Abstract
Two cDNA libraries were constructed from brain membrane and cytoskeletal preparations purified from scrapie-infected hamster brains. Four recombinants strongly preferential to the scrapie cytoskeletal preparation were identified by the differential hybridization of 7,000 recombinants. These clones were not, however, preferential to total nucleic acids extracted from scrapie-infected hamster brains. DNA sequence analysis revealed all four clones to have significant sequence similarities to the mouse mitochondrial genome. This correlation led us to consider a mitochondrial association with scrapie infectivity. Brain mitochondria were purified by sucrose gradient density centrifugation and found to contain high infectivity. Removal of mitochondrial outer membranes by osmotic shock or digitonin treatment resulted in no detectable loss of titer.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry R. A., Kent S. B., McKinley M. P., Meyer R. K., DeArmond S. J., Hood L. E., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and cellular prion proteins share polypeptide epitopes. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):848–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Van Etten R. A., Wright C. T., Walberg M. W., Clayton D. A. Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):167–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce M. E., Dickinson A. G. Biological evidence that scrapie agent has an independent genome. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):79–89. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyukmihci N., Goehring-Harmon F., Marsh R. F. Neural pathogenesis of experimental scrapie after intraocular inoculation of hamsters. Exp Neurol. 1983 Aug;81(2):396–406. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(83)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne E. Historical and current concepts in mitochondrial myopathies. Aust N Z J Med. 1983 Jun;13(3):299–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1983.tb04671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANDLER R. L. Encephalopathy in mice produced by inoculation with scrapie brain material. Lancet. 1961 Jun 24;1(7191):1378–1379. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Race R., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Bloom M., Lechner D., Bergstrom S., Robbins K., Mayer L., Keith J. M. Identification of scrapie prion protein-specific mRNA in scrapie-infected and uninfected brain. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):331–333. doi: 10.1038/315331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. B., Hayes D. J., Byrne E., Morgan-Hughes J. A. Mitochondrial myopathies: defects in mitochondrial metabolism in human skeletal muscle. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Dec;11(6):626–627. doi: 10.1042/bst0110626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A., Smith C. A. Complex mitochondrial DNA. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1975;14:1–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelio F., Di Donato S. Myopathies due to enzyme deficiencies. J Neurol. 1985;232(6):329–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00313831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees C., McMillan B. C., Wade W. F., German T. L., Marsh R. F. Characterization of nucleic acids in membrane vesicles from scrapie-infected hamster brain. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.126-132.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Meikle V. M. A comparison of some biological characteristics of the mouse-passaged scrapie agents, 22A and ME7. Genet Res. 1969 Apr;13(2):213–225. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Meikle V. M., Fraser H. Identification of a gene which controls the incubation period of some strains of scrapie agent in mice. J Comp Pathol. 1968 Jul;78(3):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(68)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Meikle V. M. Host-genotype and agent effects in scrapie incubation: change in allelic interaction with different strains of agent. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00266934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum A. M., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of mitochondrial DNA replication in mouse L-cells: RNA priming during the initiation of heavy-strand synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):353–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
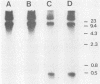
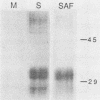
- HUNTER G. D., MILLSON G. C., MEEK G. THE INTRACELLULAR LOCATION OF THE AGENT OF MOUSE SCRAPIE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Feb;34:319–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. P., Eckroade R. J., Marsh R. F., Zu Rhein G. M., Kanitz C. L., Gustafson D. P. Susceptibility of mink to sheep scrapie. Science. 1971 May 21;172(3985):859–861. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3985.859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I. J., Harding A. E., Morgan-Hughes J. A. Deletions of muscle mitochondrial DNA in patients with mitochondrial myopathies. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):717–719. doi: 10.1038/331717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter G. D., Kimberlin R. H., Millson G. C. Absence of eclipse phase in scrapie mice. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):31–32. doi: 10.1038/newbio235031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter N., Hope J., McConnell I., Dickinson A. G. Linkage of the scrapie-associated fibril protein (PrP) gene and Sinc using congenic mice and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J Gen Virol. 1987 Oct;68(Pt 10):2711–2716. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-10-2711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Cole S., Walker C. A. Temporary and permanent modifications to a single strain of mouse scrapie on transmission to rats and hamsters. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1875–1881. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J. C., Walsh J. M., Dennis S. C., Clark J. B. Synaptic and non-synaptic mitochondria from rat brain: isolation and characterization. J Neurochem. 1977 Mar;28(3):625–631. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis E. E. Evidence suggesting that PrP is not the infectious agent in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):341–347. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Rohwer R. G., Franko M. C., Brown P., Gajdusek D. C. The sequential development of spongiform change and gliosis of scrapie in the golden Syrian hamster. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1984 May;43(3):242–252. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198405000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Iqbal K. Abnormal fibrils from scrapie-infected brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54(1):63–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00691333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millson G. C., Hunter G. D., Kimberlin R. H. An experimental examination of the scrapie agent in cell membrane mixtures. II. The association of scrapie activity with membrane fractions. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Apr;81(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
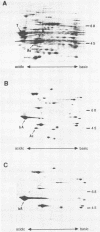
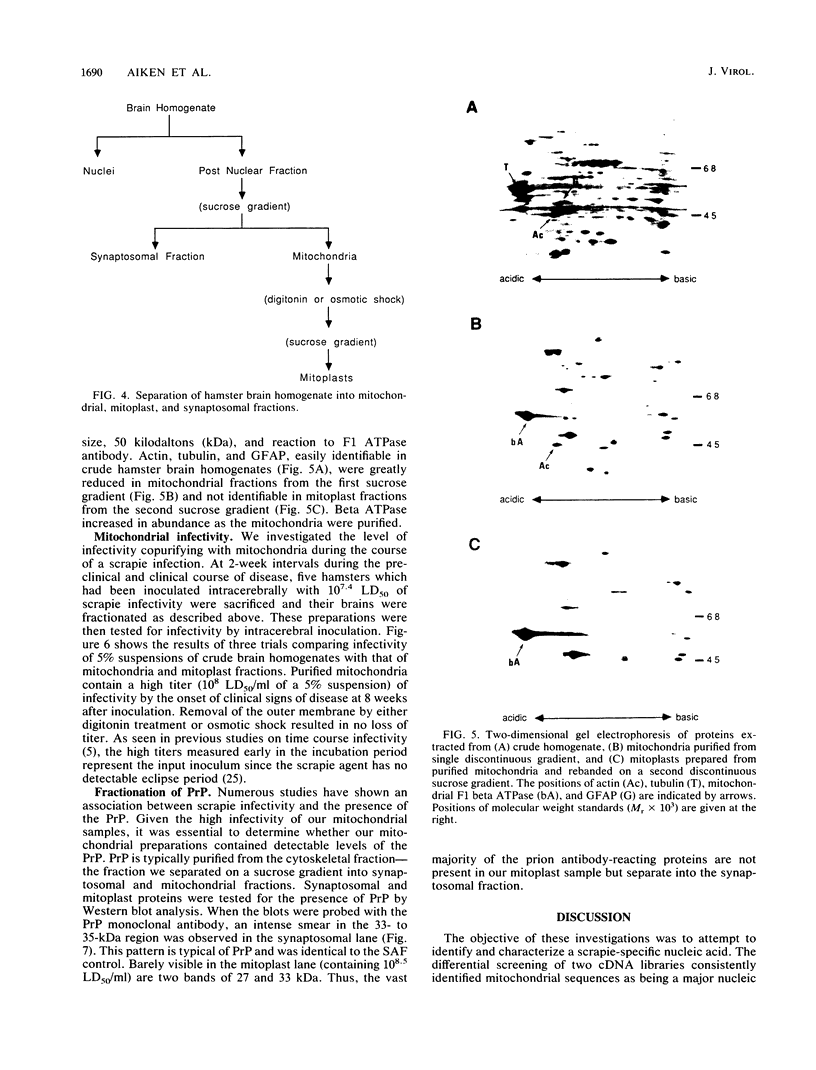
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Bolton D. C., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P. Further purification and characterization of scrapie prions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Cochran S. P., Groth D. F., Downey D. E., Bowman K. A., Martinez H. M. Measurement of the scrapie agent using an incubation time interval assay. Ann Neurol. 1982 Apr;11(4):353–358. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Bolton D. C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Purification and structural studies of a major scrapie prion protein. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Sawh P. R., Wolfe G. C., Rubenstein R., Carp R. I., Innis M. A. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding the leader peptide of prion protein and expression of the homologous gene in various tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6377–6381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semancik J. S., Marsh R. F., Geelen J. L., Hanson R. P. Properties of the scrapie agent-endomembrane complex from hamster brain. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.693-700.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu K. F., Kim Y. T., Blass J. P., Weksler M. E. An immunochemical study of the pyruvate dehydrogenase deficit in Alzheimer's disease brain. Ann Neurol. 1985 May;17(5):444–449. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims N. R., Finegan J. M., Blass J. P., Bowen D. M., Neary D. Mitochondrial function in brain tissue in primary degenerative dementia. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 8;436(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91553-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Characterization of major peptides in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6146–6150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk E., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E., Prusiner S. B. Purification and properties of the cellular and scrapie hamster prion proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H. Removal of the outer membrane from brain mitochondria. J Biochem. 1971 Feb;69(2):275–281. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Goodman P. A., Mirenda C. A., McKinley M. P., Carlson G. A., Prusiner S. B. Distinct prion proteins in short and long scrapie incubation period mice. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):651–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeviani M., Moraes C. T., DiMauro S., Nakase H., Bonilla E., Schon E. A., Rowland L. P. Deletions of mitochondrial DNA in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Neurology. 1988 Sep;38(9):1339–1346. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.9.1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]