Abstract
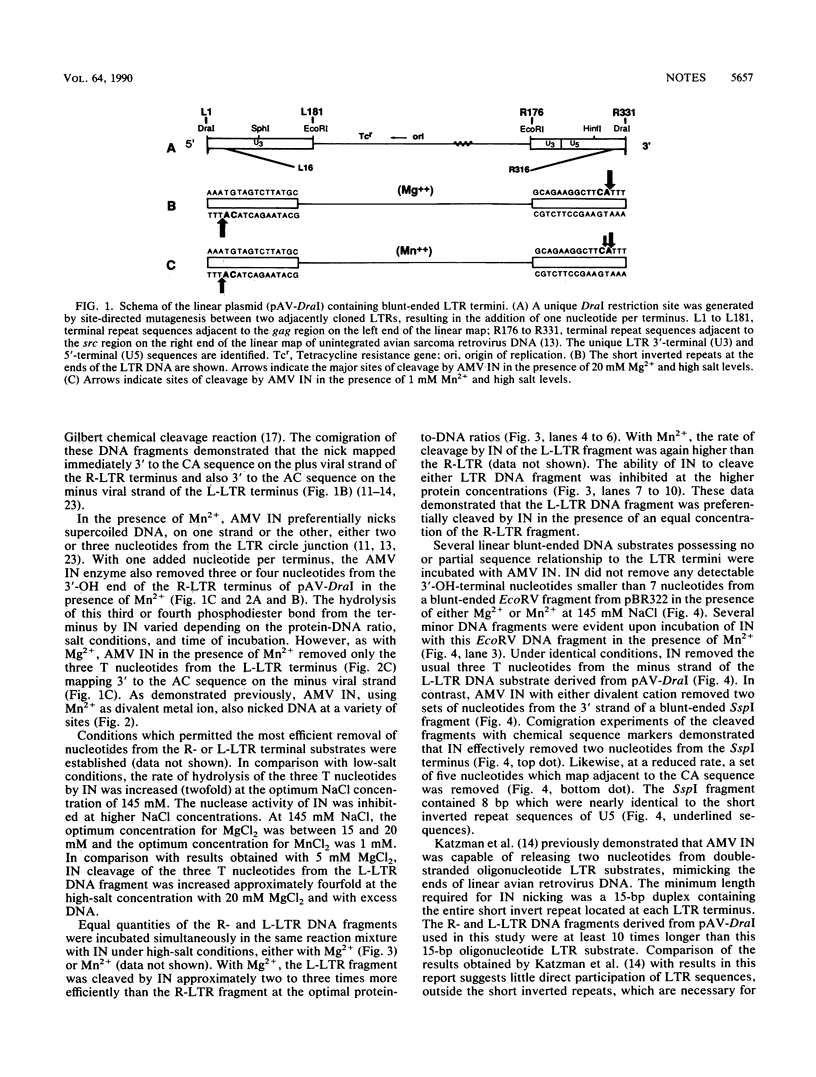
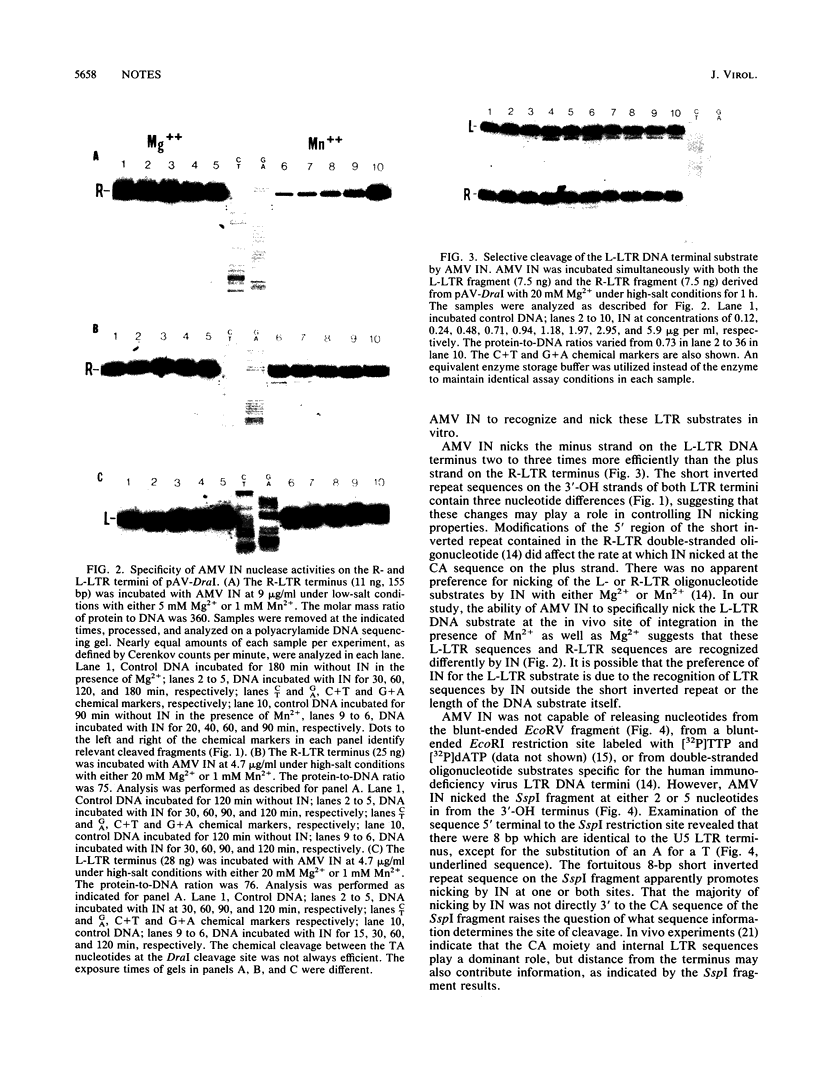
The avian myeloblastosis virus integration protein (IN) was capable of removing a specific set of 3'-OH-terminal nucleotides from blunt-ended long terminal repeat (LTR) substrates which resembled linear viral DNA in vivo. The 3'-OH-recessed ends map to the in vivo site of integration on linear viral DNA. The linear DNA plasmid substrate was formed by the generation of a unique DraI restriction enzyme site (TTT/AAA) at the circle junction of a 330-bp tandem LTR-LTR insert. IN preferentially released the three T nucleotides from the minus strand of the U3 LTR substrate compared with its ability to remove the three T nucleotides from the plus strand of the U5 LTR substrate. It was also observed that IN was capable of cleaving a non-LTR DNA substrate containing sequence homology to the U5 LTR terminus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowerman B., Brown P. O., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. A nucleoprotein complex mediates the integration of retroviral DNA. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):469–478. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Isolation of an integrated provirus of Moloney murine leukemia virus with long terminal repeats in inverted orientation: integration utilizing two U3 sequences. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):633–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.633-636.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Sequence and spacing requirements of a retrovirus integration site. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donehower L. A., Varmus H. E. A mutant murine leukemia virus with a single missense codon in pol is defective in a function affecting integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6461–6465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Mason W. S., Linial M. Synthesis and processing of polymerase proteins of wild-type and mutant avian retroviruses. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):62–78. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.62-78.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Bernstein A. Retrovirus vectors containing an internal attachment site: evidence that circles are not intermediates to murine retrovirus integration. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2844–2846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2844-2846.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Integration of mini-retroviral DNA: a cell-free reaction for biochemical analysis of retroviral integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3065–3069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C., Schiff R. D. A 32,000-dalton nucleic acid-binding protein from avian retravirus cores possesses DNA endonuclease activity. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C. Site-specific nicking at the avian retrovirus LTR circle junction by the viral pp32 DNA endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6205–6221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C., Swanstrom R., Olsen J. C. Nuclease mechanism of the avian retrovirus pp32 endonuclease. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):970–974. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.970-974.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus R. J., Hippenmeyer P. J., Misra T. K., Grandgenett D. P., Müller U. R., Fitch W. M. Avian retrovirus pp32 DNA binding protein. Preferential binding to the promoter region of long terminal repeat DNA. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):350–359. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobel L. I., Murphy J. E., Goff S. P. The palindromic LTR-LTR junction of Moloney murine leukemia virus is not an efficient substrate for proviral integration. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2629–2637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2629-2637.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The retrovirus pol gene encodes a product required for DNA integration: identification of a retrovirus int locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7885–7889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. The terminal nucleotides of retrovirus DNA are required for integration but not virus production. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):155–160. doi: 10.1038/306155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. P., Grandgenett D. P. Genetic evidence that the avian retrovirus DNA endonuclease domain of pol is necessary for viral integration. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2307–2312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2307-2312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Schwartzberg P. L., Goff S. P. Structure of the termini of DNA intermediates in the integration of retroviral DNA: dependence on IN function and terminal DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Goff S. P. Construction and analysis of deletion mutations in the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: a new viral function required for productive infection. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R., Soltis D. A., Katzman M., Cobrinik D., Leis J., Skalka A. M. Properties of avian sarcoma-leukosis virus pp32-related pol-endonucleases produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2358–2365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2358-2365.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]