Abstract
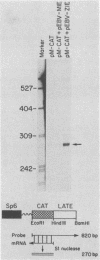
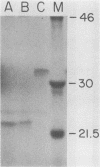
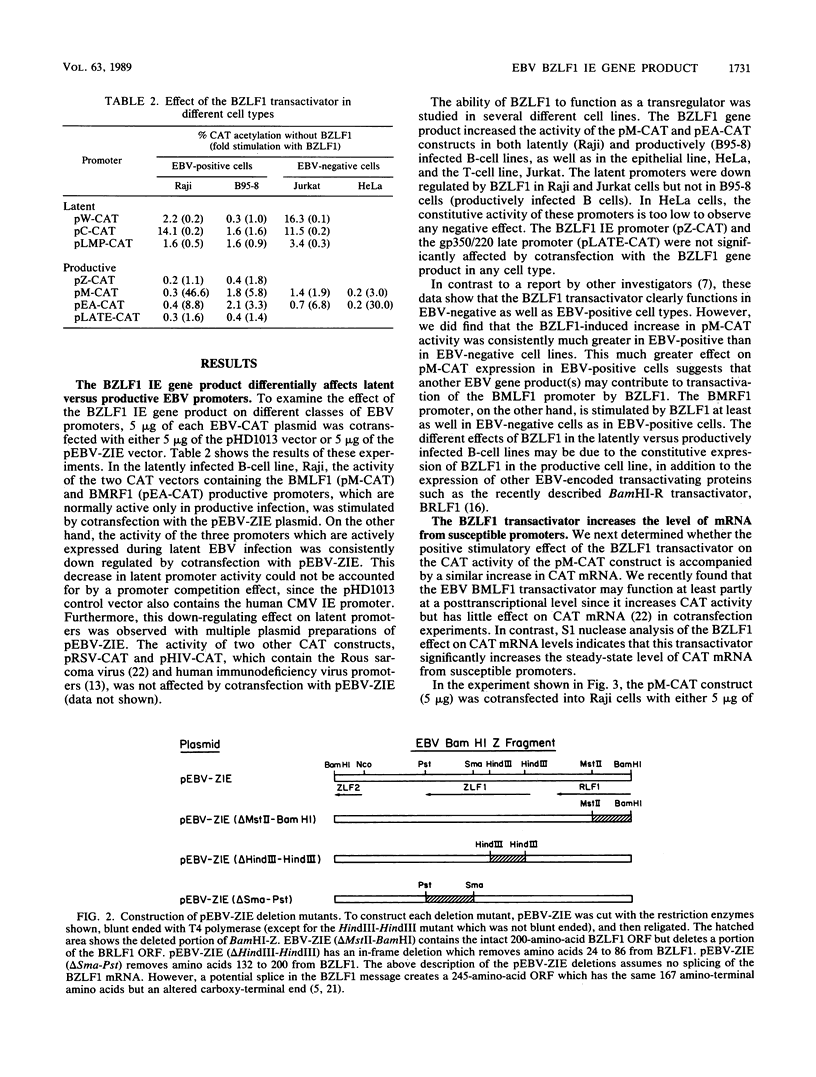
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF1 gene product is thought to mediate the disruption of latent EBV infection. We have examined the regulatory effects of BZLF1 by studying its transactivating effects on seven different EBV promoters. We find that whereas the BZLF1 gene product increases the activity of the two early promoters, BMLF1 and BMRF1, it decreases the activity of three latent promoters (the BamHI-C and BamHI-W Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen promoters and the latent membrane protein promoter). The BZLF1-induced changes in promoter-directed chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity occur in EBV-negative as well as EBV-positive cell lines and are accompanied by a similar change in chloramphenicol acetyltransferase mRNA. Deletion analysis of the BamHI Z fragment indicates that in a portion of the amino-terminal half of the BZLF1 gene product (amino acids 24 to 86) is not essential for positive transactivating effects but is required for down-regulating effects. Thus, different domains of the same EBV immediate-early gene product can either increase the function of EBV promoters active in productive infection or decrease the function of key promoters active in latent infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Latency comes of age for herpesviruses. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):787–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90419-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisel C., Tanner J., Matsuo T., Thorley-Lawson D., Kezdy F., Kieff E. Two major outer envelope glycoproteins of Epstein-Barr virus are encoded by the same gene. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):665–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.665-674.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M., Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in P3HR1-superinfected Raji cells. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3120–3132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3120-3132.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho M. S., Jeang K. T., Hayward S. D. Localization of the coding region for an Epstein-Barr virus early antigen and inducible expression of this 60-kilodalton nuclear protein in transfected fibroblast cell lines. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):852–859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.852-859.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Jenson H., Seibl R., Wolf H., Miller G. Polymorphic proteins encoded within BZLF1 of defective and standard Epstein-Barr viruses disrupt latency. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3672–3679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3672-3679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald S., van Santen V., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.411-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E., Jenson H., Countryman J., Heston L., Gradoville L., Miller G. Transfection of a rearranged viral DNA fragment, WZhet, stably converts latent Epstein-Barr viral infection to productive infection in lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1332–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Lieberman P. M., Hayward S. D. A new Epstein-Barr virus transactivator, R, induces expression of a cytoplasmic early antigen. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2274–2284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2274-2284.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA encodes part of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1396–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6304878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. A second nuclear protein is encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent infection. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2983420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. S., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. Two related but differentially expressed potential membrane proteins encoded by the EcoRI Dhet region of Epstein-Barr virus B95-8. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):528–535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.528-535.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenson H. B., Miller G. Polymorphisms of the region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome which disrupts latency. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):549–564. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90599-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Markovitz D., Fenrick R., Pagano J. An Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early gene product trans-activates gene expression from the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1652–1656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Natarajan V., Salzman N. P. Mapping 5' termini of JC virus late RNA. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):216–219. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.216-219.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., O'Hare P., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. Promiscuous trans activation of gene expression by an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded early nuclear protein. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.140-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Shaw J. E., Smith M. C., Pagano J. S. Effect of 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate on the replication of Epstein-Barr virus. I. Characterization of viral DNA. Virology. 1979 Nov;99(1):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguro M. O., Shimizu N., Ono Y., Takada K. Both the rightward and the leftward open reading frames within the BamHI M DNA fragment of Epstein-Barr virus act as trans-activators of gene expression. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3310–3313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3310-3313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Lancz G., Nonoyama M. Mapping of genes in BamHI fragment M of Epstein-Barr virus DNA that may determine the fate of viral infection. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):145–154. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.145-154.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Hayday A. C., Keating A. Electric field-mediated DNA transfer: transient and stable gene expression in human and mouse lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):703–706. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. M., Levine A. J. Identification and mapping of Epstein-Barr virus early antigens and demonstration of a viral gene activator that functions in trans. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):149–156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.149-156.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]