Abstract
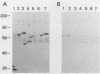
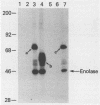
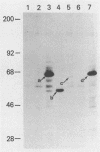
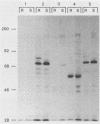
The transforming gene product, P70gag-actin-fgr, of Gardner-Rasheed feline sarcoma virus (GR-FeSV) is a single polypeptide composed of regions derived from cellular and viral genes. Gamma actin and c-fgr genes are the two known cellular components of the GR-FeSV genome. In the present study, sequences representing each cell-derived gene were deleted and the resulting constructs were tested for transforming activity by transfection of NIH 3T3 cells. Constructs lacking a portion of the c-fgr proto-oncogene failed to induce focus formation, demonstrating the essential nature of this component for GR-FeSV oncogenic activity. In contrast, the construct lacking the actin domain was more active than GR-FeSV DNA in transformation assays. Protein specified by the actin deletion mutant possessed a 2.4-fold greater specific protein-tyrosine kinase activity compared with that of the wild-type gene product. Furthermore, the actin domain had no detectable effect on the ability of the fgr kinase to associate with cytoskeleton or to phosphorylate unique cellular proteins on tyrosine. Our findings demonstrate that the actin domain inhibits focus formation and impairs protein-tyrosine kinase activity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Membrane association of the transforming protein of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and mutants temperature sensitive for cellular transformation and protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):790–797. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.790-797.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. Association of p60src with Triton X-100-resistant cellular structure correlates with morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jainchill J. L., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: assay using clonal lines of contact-inhibited mouse cells. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.549-553.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Kawakami Y., Aaronson S. A., Robbins K. C. Acquisition of transforming properties by FYN, a normal SRC-related human gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3870–3874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt J., Bushar G., Kakunaga T., Hamada H., Hirakawa T., Goldman D., Merril C. Variations in expression of mutant beta actin accompanying incremental increases in human fibroblast tumorigenicity. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90344-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Hughes S. H., Barbacid M. A human oncogene formed by the fusion of truncated tropomyosin and protein tyrosine kinase sequences. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):743–748. doi: 10.1038/319743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naharro G., Dunn C. Y., Robbins K. C. Analysis of the primary translational product and integrated DNA of a new feline sarcoma virus, GR-FeSV. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):502–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naharro G., Robbins K. C., Reddy E. P. Gene product of v-fgr onc: hybrid protein containing a portion of actin and a tyrosine-specific protein kinase. Science. 1984 Jan 6;223(4631):63–66. doi: 10.1126/science.6318314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskam R., Coulier F., Ernst M., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Frequent generation of oncogenes by in vitro recombination of TRK protooncogene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2964–2968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Predominance of tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptors during the initial response of intact cells to insulin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7131–7136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed S., Barbacid M., Aaronson S., Gardner M. B. Origin and biological properties of a new feline sarcoma virus. Virology. 1982 Feb;117(1):238–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90522-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Devare S. G., Reddy E. P., Aaronson S. A. In vivo identification of the transforming gene product of simian sarcoma virus. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1131–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.6293053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]