Abstract
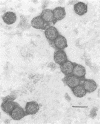
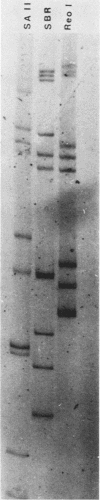
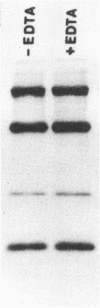
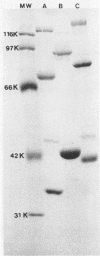
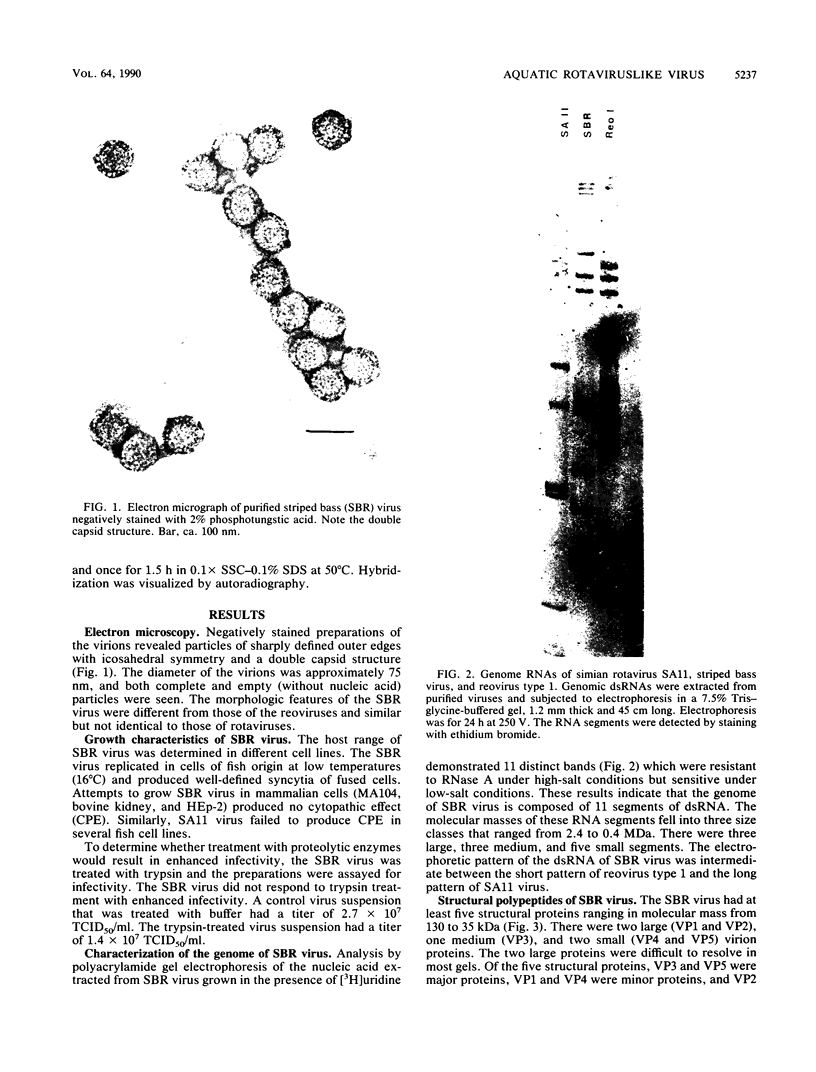
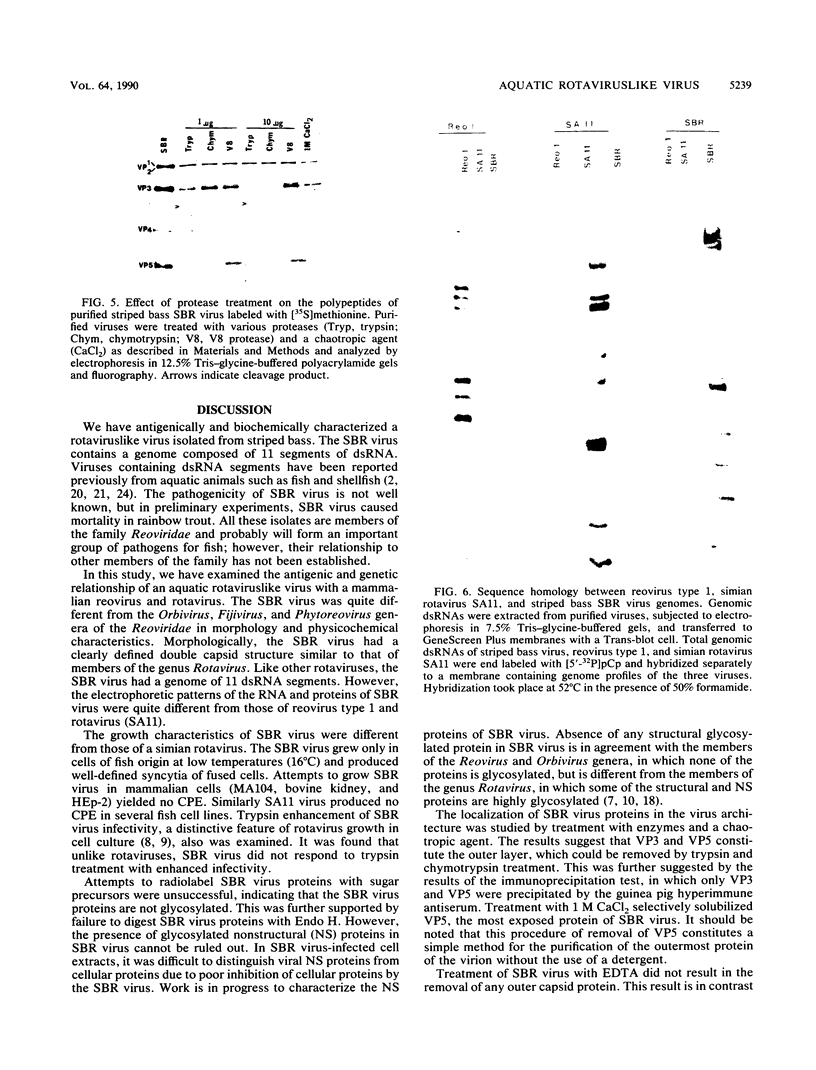
The characteristics of a rotaviruslike (SBR) virus isolated from striped bass (Morone saxatilis) were examined following purification of viruses from infected cell cultures. Virions had a double-layered capsid of icosahedral symmetry and a diameter of 75 nm. Purified viruses contained five polypeptides ranging in molecular mass from 130 to 35 kDa. None of the structural proteins were glycosylated. Treatment with EDTA did not remove the outer capsid. By using enzymes and a chaotropic agent, it was shown that VP5 was the most external polypeptide. The genome of SBR virus was composed of 11 segments of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). The electrophoretic pattern of the dsRNA of SBR virus was different from that of reovirus type 1 (Lang) and rotavirus (SA11) dsRNA. The SBR virus was compared with reovirus type 1 and SA11 virus by RNA-RNA blot hybridization. There was no cross-hybridization between any of the genome segments of the SBR, reovirus type 1, or SA11 viruses. Antigenic comparison of SBR virus and SA11 virus by cross-immunoprecipitation and cross-immunofluorescence tests did not show any relationship. These results suggest that SBR virus could represent a new genus within the family Reoviridae.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodkin D. K., Knudson D. L. Sequence relatedness of Palyam virus genes to cognates of the Palyam serogroup viruses by RNA-RNA blot hybridization. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C. Novel rotaviruses in animals and man. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;128:5–23. doi: 10.1002/9780470513460.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Laporte J., Charpilienne A., Scherrer R. Activation of rotavirus RNA polymerase by calcium chelation. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):177–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01317489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson B. L., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B., Estes M. K. Identification, synthesis, and modifications of simian rotavirus SA11 polypeptides in infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):825–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.825-839.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Mason B. B. Proteolytic enhancement of rotavirus infectivity: molecular mechanisms. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):879–888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.879-888.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Proteolytic enhancement of rotavirus infectivity: biology mechanism. Virology. 1980 Mar;101(2):432–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90456-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath R. L., Birch C. J. Synthesis of human rotavirus polypeptides in cell culture. J Med Virol. 1988 May;25(1):91–103. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick R. P., Rosemark R., Aronstein D., Winton J. R., McDowell T., Amend D. F. Characteristics of a new reovirus from channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1527–1534. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Faulkner-Valle G. P. Molecular biology of rotaviruses. I. Characterization of basic growth parameters and pattern of macromolecular synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.490-496.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Joklik W. K. The nature of the polypeptide encoded by each of the 10 double-stranded RNA segments of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):578–593. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A. Nucleic acid-based analyses of non-group A rotaviruses. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;128:24–48. doi: 10.1002/9780470513460.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramig R. F., Cross R. K., Fields B. N. Genome RNAs and polypeptides of reovirus serotypes 1, 2, and 3. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):726–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.726-733.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Street J. E., Croxson M. C., Chadderton W. F., Bellamy A. R. Sequence diversity of human rotavirus strains investigated by northern blot hybridization analysis. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):369–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.369-378.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winton J. R., Lannan C. N., Fryer J. L., Hedrick R. P., Meyers T. R., Plumb J. A., Yamamoto T. Morphological and biochemical properties of four members of a novel group of reoviruses isolated from aquatic animals. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):353–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]