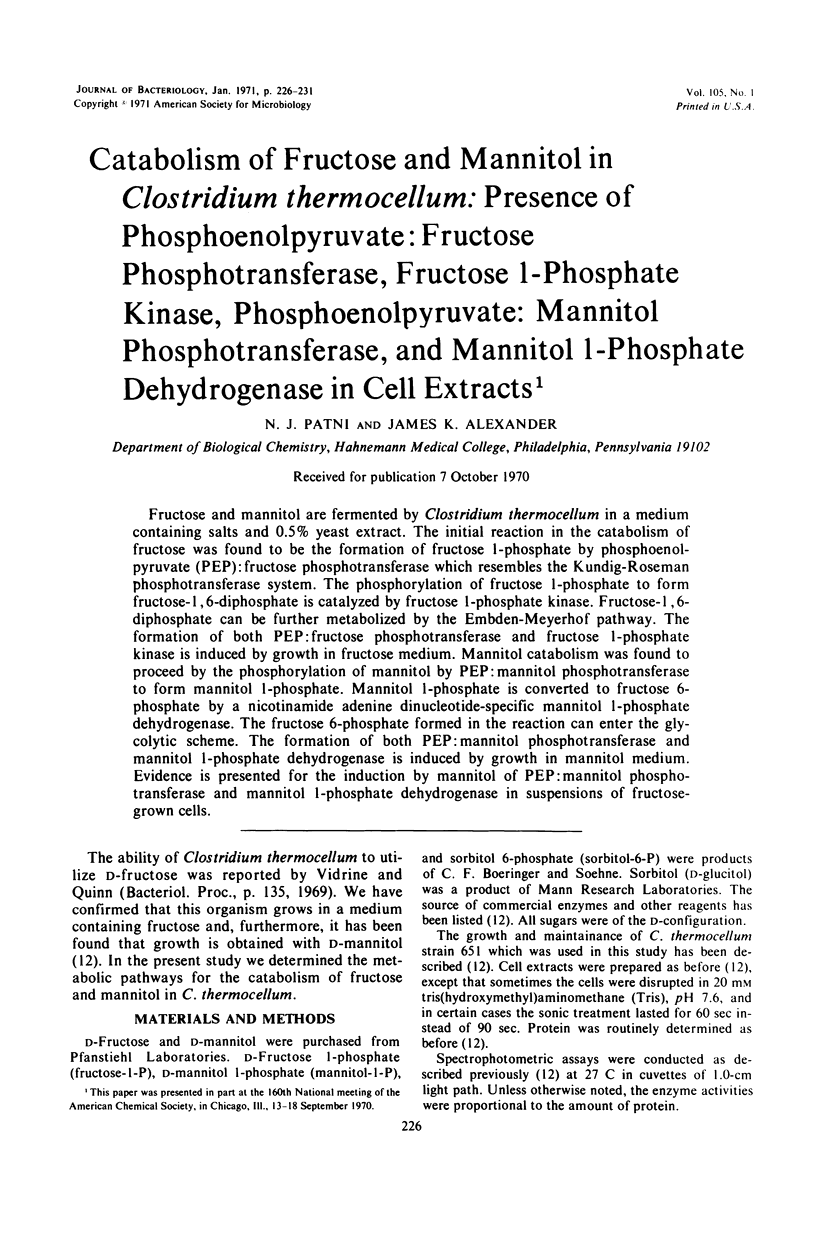



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. L., Wood W. A. Carbohydrate metabolism in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:539–578. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G. The phosphoenolpyruvate-initiated pathway of fructose metabolism in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6458–6463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson T. E., Anderson R. L. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent formation of D-fructose 1-phosphate by a four-component phosphotransferase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):269–276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D. S., Reeves R. E. Improved purification of 1-phosphofructokinase from Bacteroides symbiosus and some properties of the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Mar;137(1):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90410-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotzé J. P. Glycolytic and related enzymes in clostridial classification. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):744–747. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.744-747.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. E., Warren L. G., Hsu D. S. 1-Phosphofructokinase from an anaerobe. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1257–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico V., Anderson R. L. D-fructose 1-phosphate kinase and D-fructose 6-phosphate kinase from Aerobacter aerogenes. A comparative study of regulatory properties. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6280–6288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapico V., Hanson T. E., Walter R. W., Anderson R. L. Metabolism of D-fructose in Aerobacter aerogenes: analysis of mutants lacking D-fructose 6-phosphate kinase and D-fructose 1,6-diphosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):51–54. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.51-54.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



