Abstract
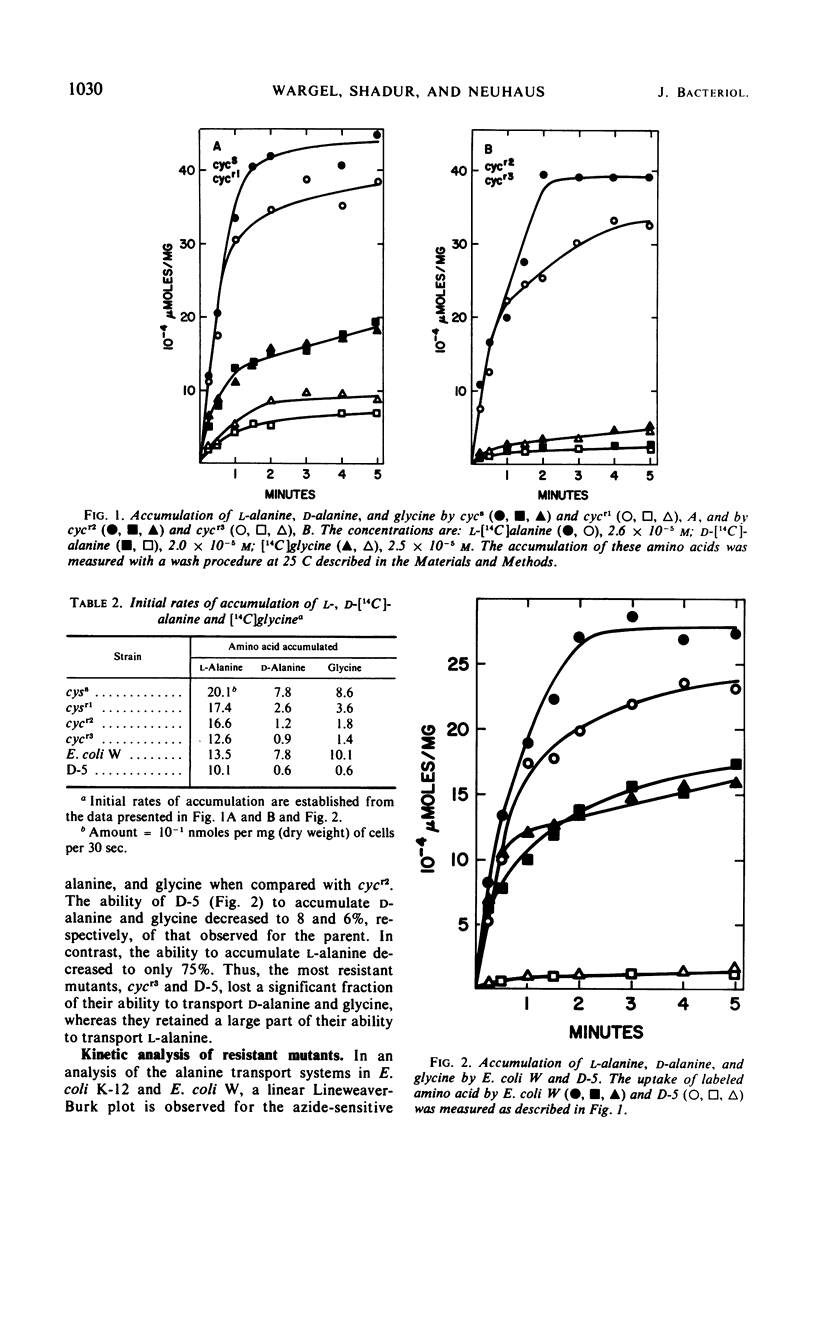
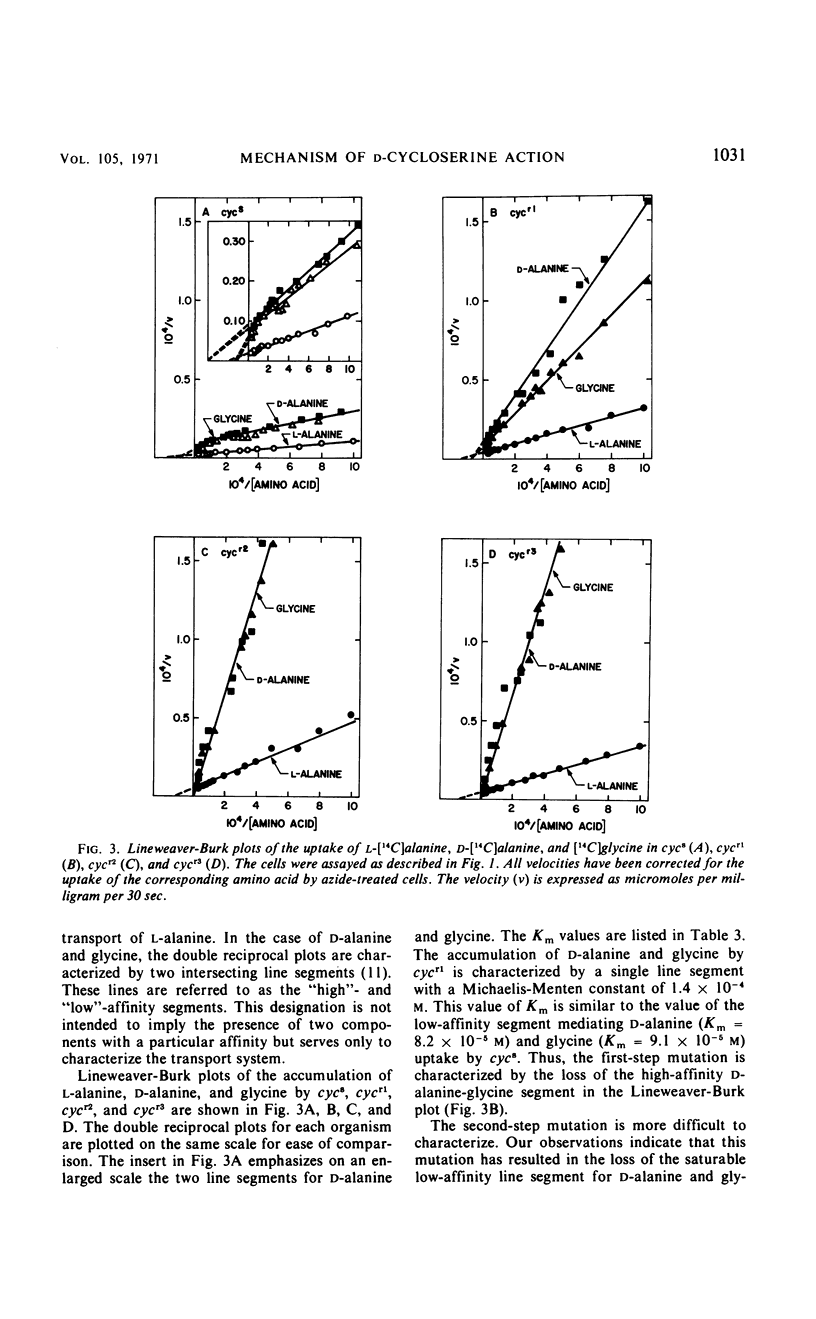
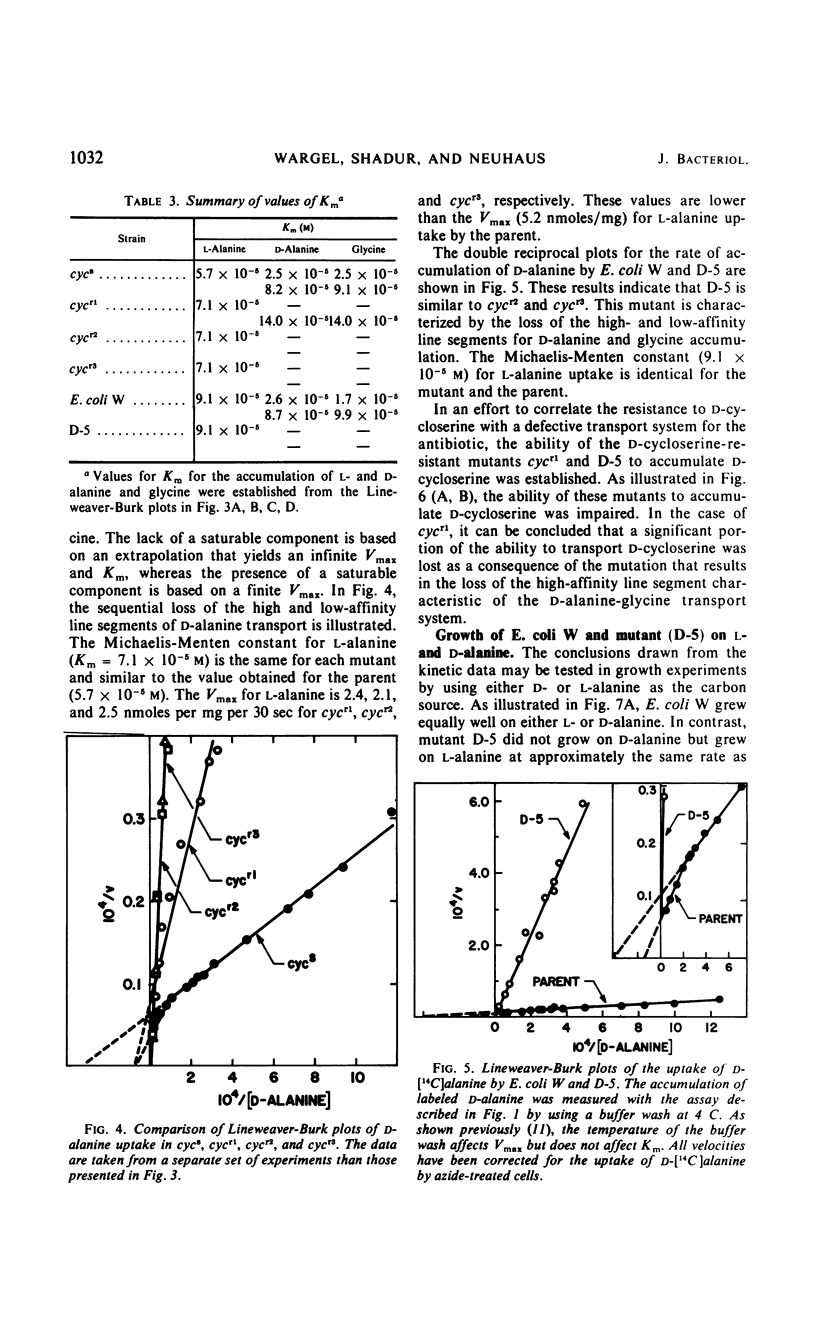
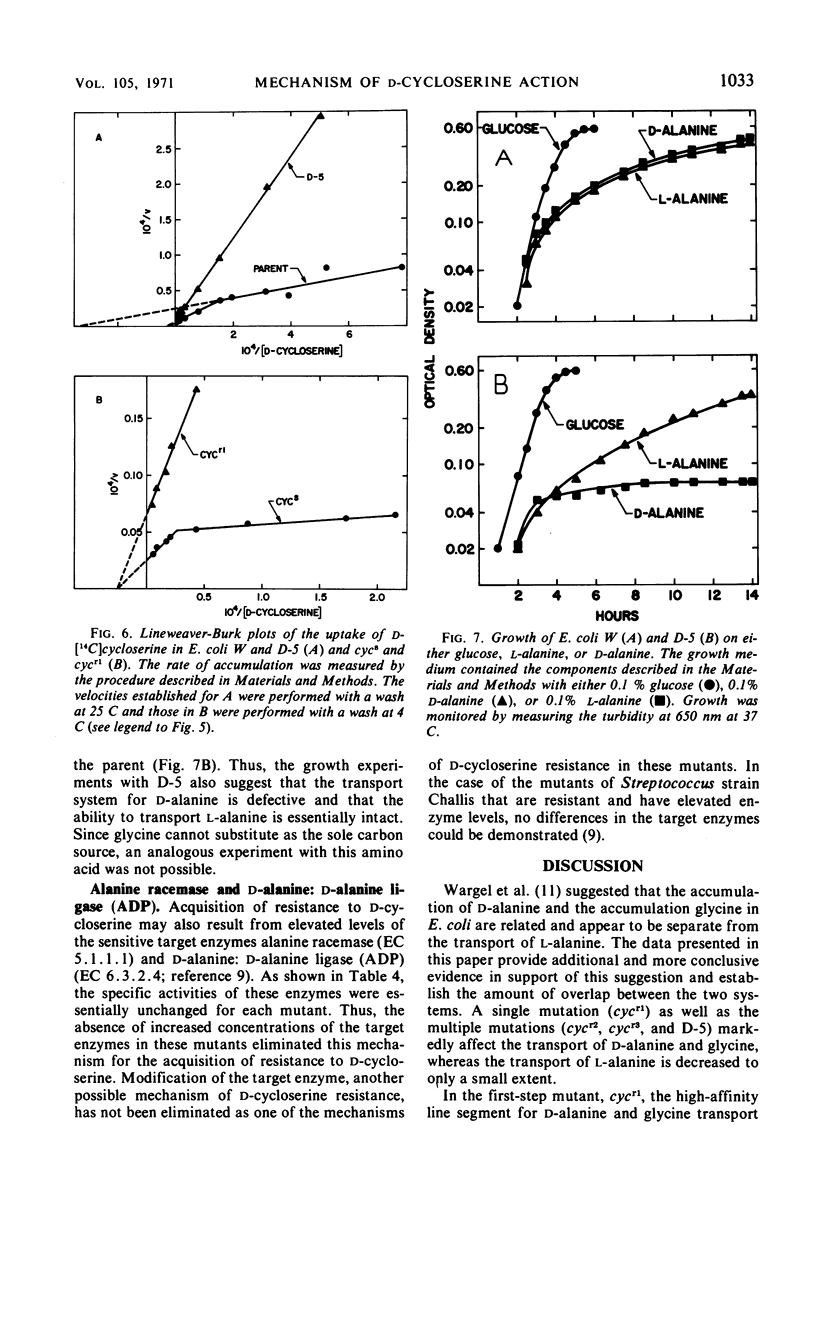
The accumulation of d-alanine and the accumulation of glycine in Escherichia coli are related and appear to be separate from the transport of l-alanine. The analysis of four d-cycloserine-resistant mutants provides additional support for this conclusion. The first-step mutant from E. coli K-12 that is resistant to d-cycloserine was characterized by the loss of the high-affinity line segment of the d-alanine-glycine transport system in the Lineweaver-Burk plot. This mutation, which is linked to the met1 locus, also resulted in the loss of the ability to transport d-cycloserine. The second-step mutation that is located 0.5 min from the first-step mutation resulted in the loss of the low-affinity line segment for the d-alanine-glycine transport system. The transport of l-alanine was decreased only 20 to 30% in each of these mutants. A multistep mutant from E. coli W that is 80-fold resistant to d-cycloserine lost >90% of the transport activity for d-alanine and glycine, whereas 75% of the transport activity for l-alanine was retained. E. coli W could utilize either d- or l-alanine as a carbon source, whereas the multistep mutant could only utilize l-alanine. Thus, a functioning transport system for d-alanine and glycine is required for both d-cycloserine action and growth on d-alanine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Charamella L. J., Berg C. M., Harris P. E. Kinetic and genetic analyses of D-cycloserine inhibition and resistance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1238–1250. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1238-1250.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KESSEL D., LUBIN M. STABILITY OF ALPHA-HYDROGEN OF AMINO ACIDS DURING ACTIVE TRANSPORT. Biochemistry. 1965 Mar;4:561–565. doi: 10.1021/bi00879a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. L., Neuhaus F. C. On the mechanism of action of the antibiotic O-carbamyld-serine in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):449–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.449-460.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON M. S., GREENE R. C. MEASUREMENT OF LOW ENERGY BETA-EMITTERS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION BY LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF EMULSIONS. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:854–857. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz R. H., Slade H. D., Neuhaus F. C. The biochemical mechanisms of resistance by streptococci to the antibiotics D-cycloserine and O-carbamyl-D-serine. Biochemistry. 1967 Aug;6(8):2561–2570. doi: 10.1021/bi00860a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J. H., MAAS W. K., SIMON E. J. An impaired concentrating mechanism for amino acids in mutants of Escherichia coli resistant to L-canavanine and D-serine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:582–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90650-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wargel R. J., Shadur C. A., Neuhaus F. C. Mechanism of D-cycloserine action: transport systems for D-alanine, D-cycloserine, L-alanine, and glycine. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):778–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.778-788.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



